Identifying the Psychological and Somatic Dimensions of Neuroticism: A Qualitative Approach
Keywords:
Neuroticism, emotional dysregulation, cognitive rumination, somatic symptoms, coping strategies, qualitative research, psychological distressAbstract
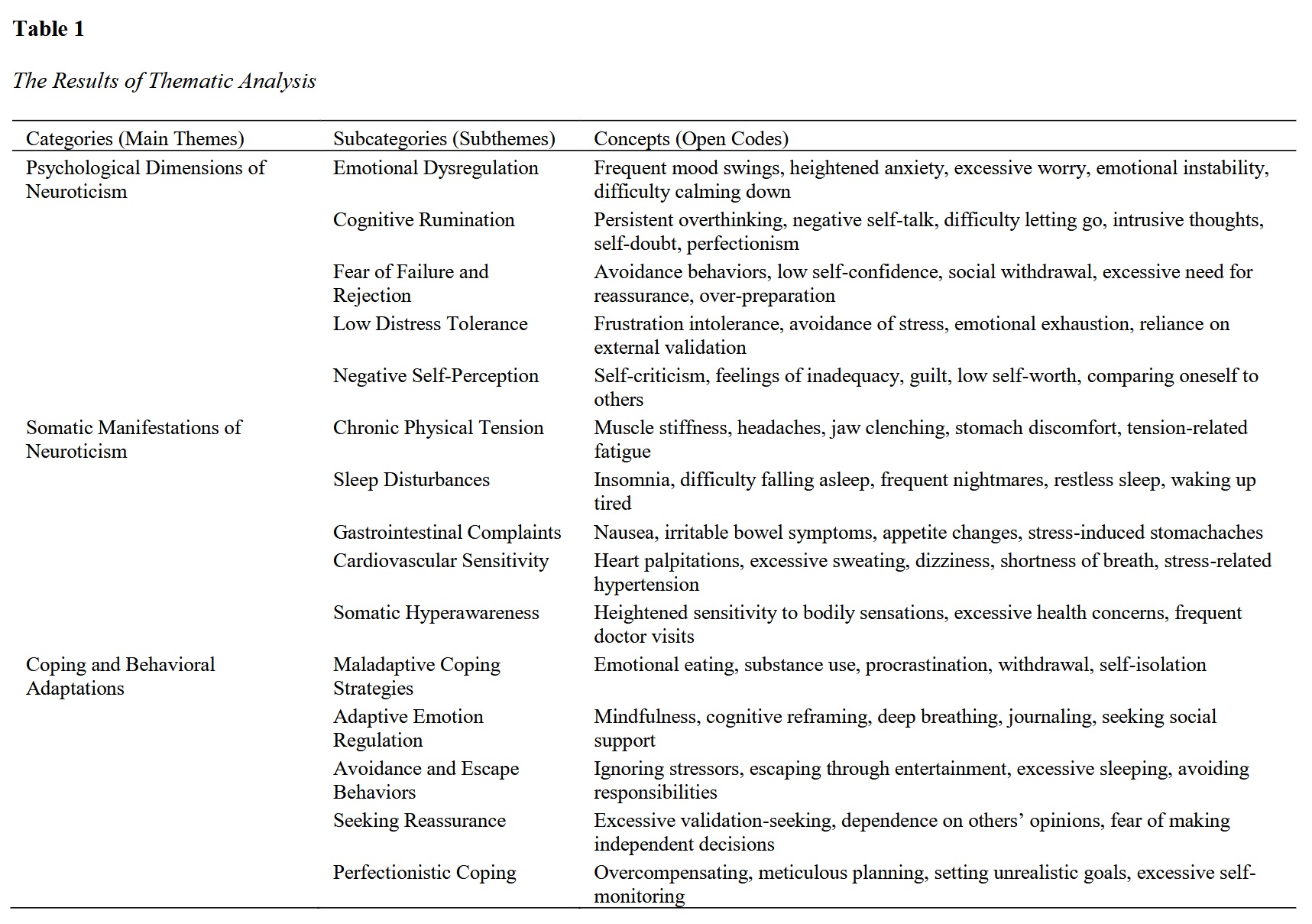
This study aimed to explore the psychological and somatic dimensions of neuroticism through a qualitative approach. This qualitative study utilized semi-structured interviews with 24 participants recruited through online platforms. A phenomenological approach was employed to capture the lived experiences of individuals exhibiting neurotic traits, with data collection continuing until theoretical saturation was achieved. The interviews were transcribed and analyzed using NVivo software, following an iterative thematic analysis process involving open, axial, and selective coding to identify core themes related to neuroticism’s psychological and somatic dimensions. Thematic analysis revealed three primary themes: psychological dimensions, somatic manifestations, and coping and behavioral adaptations. Participants reported significant emotional dysregulation, including heightened anxiety, excessive worry, and cognitive rumination. They also exhibited somatic symptoms such as chronic physical tension, sleep disturbances, and gastrointestinal complaints. Maladaptive coping strategies, including avoidance behaviors, reassurance-seeking, and emotional eating, were prevalent, although some participants engaged in adaptive techniques such as mindfulness and cognitive reframing. The results underscored the complex interplay between neuroticism’s psychological and physiological aspects, contributing to persistent distress and functional impairment. The findings highlight the pervasive impact of neuroticism on emotional, cognitive, and somatic functioning, reinforcing its role as a significant risk factor for psychological distress and health-related concerns. Understanding the lived experiences of individuals with high neurotic traits provides valuable insights for developing targeted interventions focused on emotion regulation, stress management, and adaptive coping mechanisms to mitigate neuroticism’s adverse effects.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mehdi Shomali Ahmadabadi (Corresponding Author); Atefe Brkhordari Ahmadabadi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






