A Model of School Social Well-Being for Elementary School Students: A Mixed-Methods Approach
Keywords:
social well-being, elementary school students, individual factors and personal interactions, structural and managerial factors, school environment and atmosphereAbstract
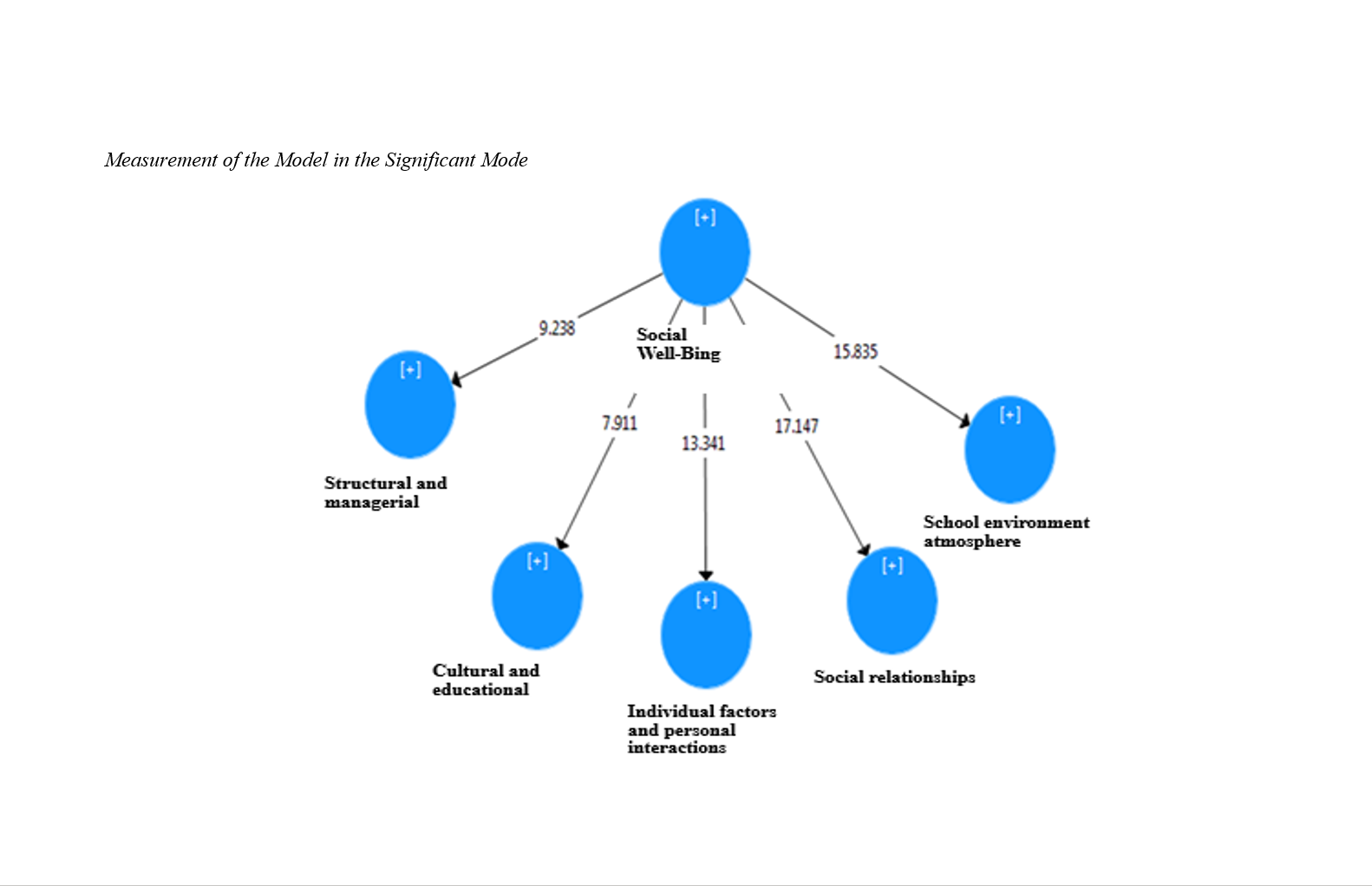
This study aimed to develop and validate a comprehensive model of school social well-being for elementary school students. The study employed a sequential exploratory mixed-methods design. In the qualitative phase, thematic analysis was conducted based on research synthesis and semi-structured interviews with 15 academic experts and education practitioners, selected through purposive sampling until theoretical saturation was achieved. In the quantitative phase, a fuzzy Delphi method was used to screen and confirm the importance of the identified components and indicators. Subsequently, a researcher-developed questionnaire was administered to 375 elementary school principals and teachers selected through simple random sampling. Data were analyzed using confirmatory factor analysis, partial least squares structural equation modeling, and the Best–Worst Method for prioritization, with analyses performed in SPSS, SmartPLS, and LINGO software. Inferential results supported a five-dimensional model of school social well-being, including social relationships, school environment and atmosphere, individual factors and personal interactions, cultural and educational factors, and structural and managerial factors. All factor loadings exceeded the acceptable threshold and were statistically significant. The measurement and structural models demonstrated adequate reliability, convergent validity, and discriminant validity. Path analysis indicated that all five dimensions had significant positive effects on school social well-being. Model fit indices and predictive relevance measures confirmed a strong overall model fit. Prioritization results showed that social relationships had the highest relative importance, followed by school environment and atmosphere, individual factors and personal interactions, cultural and educational factors, and structural and managerial factors. The findings indicate that school social well-being among elementary students is a multidimensional construct shaped by relational, environmental, individual, cultural, and organizational factors.
Downloads
References
Alemi, Q., Panter‐Brick, C., Oriya, S., Ahmady, M., Alimi, A. Q., Faiz, H., Hakim, N., Hashemi, S. A. S., Manaly, M. A., Naseri, R., Parwiz, K., Sadat, S. J., Sharifi, M. Z., Shinwari, Z., Ahmadi, S. J., Amin, R., Azimi, S., Hewad, A., Musavi, Z., . . . Ventevogel, P. (2023). Afghan Mental Health and Psychosocial Well-Being: Thematic Review of Four Decades of Research and Interventions. BJPsych Open, 9(4). https://doi.org/10.1192/bjo.2023.502
Bilbao, M., López, V., Torres-Vallejos, J., Ascorra, P., & Páez, D. (2025). Adaptation of the social well-being scale for teachers and school staff. Revista de Psicología, 43(1), 29-52. https://doi.org/10.18800/psico.202501.002
Danmaisoro, H. B., & Mozayani, A. (2024). Effects of Screen Time on the Social Well-Being of Adolescents. Forensic Research & Criminology International Journal, 12(2), 155-157. https://doi.org/10.15406/frcij.2024.12.00412
Diakova, V. V., Kargapolova, E., & Petrova, P. I. (2023). State of Mind as a Component of Youth’s Social Well-Being. Tyumen State University Herald Social Economic and Law Research, 9(2), 6-19. https://doi.org/10.21684/2411-7897-2023-9-2-6-19
Esmaeili, R., & Zargar Moradi, M. S. (2025). Predicting psychological well-being and social well-being based on psychological capital in patients with multiple sclerosis supported by the Imam Khomeini Relief Foundation. Scientific Journal of Empowerment and Deprivation, 1(4), 33-48. https://pajoohesh.emdad.ir/article_713363_en.html
Gull, M., Kaur, N., & Akhouri, D. (2022). Perceived Social Support as Related to Social Wellbeing in Patients With Emotionally Unstable Personality Disorder (EUPD). Middle East Current Psychiatry, 29(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43045-022-00264-3
Jordan, M. (2023). The power of connection: Self-care strategies of social wellbeing. Journal of Interprofessional Education & Practice, 100586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xjep.2022.100586
Kitoshvili, N. (2023). Marital Conflict and Adolescent’s Psycho-Social Well-Being: Mediation and Moderation Analysis. Scientific Bulletin of Mukachevo State University Series “Pedagogy and Psychology”, 9(4), 57-64. https://doi.org/10.52534/msu-pp4.2023.57
Mosafid, M., & Mehr Mohammadi, M. (2022). Predicting social well-being based on health-oriented lifestyle and irrational beliefs in women with panic disorder. Journal of Rehabilitation Research in Nursing, 8(4), 65-75. https://doi.org/10.22034/IJRN.8.4.65
Murari, K., Shukla, S., & Dulal, L. (2024). Social Media Use and Social Well-Being: A Systematic Review and Future Research Agenda. Online Information Review, 48(5), 959-982. https://doi.org/10.1108/oir-11-2022-0608
Nazdar Qudrat, A. (2019). Impairment of School performance, Psychological and Social Wellbeing and the Role of Counselors at Kalar Schools: A Qualitative Study. Journal of Garmian University, 6(5th Conferance of Human sciences), 1040-1046. https://doi.org/10.24271/garmian.5thc72
Podineh Aghaei, M., & Nasti Zeiai, N. (2025). The effect of school climate on students' social well-being with the mediating role of social capital. Family and Research Quarterly, 21(1), 39-58. https://qjfr.ir/article-1-2142-en.html
Sadat S, V. S., Fathiazar E, Badri Gargari R (2022). Designing a School-Based Positive Education Package and Evaluating Its’ Effectiveness on Social Well-Being Levels of Sixth Grade Male Students in District One of Tehran. Biquarterly Journal of Cognitive Strategies in Learning, 10(18), 59-88. https://www.magiran.com/paper/2504641
Saffarinia, M., & Dortaj, A. (2018). Effect of group logotherapy on life expectancy and mental and social wellbeing of the female elderly residents of nursing homes in Dubai. Iranian Journal of Ageing, 12(4), 482-493. https://doi.org/10.21859/sija.12.4.482
Šauerová, M. Š., & Jirásková, J. (2023). Social Wellbeing – A Key Factor in the Mental Health of Children and Adolescent. Acta Salus Vitae, 11(2). https://doi.org/10.58743/asv2023vol11no2.331
Shasizadeh, E., Eftekhar Saadi, Z., Jayrvand, H., Bakhtiarpoor, S., & Makvandi, B. (2022). Evaluation of social well-being and emotional self-awareness based on the quality of relationship with parents due to smartphone addiction in high-intelligence students. Journal of Pediatric Nursing, 8(3), 16-26. https://jpen.ir/browse.php?a_id=626&sid=1&slc_lang=en
Shikari, N. (2025). A Probe Into the Effect of Self-Concept on the Development of Academic Motivation of the School-Going Adolescents of Nadia District. International Journal of Research and Innovation in Social Science, IX(XVII), 585-599. https://doi.org/10.47772/ijriss.2025.917psy0053
Silan, M. A. A. (2023). Are the Kids Alright? The Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on the Mental Health and Psychosocial Wellbeing of Filipino Children in Selected Cities in Metro Manila. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/v2ygm
Soest, T. v., Kozák, M., Rodríguez‐Cano, R., Fluit, S., Cortés‐García, L., Ulset, V., Haghish, E. F., & Bakken, A. (2022). Adolescents’ Psychosocial Well-Being One Year After the Outbreak of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Norway. Nature Human Behaviour, 6(2), 217-228. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-021-01255-w
Ünlü, S., Uzun, K., & Arslan, G. (2025). Mindfulness-Based Intervention in Schools: Addressing Social Media Burnout and Enhancing Well-Being in Adolescents. Children, 12(7), 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12070826
Wong, R. S., Tung, K. T. S., Li, X., Chui, C. S. L., Tso, W. W. Y., Lee, T. M., Chan, K. L., Wing, Y. K., Fu, K. W., Wong, I. C. K., & lp, P. (2022). Examining Family Pre-Pandemic Influences on Adolescent Psychosocial Wellbeing During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Current Psychology, 43(13), 12034-12044. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-02736-5
Yang, L., & Lian, L. H. (2025). Perceive Social Support, Academic Self-Efficacy, and Learning Engagement Among High School Students in China. International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education (Ijere), 14(1), 629. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijere.v14i1.31029
Yuan, H., Yan, Z., Yue, Y., Zhao, Y., & Lei, J. (2025). The Relationship Between Family Socio‐Economic Status and Preschool Children Parents' Parenting Sense of Competence: The Chain Mediating Role of Social Support and Psychological Capital. Child & Family Social Work. https://doi.org/10.1111/cfs.13263
Zhan, Y. (2025). Characterizing Social Problem-Solving Skills in STEAM Activities for Preschool Children. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 174, 2922-2929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2025.01.180