Investigating the Impact of Psychological Employee Empowerment on Job Embeddedness of Human Resources in National Sports Federations
Keywords:
Psychological Empowerment, Job Embeddedness, National Sports Federations, Employee Retention, Organizational BehaviorAbstract
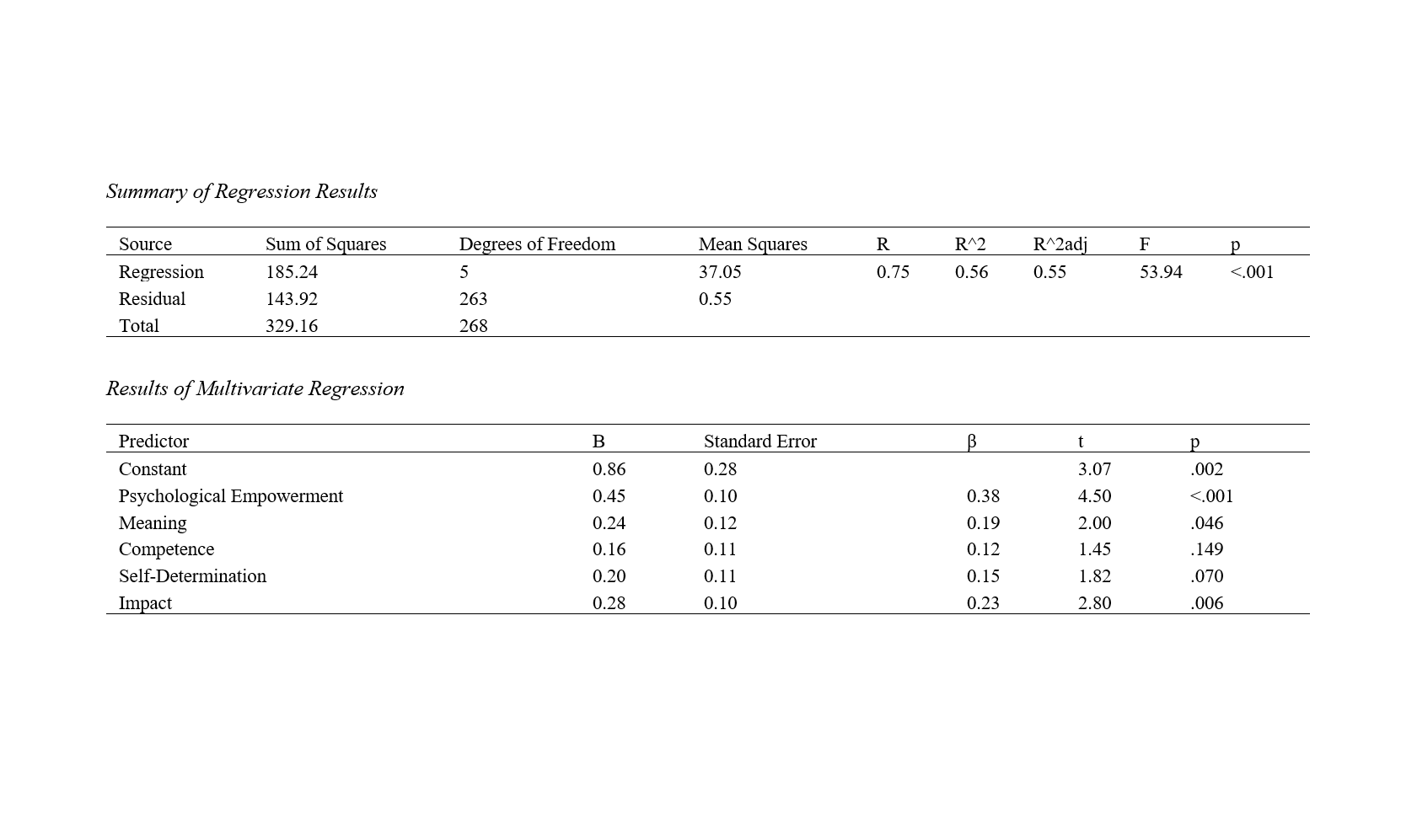
This study aims to investigate the impact of employee empowerment on job embeddedness among human resources in national sports federations. A cross-sectional design was employed, with a sample size of 269 participants selected from 901 employees in national sports federations using stratified random sampling. Psychological empowerment was measured using Spreitzer's Psychological Empowerment Instrument, while job embeddedness was assessed using Mitchell et al.'s Job Embeddedness Questionnaire. Data were analyzed using SPSS-27, applying Pearson correlation to explore relationships between variables and linear regression to predict job embeddedness from psychological empowerment and its subscales. Descriptive statistics revealed mean scores of 5.32 (SD = 0.85) for psychological empowerment and 4.89 (SD = 0.91) for job embeddedness. Significant positive correlations were found between job embeddedness and psychological empowerment (r = 0.61, p < .01), as well as its subscales. Regression analysis indicated that psychological empowerment (β = 0.38, p < .001), meaning (β = 0.19, p = .046), and impact (β = 0.23, p = .006) significantly predicted job embeddedness, explaining 56% of the variance (R^2 = 0.56, F(5, 263) = 53.94, p < .001). The study confirms the significant positive impact of psychological empowerment on job embeddedness among employees in national sports federations. Empowerment initiatives that enhance employees' sense of meaning and impact are particularly effective in promoting job embeddedness. These findings underscore the importance of creating empowering work environments to improve employee retention and organizational performance in sports federations.
Downloads
References
1. Al-Hosam A, Ahmed S, Ahmad F, Joarder MHR. Impact of Transformational Leadership on Psychological Empowerment and Job Satisfaction Relationship: A Case of Yemeni Banking. Binus Business Review. 2016;7(2):109. [DOI]
2. Nwachukwu C, Vu HM, Agboga RS. Psychological Empowerment and Employee Engagement: Role of Job Satisfaction and Religiosity in Nigeria. Industrial and Commercial Training. 2022;54(4):666-87. [DOI]
3. Emery C, Booth JE, Michaelides G, Swaab A. The Importance of Being Psychologically Empowered: Buffering the Negative Effects of Employee Perceptions of Leader–member Exchange Differentiation. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology. 2019;92(3):566-92. [DOI]
4. Sun X. Psychological Empowerment on Job Performance—Mediating Effect of Job Satisfaction. Psychology. 2016;07(04):584-90. [DOI]
5. Lan X. How Psychological Capital Promotes Innovative Behavior: A Mutilevel Modeling. American Journal of Industrial and Business Management. 2019;09(12):2202-19. [DOI]
6. Araslı H, Arıcı HE, Ilgen H. Blackbox Between Job Crafting and Job Embeddedness of Immigrant Hotel Employees: A Serial Mediation Model. Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja. 2019;32(1):3935-62. [DOI]
7. Robinson R, Kralj A, Solnet D, Goh E, Callan VJ. Thinking Job Embeddedness Not Turnover: Towards a Better Understanding of Frontline Hotel Worker Retention. International Journal of Hospitality Management. 2014;36:101-9. [DOI]
8. Ali A, Khan RA, Alam W, Adil A, Aabbas Z. Ethical Leadership Enhance Positive Work Outcome: A Mediation Model. Humanities & Social Sciences Reviews. 2021;9(3):111-20. [DOI]
9. Altaf M, Shahzad A. “That’s My Job” Exploring the Effect of Brand Empowerment Towards Employee Brand Equity: Mediating Role of Employee Critical Psychological States. Review of Business Management. 2018;20(4):599-618. [DOI]
10. Yoon D-Y, Han CS, Lee S-Y, Cho J, Sung M, Han SK. The Critical Role of Job Embeddedness: The Impact of Psychological Empowerment and Learning Orientation on Organizational Commitment. Frontiers in Psychology. 2022;13. [PMID: 36544436] [PMCID: PMC9760925] [DOI]
11. Arif S. Impact of Organizational Justice on Turnover Intentions: Moderating Role of Job Embeddedness. Seisense Journal of Management. 2018;1(2):34-52. [DOI]
12. Dechawatanapaisal D. The Moderating Effects of Demographic Characteristics and Certain Psychological Factors on the Job Embeddedness – Turnover Relationship Among Thai Health-Care Employees. International Journal of Organizational Analysis. 2018;26(1):43-62. [DOI]
13. Bibi A, Jadoon B. The Mediating Effect of Exploitative and Explorative Learning on the Relationship Between Job Embeddedness and Innovative Work Behavior. Science Journal of Business and Management. 2018;6(1):1. [DOI]
14. Marasi S, Cox SS, Bennett RJ. Job Embeddedness: Is It Always a Good Thing? Journal of Managerial Psychology. 2016;31(1):141-53. [DOI]
15. Martadiani AM, Pulawan NIM, Nitiwidari DA. Role of Job Satisfaction, Work-Life Balance and Job Embeddedness on Turnover Intention Nurse in Denpasar. Epra International Journal of Economic and Business Review. 2022:35-45. [DOI]
16. Karatepe OM. The Importance of Supervisor Support for Effective Hotel Employees. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly. 2013;55(4):388-97. [DOI]
17. Karatepe OM, Karadaş G. The Effect of Management Commitment to Service Quality on Job Embeddedness and Performance Outcomes. Journal of Business Economics and Management. 2012;13(4):614-36. [DOI]
18. Luoh H-F, Tsaur SH, Tang Y. Empowering Employees: Job Standardization and Innovative Behavior. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management. 2014;26(7):1100-17. [DOI]
19. Rahmawati S. POS and Psychological Empowerment as Moderating Variables on the Effect of Job Insecurity on Employee Performance in Islamic Banks. Jurnal Manajemen Teknologi. 2023;22(2):124-34. [DOI]
20. Purba DE. Employee Embeddedness and Turnover Intentions: Exploring the Moderating Effects of Commute Time and Family Embeddedness. Makara Human Behavior Studies in Asia. 2015;19(1):39. [DOI]
21. Meirun T, Lockey S, Blenkinsopp J, Yueyong H, Ling L. The Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Corporate Social Responsibility and Job Embeddedness in China. Frontiers in Psychology. 2022;13. [PMID: 35496231] [PMCID: PMC9051387] [DOI]
22. Karavardar G. Perceived Organizational Support, Psychological Empowerment, Organizational Citizenship Behavior, Job Performance and Job Embeddedness: A Research on the Fast Food Industry in Istanbul, Turkey. International Journal of Business and Management. 2014;9(4). [DOI]
23. Kosar R, Sayyed Muhammad Mehdi Raza N. Psychological Empowerment and Employee Behaviors: Employee Engagement as Mediator and Leader-Member Exchange as Moderator. Journal of International Business Research and Marketing. 2015;1(6):24-30. [DOI]
24. Ling LL, Theresa CFH, Othman RM, Kelana BWY, Hee OC. The Effect of Psychological Empowerment and Job Satisfaction Towards Organizational Commitment Among Malaysian Employees in Small and Medium Enterprises. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences. 2019;9(11). [DOI]
25. Ma’rof AA, Fadzilan DAM, Hamsan HH. The Role of Psychological Empowerment on Job Satisfaction Among Malaysian Public Sector Workers. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences. 2021;11(12). [DOI]
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















