Quantitative Assessment of H Reflex and F Response Values in Healthy and Paralyzed Limbs and Their Correlation with the Prognosis of CVA Patients
Keywords:
H reflex, F response, stroke, EMGAbstract
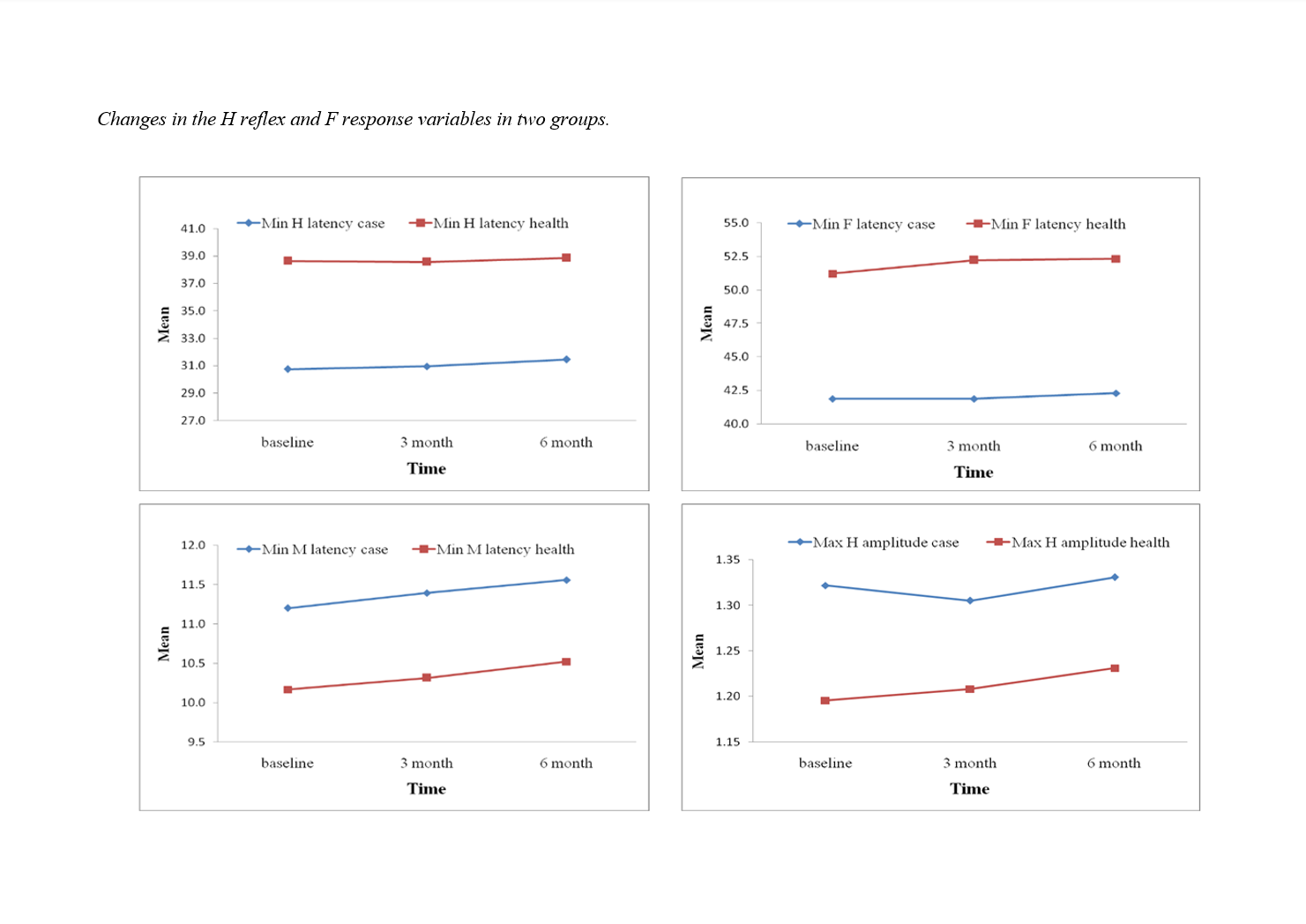
Quantitative and objective evaluation of stroke patients with limb paralysis provides valuable insights into functional decline and treatment prognosis. The present study aims to quantitatively assess the H reflex and F response values in both healthy and paralyzed limbs and their relationship with the prognosis of recovery in paralyzed limbs of stroke patients. This descriptive-analytical study was conducted on 60 stroke patients hospitalized at Valiasr Hospital in Qaemshahr during 2022-2023. H reflex and F response values were measured using EMG-NCV for both healthy and paralyzed limbs at the onset of the disease, three months later, and six months later. The results were analyzed using the repeated measures test with SPSS software. The mean age of patients was 65.47 ± 8.57 years, with 58.3% (35 individuals) being male. The results revealed significant differences in Min F latency, Min M latency, and Min H latency in F response, as well as Max H amplitude in H reflex between healthy and paralyzed limbs (P<0.05). However, there were no significant differences in H reflex and F response values across different time points (baseline, three months, six months) (P>0.05). H reflex and F response measurements offer valuable insights into patient recovery and the therapeutic management of stroke patients with paralyzed limbs.
Downloads
References
1. Murphy SJ, Werring DJ. Stroke: causes and clinical features. Medicine. 2020;48(9):561-6. [PMID: 32837228] [PMCID: PMC7409792] [DOI]
2. Lingo VanGilder J, Hooyman A, Peterson DS, Schaefer SY. Post-stroke cognitive impairments and responsiveness to motor rehabilitation: a review. Current physical medicine and rehabilitation reports. 2020;8:461-8. [PMID: 33767922] [PMCID: PMC7987128] [DOI]
3. van der Vliet R, Selles RW, Andrinopoulou ER, Nijland R, Ribbers GM, Frens MA, et al. Predicting upper limb motor impairment recovery after stroke: a mixture model. Annals of neurology. 2020;87(3):383-93. [PMID: 31925838] [PMCID: PMC7065018] [DOI]
4. Todhunter-Brown A, Baer G, Campbell P, Choo PL, Forster A, Morris J, et al. Physical rehabilitation approaches for the recovery of function and mobility following stroke. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2014(4). [PMID: 24756870] [PMCID: PMC6465059] [DOI]
5. Lu Q, Wang X, Tian J. A new biological central pattern generator model and its relationship with the motor units. Cognitive Neurodynamics. 2022;16(1):135-47. [PMID: 35126774] [PMCID: PMC8807781] [DOI]
6. Kim S-C, Cho S-H. Effects of H-reflex onset latency on gait in elderly and hemiplegic individuals. Medicina. 2022;58(6):716. [PMID: 35743979] [PMCID: PMC9228972] [DOI]
7. Sathya G, Krishnamurthy N, Veliath S, Arulneyam J, Venkatachalam J. F wave index: A diagnostic tool for peripheral neuropathy. Indian Journal of Medical Research. 2017;145(3):353-7. [PMID: 28749398] [PMCID: PMC5555064] [DOI]
8. Tahayori B, Koceja D. Exercise induced operant conditioning of the H-reflex in stroke patients: Hopes for improving motor function through inducing plastic changes in the spinal pathways. J Neurol Neurol Sci Disord. 2019;5(1):001-5. [DOI]
9. Chhatlani R, Solanki C, Mehta P. A Study to Correlate Modified Modified Ashworth Scale (Mmas) and Modified Tardieu Scale (Mts) with H-Reflex to Assess Planterflexor Spasticity in Chronic Post-Stroke Patients-An Observational Study. Indian Journal of Physiotherapy & Occupational Therapy Print-(ISSN 0973-5666) and Electronic–(ISSN 0973-5674). 2020;14(3):199-205.
10. Hofstoetter US, Freundl B, Binder H, Minassian K. Recovery cycles of posterior root-muscle reflexes evoked by transcutaneous spinal cord stimulation and of the H reflex in individuals with intact and injured spinal cord. PLoS One. 2019;14(12):e0227057. [PMID: 31877192] [PMCID: PMC6932776] [DOI]
11. Çakır T, Evcik FD, Subaşı V, Demirdal ÜS, Kavuncu V. Investigation of the H reflexes, F waves and sympathetic skin response with electromyography (EMG) in patients with stroke and the determination of the relationship with functional capacity. Acta Neurologica Belgica. 2015;115:295-301. [PMID: 25481720] [DOI]
12. Bourbonnais D, VANDEN NOVEN S, Carey KM, Rymer WZ. Abnormal spatial patterns of elbow muscle activation in hemiparetic human subjects. Brain. 1989;112(1):85-102. [PMID: 2917281] [DOI]
13. Werner C, Von Frankenberg S, Treig T, Konrad M, Hesse S. Treadmill training with partial body weight support and an electromechanical gait trainer for restoration of gait in subacute stroke patients: a randomized crossover study. Stroke. 2002;33(12):2895-901. [PMID: 12468788] [DOI]
14. Walker C, Brouwer BJ, Culham EG. Use of visual feedback in retraining balance following acute stroke. Physical therapy. 2000;80(9):886-95. [PMID: 10960936] [DOI]
15. Hara Y, Akaboshi K, Masakado Y, Chino N. Physiologic decrease of single thenar motor units in the F-response in stroke patients. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 2000;81(4):418-23. [PMID: 10768529] [DOI]
16. Thibaut A, Chatelle C, Ziegler E, Bruno M-A, Laureys S, Gosseries O. Spasticity after stroke: physiology, assessment and treatment. Brain injury. 2013;27(10):1093-105. [PMID: 23885710] [DOI]
17. Li S. Spasticity, motor recovery, and neural plasticity after stroke. Frontiers in neurology. 2017;8:120. [PMID: 28421032] [PMCID: PMC5377239] [DOI]
18. Garrett M, Caulfield B. Increased Hmax: Mmax ratio in community walkers poststroke without increase in ankle plantarflexion during walking. Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation. 2001;82(8):1066-72. [PMID: 11494186] [DOI]
19. Qin W, Zhang A, Yang M, Chen C, Zhen L, Yang H, et al. Soleus H‐Reflex Change in Poststroke Spasticity: Modulation due to Body Position. Neural Plasticity. 2021;2021(1):9955153. [PMID: 34917144] [PMCID: PMC8670919] [DOI]
20. Cho S-H, Lee J-H. Comparison of the amplitudes of the H-reflex of post-stroke hemiplegia patients and normal adults during walking. Journal of physical therapy science. 2013;25(6):729-32. [PMID: 24259840] [PMCID: PMC3805002] [DOI]
21. Drory V, Neufeld M, Korczyn A. F-wave characteristics following acute and chronic upper motor neuron lesions. Electromyography and clinical neurophysiology. 1993;33(7):441-6.
22. Grindstaff TL, Beazell JR, Sauer LD, Magrum EM, Ingersoll CD, Hertel J. Immediate effects of a tibiofibular joint manipulation on lower extremity H-reflex measurements in individuals with chronic ankle instability. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology. 2011;21(4):652-8. [PMID: 21546263] [DOI]
23. McComas A, Sica R, Upton A, Aguilera N, Currie S. Motoneurone dysfunction in patients with hemiplegie atrophy. Nature New Biology. 1971;233(35):21-3. [PMID: 5286222] [DOI]
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ali Heidari, SeyedHasan Mortazavi (Author); Melody Omraninava (Corresponding Author); Amirreza Hayati , Reza Yousefi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















