Does Alteration of Balance Control After Ankle Muscle Fatigue in National Judo Athletes Depend on Postural Task Difficulty?
Keywords:
Lower Limb, Muscle Fatigue, Balance, Judo, PostureAbstract
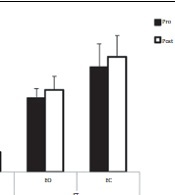
Background: The purpose of the present study was to assess the impacts of plantar-flexors and dorsi-flexors fatigue following isokinetic contractions on postural control in nine young healthy national level judo athletes. Methods: Participants were required to stand still on a force plate with opened and closed eyes in feet together (FT) and single leg (SL) stance before (PRE) and after (POST) an isokinetic fatigue protocol. Mediolateral sway (ML sway), anteroposterior sway (AP sway), and velocity sway were calculated and used to assess the postural control. Results: Velocity sway POST was significantly (P < 0.001) higher than PRE in FT stance and SL stance. Velocity sway POST was significantly higher in the SL stance than the FT stance (P = 0.01). During eyes closed, a significant interaction postural task by fatigue for all parameters was found. All parameters increased significantly after fatigue compared to PRE. After fatigue, ML sway, AP sway, and velocity sway were significantly higher for the SL stance than the FT stance. Conclusions: Ankle muscle fatigue led to reduced postural stability during different stances in young healthy judo athletes. This effect was more accentuated when vision was removed and the base of support was reduced. Alteration of postural control depended on the difficulty of the postural stance.
Downloads