The Impact of Aerobic Exercise on Athletic Performance in Recovered and Uninfected COVID-19 Athletes during Post-COVID-19 Period
Keywords:
Aerobic Exercise, VO 2 Max, Anaerobic Power, Post COVID-19Abstract
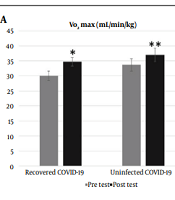
Background: The global COVID-19 pandemic has significantly influenced athletes worldwide. Objectives: This research aims to investigate the effects of a 4-week aerobic exercise program on athletic performance in both recovered and uninfected COVID-19 athletes during the post-COVID-19 period. Methods: Fourteen male student-athletes aged 18 - 25 years from Imam Khomeini International University participated in this study. The participants comprised 7 recovered COVID-19 athletes and 7 athletes with no prior COVID-19 infection. The study employed a pre-test/post-test design conducted in 2 phases. During the pre and post-test phases, participants underwent baseline assessments of athletic performance, including maximum oxygen consumption (VO2 max) and anaerobic power. Subsequently, the participants engaged in a 4-week aerobic exercise intervention. Pre- and post-intervention outcomes within groups were compared using paired t-tests, while independent t-tests were utilized for comparisons between the recovered COVID-19 athlete group and the uninfected athlete group. Results: Independent t-tests demonstrated significant increases in VO2 max and peak power after 4 weeks of aerobic exercise in both the recovered COVID-19 group (P = 0.001, P = 0.0001) and the uninfected COVID-19 group (P = 0.012, P = 0.001). However, dependent t-tests revealed a significant difference between the recovered COVID-19 group and the uninfected COVID-19 group in the post-test of VO2 max (P = 0.044) and peak power (P = 0.001). Conclusions: This study indicates that a 4-week aerobic exercise regimen can improve athletic performance in both recovered and uninfected COVID-19 athletes. However, recovered COVID-19 athletes exhibited a notably slower rate of improvement compared to their uninfected counterparts. Therefore, it is recommended that, in addition to aerobic exercise, recovered athletes integrate supplementary strategies to optimize their return-to-sport timeline and maximize performance recovery.
Downloads
References
1. Taheri M, Esmaeili A, Irandoust K, Mirmoezzi M, Souissi A, Laher
I, et al. Mental health, eating habits and physical activity levels
of elite Iranian athletes during the COVID-19 pandemic. Sci Sports.
2023;38(5-6):527–33. [PubMed ID: 37362084]. [PubMed Central ID:
PMC10243596]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scispo.2023.01.002.
2. Barbisch D, Koenig KL, Shih FY. Is There a Case for Quarantine?
Perspectives from SARS to Ebola. Disaster Med Public Health Prep.
2015;9(5):547–53. [PubMed ID: 25797363]. https://doi.org/10.1017/dmp.
2015.38.
3. Romero Starke K, Petereit-Haack G, Schubert M, Kampf D, Schliebner
A, Hegewald J, et al. The Age-Related Risk of Severe Outcomes
Due to COVID-19 Infection: A Rapid Review, Meta-Analysis, and
Meta-Regression. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(16):5974.
[PubMed ID: 32824596]. [PubMed Central ID: PMC7460443]. https://
doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165974.
4. Richardson S, Hirsch JS, Narasimhan M, Crawford JM, McGinn T,
Davidson KW, et al. Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities,
and Outcomes Among 5700 Patients Hospitalized With
COVID-19 in the New York City Area. JAMA. 2020;323(20):2052–9.
[PubMed ID: 32320003]. [PubMed Central ID: PMC7177629].
https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.6775.
5. Barker-Davies RM, Ladlow P, Chamley R, Nicol E, Holdsworth DA.
Reduced athletic performance post-COVID-19 is associated with
reduced anaerobic threshold. BMJ Case Rep. 2023;16(2):e250191.
[PubMed ID: 36805865]. [PubMed Central ID: PMC9943905].
https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2022-250191.
6. Chu DK, Akl EA, Duda S, Solo K, Yaacoub S, Schunemann HJ,
et al. Physical distancing, face masks, and eye protection to
prevent person-to-person transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and
COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet.
2020;395(10242):1973–87. [PubMed ID: 32497510]. [PubMed Central
ID: PMC7263814]. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31142-9.
7. Arica-Polat BS, Gundogdu AA, Cinar N, Uncu G, Ayas ZO, Iseri P, et al.
Evaluation of cognitive deficits in patients infected with COVID-19.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022;26(2):678–85. [PubMed ID: 35113443].
https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev 202201 27894.
8. Di Sebastiano KM, Chulak-Bozzer T, Vanderloo LM, Faulkner G. Don’t
Walk So Close to Me: Physical Distancing and Adult Physical Activity in
Canada. Front Psychol. 2020;11:1895. [PubMed ID: 32849110]. [PubMed
Central ID: PMC7396577]. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01895.
9. Rajpal S, Tong MS, Borchers J, Zareba KM, Obarski TP, Simonetti
OP, et al. Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Findings in
Competitive Athletes Recovering From COVID-19 Infection. JAMA
Cardiol. 2021;6(1):116–8. [PubMed ID: 32915194]. [PubMed Central ID:
PMC7489396]. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamacardio.2020.4916.
10. Mujika I, Padilla S. Detraining: loss of training-induced physiological
and performance adaptations. Part II: Long term insufficient training
stimulus. Sports Med. 2000;30(3):145–54. [PubMed ID: 10999420].
https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-200030030-00001.
11. Schinke R, Papaioannou A, Henriksen K, Si G, Zhang L, Haberl P. Sport
psychology services to high performance athletes during COVID-19.
Int J Sport Exerc Psychol. 2020;18(3):269–72. https://doi.org/10.1080/
1612197x.2020.1754616.
12. Joyner MJ. Physiological limiting factors and distance running:
influence of gender and age on record performances. Exerc Sport Sci
Rev. 1993;21:103–33. [PubMed ID: 8504840].
13. Bishop D, Edge J, Goodman C. Muscle buffer capacity and aerobic
fitness are associated with repeated-sprint ability in women. Eur J Appl
Physiol. 2004;92(4-5):540–7. [PubMed ID: 15168128]. https://doi.org/10.
1007/s00421-004-1150-1.
14. Huang C, Huang L, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Gu X, et al. 6-month
consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: a
cohort study. Lancet. 2021;397(10270):220–32. [PubMed ID: 33428867].
[PubMed Central ID: PMC7833295]. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-
6736(20)32656-8.
15. Ahmed OF, Kakamad FH, Hama Amin BJ, Abdullah BA, Hassan
MN, Salih RQ, et al. Post COVID-19 pulmonary complications; a
single center experience. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2021;72:103052.
[PubMed ID: 34777798]. [PubMed Central ID: PMC8578026].
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amsu.2021.103052.
16. Mohamed AA, Alawna M. The effect of aerobic exercise on
immune biomarkers and symptoms severity and progression in
patients with COVID-19: A randomized control trial. J Bodyw Mov
Ther. 2021;28:425–32. [PubMed ID: 34776174]. [PubMed Central ID:
PMC8339452]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbmt.2021.07.012.
17. Sozen H, Akyıldız C. The Effects of Aerobic and Anaerobic Training on ¨
Aerobic and Anaerobic Capacity. Int J Anatolia Sport Sci. 2018;3(3):331–7.
https://doi.org/10.5505/jiasscience.2018.68077.
18. Short KR, Vittone JL, Bigelow ML, Proctor DN, Nair KS. Age and
aerobic exercise training effects on whole body and muscle protein
metabolism. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2004;286(1):E92–101.
[PubMed ID: 14506079]. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00366.2003.
19. Burgomaster KA, Howarth KR, Phillips SM, Rakobowchuk M,
Macdonald MJ, McGee SL, et al. Similar metabolic adaptations
during exercise after low volume sprint interval and traditional
endurance training in humans. J Physiol. 2008;586(1):151–60.
[PubMed ID: 17991697]. [PubMed Central ID: PMC2375551].
https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2007.142109.
20. Keren G, Epstein Y. The effect of pure aerobic training on
aerobic and anaerobic capacity. Br J Sports Med. 1981;15(1):27–9.
[PubMed ID: 7248677]. [PubMed Central ID: PMC1859056].
https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsm.15.1.27.
21. Wilson JM, Loenneke JP, Jo E, Wilson GJ, Zourdos MC, Kim JS. The effects
of endurance, strength, and power training on muscle fiber type
shifting. J Strength Cond Res. 2012;26(6):1724–9. [PubMed ID: 21912291].
https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0b013e318234eb6f.
22. Hazell TJ, Olver TD, Hamilton CD, Lemon PWR. Two minutes of
sprint-interval exercise elicits 24-hr oxygen consumption similar to
that of 30 min of continuous endurance exercise. Int J Sport Nutr
Exerc Metab. 2012;22(4):276–83. [PubMed ID: 22710610]. https://doi.org/
10.1123/ijsnem.22.4.276.
23. Astorino TA, Allen RP, Roberson DW, Jurancich M. Effect of
high-intensity interval training on cardiovascular function,
VO2max, and muscular force. J Strength Cond Res. 2012;26(1):138–45.
[PubMed ID: 22201691]. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0b013e318218dd77.
24. Wilson JM, Marin PJ, Rhea MR, Wilson SM, Loenneke JP,
Anderson JC. Concurrent training: a meta-analysis examining
interference of aerobic and resistance exercises. J Strength
Cond Res. 2012;26(8):2293–307. [PubMed ID: 22002517]. https:
//doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0b013e31823a3e2d.
25. Townsend L, Dyer AH, Jones K, Dunne J, Mooney A, Gaffney F, et
al. Persistent fatigue following SARS-CoV-2 infection is common
and independent of severity of initial infection. PLoS One.
2020;15(11):e0240784. [PubMed ID: 33166287]. [PubMed Central
ID: PMC7652254]. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240784.
26. Dudley GA, Abraham WM, Terjung RL. Influence of exercise
intensity and duration on biochemical adaptations in skeletal
muscle. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982;53(4):844–50.
[PubMed ID: 6295989]. https://doi.org/10.1152/jappl.1982.53.4.844.
27. Korkmaz S, Aslan CS, Eyuboglu E, Celebi M, Kır R, Karakulak I, et ˘
al. Impact of detraining process experienced during the COVID-19
pandemic on the selected physical and motor features of football
players. Prog Nutr. 2020;22(Suppl 2):e2020029.
28. Parpa K, Michaelides M. Aerobic capacity of professional soccer
players before and after COVID-19 infection. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):11850.
[PubMed ID: 35831351]. [PubMed Central ID: PMC9279307]. https://doi.
org/10.1038/s41598-022-16031-7.
29. Hull JH, Wootten M, Moghal M, Heron N, Martin R, Walsted ES,
et al. Clinical patterns, recovery time and prolonged impact of
COVID-19 illness in international athletes: the UK experience. Br J
Sports Med. 2022;56(1):4–11. [PubMed ID: 34340972]. https://doi.org/10.
1136/bjsports-2021-104392.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







