The Comparison of Validity and Reliability of a Novel Smartphone-based Tool with Foot Scanner for Hallux Valgus Angle Measurement
Keywords:
Hallux valgus angle, mobile health, reliability, validityAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to assess the validity and reliability of a novel smartphone-based tool (NSBT) for measuring the hallux valgus angle (HVA) compared to a foot scanner.
Methods: Thirty-five feet with hallux valgus underwent two measurement sessions using both the NSBT (Hallux-Valgus-meter app) and a DSI foot scanner (Iranian Daneshsalar Company). Intra- and inter-rater reliability for each tool were assessed using Cronbach's alpha and ICC(2,K). Agreement between tools was evaluated using Pearson's correlation coefficient and Bland-Altman analysis. Statistical analyses were performed in SPSS v27 (α = 0.05).
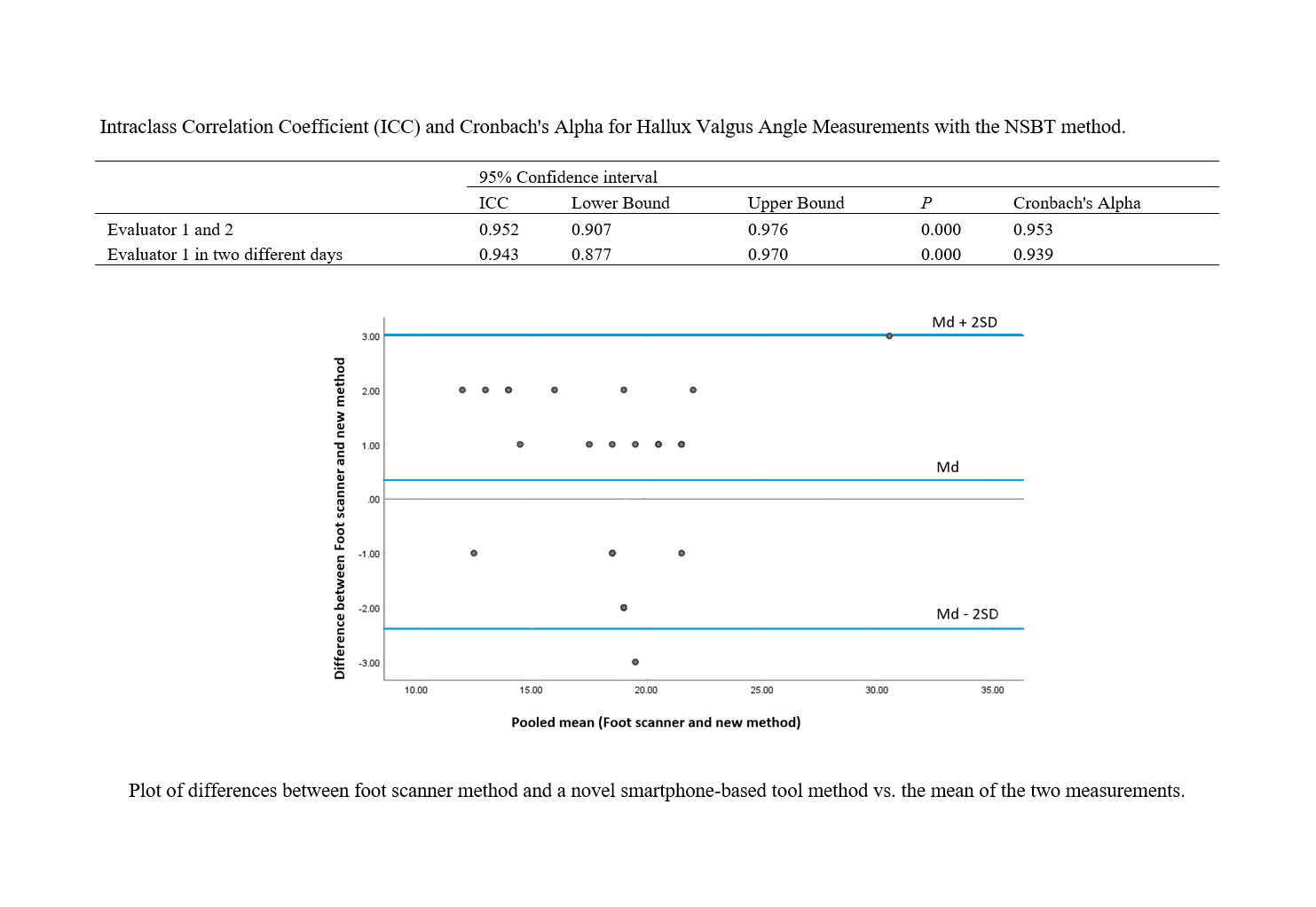
Results: The NSBT demonstrated excellent inter-evaluator reliability (ICC = 0.952, Cronbach's alpha = 0.953) and intra-evaluator reliability (ICC = 0.943, Cronbach's alpha = 0.939) (all p < 0.001). The NSBT also showed strong agreement with the foot scanner (r = 0.93, p < 0.001). Bland-Altman analysis confirmed this agreement with a small mean difference (0.34 degrees) and minimal data scatter.
Conclusion: The NSBT offers a valid, reliable, and consistent method for HVA measurement. Compared to traditional methods, it presents advantages of portability, ease of use, reduced cost, and eliminates radiation exposure. This technology has the potential to improve accessibility and efficiency in hallux valgus assessment within physiotherapy practice.
Downloads
References
1. R. R, H. S. Corrective exercise laboratory. Tehran:
Tehran University Press Institute. ; 2023.
2. Samadi H, Alavi Z, Kalantarian M. The effect of eight
weeks of core stability exercises on lumbar lordosis, pregnancy
back pain, functional disability and quality of life of nulliparous
women. Journal Of Anesthesiology And Pain. 2023;14(2):39-49.
3. Seidi F, Minonezhad H, Shahrbanian S, Khandani B.
Combined Exercise-Bandage Protocol on Hallux Valgus Angle in
Women with Hallux Valgus Deformity. Journal Of Disability
Studies. 2020;10(1).
4. Sabaghzadeh A, Tadayon N, Biglari F, Jafari KM,
Moteshakereh S, Zarei KH. The Correlation between Hallux
Valgus Angle and Radiological Indices in Patients with Hallux
Valgus. Journal of Research in Rehabilitation Sciences.
2023;11(3):207.
5. Fong DTP, Heng ML-w, Pan JW, Lim YY, Lee P-Y,
Kong PW. A Clinician-Free Method Using Top-View Photography
for Screening and Monitoring Hallux Valgus. Journal of the
American Podiatric Medical Association. 2021;111(5):08. [PMID:
34861682] [DOI]
6. Zhong Z, Zhang P, Duan H, Yang H, Li Q, He F. A
Comparison Between X-ray Imaging and an Innovative Computeraided Design Method Based on Weightbearing CT Scan Images for
Assessing Hallux Valgus. The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery.
2021;60(1):6-10. [PMID: 32253154] [DOI]
7. Lee KM, Ahn S, Chung CY, Sung KH, Park MS.
Reliability and Relationship of Radiographic Measurements in
Hallux Valgus. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research®.
2012;470(9):2613-21. [PMID: 22544667] [PMCID:
PMC3830090] [DOI]
8. Wang L, Zhang C, Liang H, Zhang J, Zhong W, Zhao Z,
et al. Reliability of different smartphones measuring the hallux
valgus parameters in a new rapid method: a follow-up study. BMC
Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2022;23(1):315. [PMID: 35366850]
[PMCID: PMC8976351] [DOI]
9. Cortês Padilha LF, Almeida de Sousa Nogueira T,
Povoleri Marano B, Monteiro Camisão R, Costa Barreto Brígido
JV, Almeida Ribeiro de Miranda V. Reproducibility of the point
connection technique for measuring hallux valgus angles using a
smartphone application. Journal of the Foot & Ankle.
2022;16(2):138-45. [DOI]
10. Otter SJ, Agalliu B, Baer N, Hales G, Harvey K, James
K, et al. The reliability of a smartphone goniometer application
compared with a traditional goniometer for measuring first
metatarsophalangeal joint dorsiflexion. Journal of Foot and Ankle
Research. 2015;8(1):30. [PMID: 26207142] [PMCID:
PMC4512018] [DOI]
11. Huang T, Wang L, Lu C, Zhong W, Zhao Z, Luo X. A
novel rapid measurement of hallux valgus parameters using the
built-in photo edit function of smartphones. BMC Musculoskeletal
Disorders. 2021;22(1):716. [PMID: 34419028] [PMCID:
PMC8380395] [DOI]
12. Nix S, Russell T, Vicenzino B, Smith M. Validity and
Reliability of Hallux Valgus Angle Measured on Digital
Photographs. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy.
2012;42(7):642-8. [PMID: 22282040] [DOI]
13. Hopson M, McPoil T, Cornwall M. Motion of the first
metatarsophalangeal joint. Reliability and validity of four
measurement techniques. Journal of the American Podiatric
Medical Association. 1995;85(4):198-204. [PMID: 7738816]
[DOI]
14. Zhou J, Hlavacek P, Xu B, Chen W. Approach for
measuring the angle of hallux valgus. Indian Journal of
Orthopaedics. 2013;47(3):278-82. [PMID: 23798759] [PMCID:
PMC3687905] [DOI]
15. Ghaderiyan M, Ghasemi GA, Zolaktaf V. Effect of rope
jumping exercise on foot arch in boy students with cavus, planus,
and normal foot types. Journal of Research in Rehabilitation
Sciences. 2015;11(3):212-9. [DOI]
16. Jiao Y, Džeroski S, Jurca A. Analysis of hallux valgus
angles automatically extracted from 3D foot scans taken in North
America, Europe, and Asia. Ergonomics. 2023;66(8):1164-75.
[PMID: 36269073] [DOI]
17. Fleiss JL, Levin B, Paik MC. Statistical methods for rates
and proportions: john wiley & sons; 2013.
18. Meng H-Z, Zhang W-L, Li X-C, Yang M-W.
Radiographic angles in hallux valgus: Comparison between
protractor and iPhone measurements. Journal of Orthopaedic
Research. 2015;33(8):1250-4. [PMID: 25763918] [PMCID:
PMC6680276] [DOI]
19. Hayatoshi S, Nakasa T, Sawa M, Tsuyuguchi Y,
Kanemitsu M, Ota Y, et al. New screening method for hallux valgus
with using smartphone. Foot & Ankle Orthopaedics.
2018;3(3):2473011418S00242. [DOI]
20. Walter R, Kosy JD, Cove R. Inter- and intra-observer
reliability of a smartphone application for measuring hallux valgus
angles. Foot and Ankle Surgery. 2013;19(1):18-21. [PMID:
23337271] [DOI]
21. Yamaguchi S, Sadamasu A, Kimura S, Akagi R,
Yamamoto Y, Sato Y, et al. Nonradiographic Measurement of
Hallux Valgus Angle Using Self-photography. Journal of
Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy. 2019;49(2):80-6. [PMID:
30208796] [DOI]
22. Catal H, Corumluoglu O. Using 3D models from
multidetector computed tomography images for diagnostic of
Hallux-valgus. 12th International Multidisciplinary Scientific
GeoConference and EXPO-Modern Management of Mine
Producing, Geology and Environmental Protection, SGEM 2012.
2012. [DOI]
23. Janssen DM, Sanders AP, Guldemond NA, Hermus J,
Walenkamp GH, van Rhijn LW. A comparison of hallux valgus
angles assessed with computerised plantar pressure measurements,
clinical examination and radiography in patients with diabetes.
Journal of Foot and Ankle Research. 2014;7(1):33. [PMID:
25075224] [PMCID: PMC4114410] [DOI]
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







