Unraveling Age-Driven Shifts in Adolescent Cardiorespiratory Fitness: A Comprehensive Analysis Using the Yo-Yo Intermittent Endurance Test
Keywords:
Adolescents, Maturity, Endurance, Aerobic Capacity, Yo-Yo Test, Physical EducationAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to examine cardiorespiratory responses during the Yo-Yo Intermittent Endurance Test in adolescents aged 14–18 years.
Methods and Materials: A total of 80 male high school students participated, with 20 from each grade (9–12) at Pendik Vocational and Technical Anatolian High School in Istanbul. Anthropometric measurements, including height and weight, were recorded. Body composition was assessed using a Tanita body impedance analyzer, and aerobic capacity was evaluated using the Yo-Yo IR1 test. Statistical analyses, including ANOVA and Pearson correlation, were performed using SPSS v25.
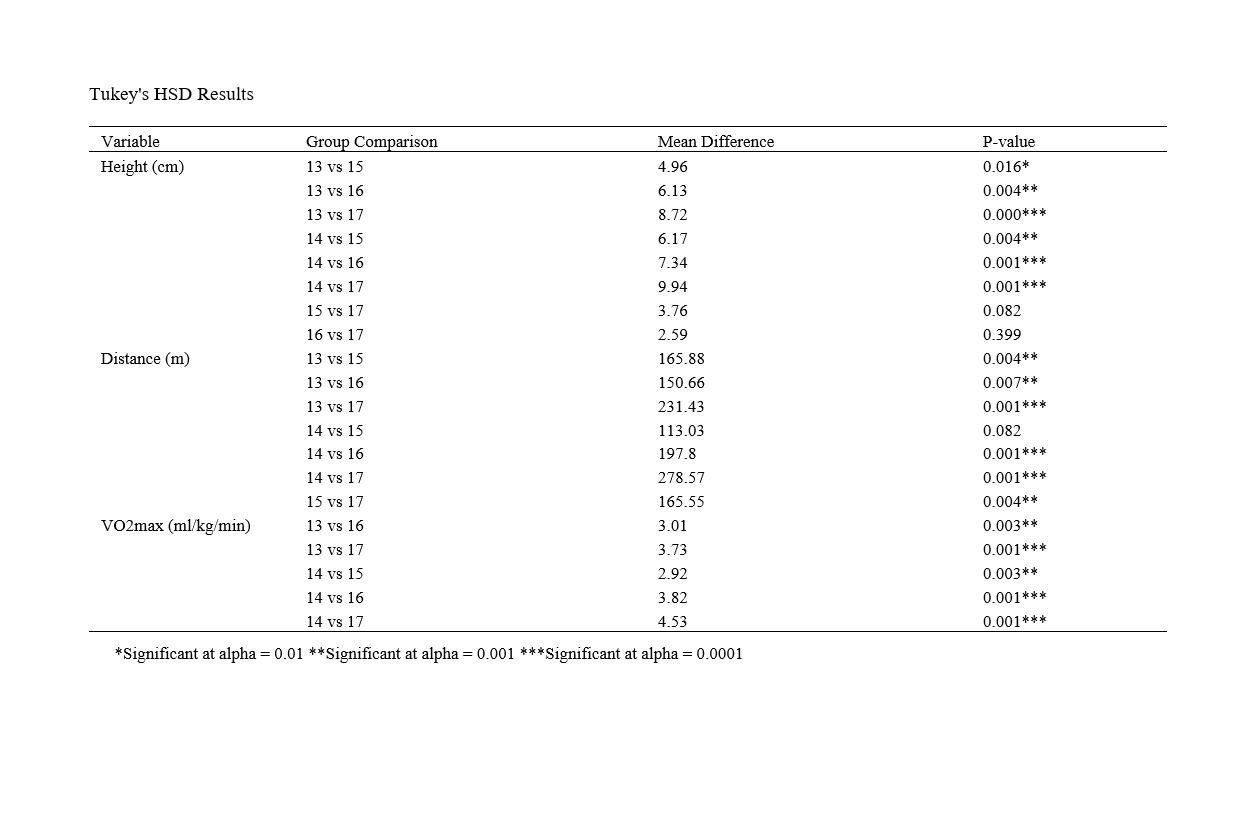
Findings: Significant differences were observed in height, distance covered, and VO2max across age groups. ANOVA revealed significant variations in height and distance covered, with older students performing better. Pearson correlation indicated strong positive relationships between Yo-Yo test levels, VO2max, and distance covered.
Conclusion: The findings underscore the need for age-specific fitness assessments in physical education programs to optimize athletic performance during adolescence.
Downloads
References
1. Shahidi SH, Carlberg B, Kingsley D. Talent
identification and development in youth sports: A systematic
review. International Journal of Kinanthropometry. 2023;3:73-84.
[DOI]
2. Shahidi SH, Yilmaz L, Esformes J, et al. Effect of
maturity status and relative age effect on anthropometrics and
physical performance of soccer players aged 12 to 15 years.
International Journal of Kinanthropometry. 2023;3:58-72. [DOI]
3. Michailidis Y. The relationship between aerobic
capacity, anthropometric characteristics, and performance in the
Yo-Yo Intermittent Recovery Test among elite young football
players: Differences between playing positions. Applied Sciences.
2024;14:3413. [DOI]
4. Frade MCM, Beltrame T, Gois MdO, et al. Toward
characterizing cardiovascular fitness using machine learning based
on unobtrusive data. PLoS One. 2023;18:e0282398. [DOI]
5. Men J, Zou S, Ma J, et al. Effects of high-intensity
interval training on physical morphology, cardiorespiratory fitness
and metabolic risk factors of cardiovascular disease in children and
adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One.
2023;18:e0271845. [DOI]
6. Mintjens S, Menting MD, Daams JG, et al.
Cardiorespiratory fitness in childhood and adolescence affects
future cardiovascular risk factors: A systematic review of
longitudinal studies. Sports Medicine. 2018;48:2577-605. [DOI]
7. Azegami T, Uchida K, Sato Y, et al. Secular trends and
age-specific distribution of blood pressure in Japanese adolescents
aged 12–18 years in 2000–2019. Hypertension Research.
2024;47:184-94. [DOI]
8. Viitasalo A, Schnurr TM, Pitkänen N, et al. Genetic
predisposition to higher body fat yet lower cardiometabolic risk in
children and adolescents. International Journal of Obesity.
2019;43:2007-16. [DOI]
9. Bangsbo J, Fiorenza M. The application of the Yo-Yo
intermittent recovery tests to the soccer population. Science and
Football VIII2016. p. 13-29[DOI]
10. Fink B, Freitas TT, De Marzo C, et al. Relative age,
biological maturation, body composition, and physical
performance in under-16 academy soccer players: Differences and
associations among early and late born athletes. Sport Science
Health. 2024;20:165-76. [DOI]
11. Briscoe T, Darrall-Jones J, Heyward O, et al. Validity,
reliability, and the contributing physical characteristics of a
modified 15m prone Yo-Yo Intermittent Recovery Test Level-1
test in elite female rugby league players. PLoS One.
2024;19:e0306171. [DOI]
12. Paes MR, Fernandez R. Use of a modified Yo-Yo
intermittent endurance level 2 test for evaluation of field soccer
referees. Sport Science Health. 2024:1-10. [DOI]
13. Schmitz B, Pfeifer C, Kreitz K, et al. Normative yo-yo
intermittent recovery level 1 and yo-yo intermittent endurance level
1 test values of boys aged 9–16 years. Journal of Science and
Medicine in Sport. 2019;22:1030-7. [DOI]
14. Vernillo G, Silvestri A, La Torre A. The yo-yo
intermittent recovery test in junior basketball players according to
performance level and age group. Journal of Strength and
Conditioning Research. 2012;26:2490-4. [DOI]
15. Till K, Morley D, O'Hara J, et al. A retrospective
longitudinal analysis of anthropometric and physical qualities that
associate with adult career attainment in junior rugby league
players. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport. 2017;20:1029-
33. [DOI]
16. Bezmylov M, Shynkaruk O, Griban G, et al. Peculiarities
of physical fitness of 17-20 years old basketball players taking into
account their playing role. International Journal of Human
Movement and Sports Sciences. 2022;10:1163-72. [DOI]
17. Jakobsson J, Julin AL, Persson G, Malm C. Darwinian
selection discriminates young athletes: The relative age effect in
relation to sporting performance. Sports Medicine Open. 2021;7:1-
18. [DOI]
18. Ahler T, Bendiksen M, Krustrup P, et al. Aerobic fitness
testing in 6-to 9-year-old children: Reliability and validity of a
modified Yo–Yo IR1 test and the Andersen test. European Journal
of Applied Physiology. 2012;112:871-6. [DOI]
19. Chauhan BS, Kumar S. Impact of physical training on
aerobic capacity on under-graduate students. Sports Science Health
Advances. 2023;1:39-42. [DOI]
20. D'Agostino EM, Day SE, Konty KJ, et al. Longitudinal
association between weight status, aerobic capacity, muscular
strength, and endurance among New York City youth, 2010–2017.
Childhood Obesity. 2023;19:203-12. [DOI]
21. Towlson C, Salter J, Ade JD, et al. Maturityassociated considerations for training load, injury risk, and
physical performance in youth soccer: One size does not fit
all. Journal of Sport Health Science. 2021;10:403-12.
[DOI]
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Seyed Houtan Shahidi, Burak Özsakınç, Amirali Salehi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







