Comparison of the Effects of Rapid, Moderate, and Slow Weight Loss Combined with a Low-Calorie Diet and Physical Activity on Inflammatory Factors in Obese Women
Keywords:
Weight loss, inflammatory factors, obese womenAbstract
Objective: Obesity and overweight are defined as the excessive accumulation of fat in the body, which generally occurs when energy intake exceeds energy expenditure. Currently, obesity is considered one of the largest public health challenges worldwide and is inversely associated with various health outcomes. Obesity is often linked to inflammatory factors. The purpose of this study was to compare the effects of rapid, moderate, and slow weight loss combined with a low-calorie diet and physical activity on inflammatory markers in obese women.
Methods and Materials: In this study, 36 obese women (ages 20 to 45 years) with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher were randomly divided into three groups: rapid weight loss (combined training with 30-35% caloric deficit, 12 weeks, 12 participants), moderate weight loss (combined training with 20-25% caloric deficit, 10 weeks, 12 participants), and slow weight loss (combined training with 15-20% caloric deficit, 15 weeks, 12 participants). Participants underwent interventions for rapid, moderate, or slow weight loss, which included exercise and nutritional programs. Aerobic exercise consisted of walking and jogging on a treadmill at an intensity of 50-65% of maximum heart rate, and resistance training at 40% of one-repetition maximum (1RM), including dumbbell cross movements, biceps curls, and triceps extensions. Inflammatory markers, including Interleukin-1 (IL-1) and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), were measured at the beginning and end of the study. Data analysis was performed using ANOVA, Shapiro-Wilk, Levene's test, and covariance analysis. Statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS version 23 at a significance level of 0.05.
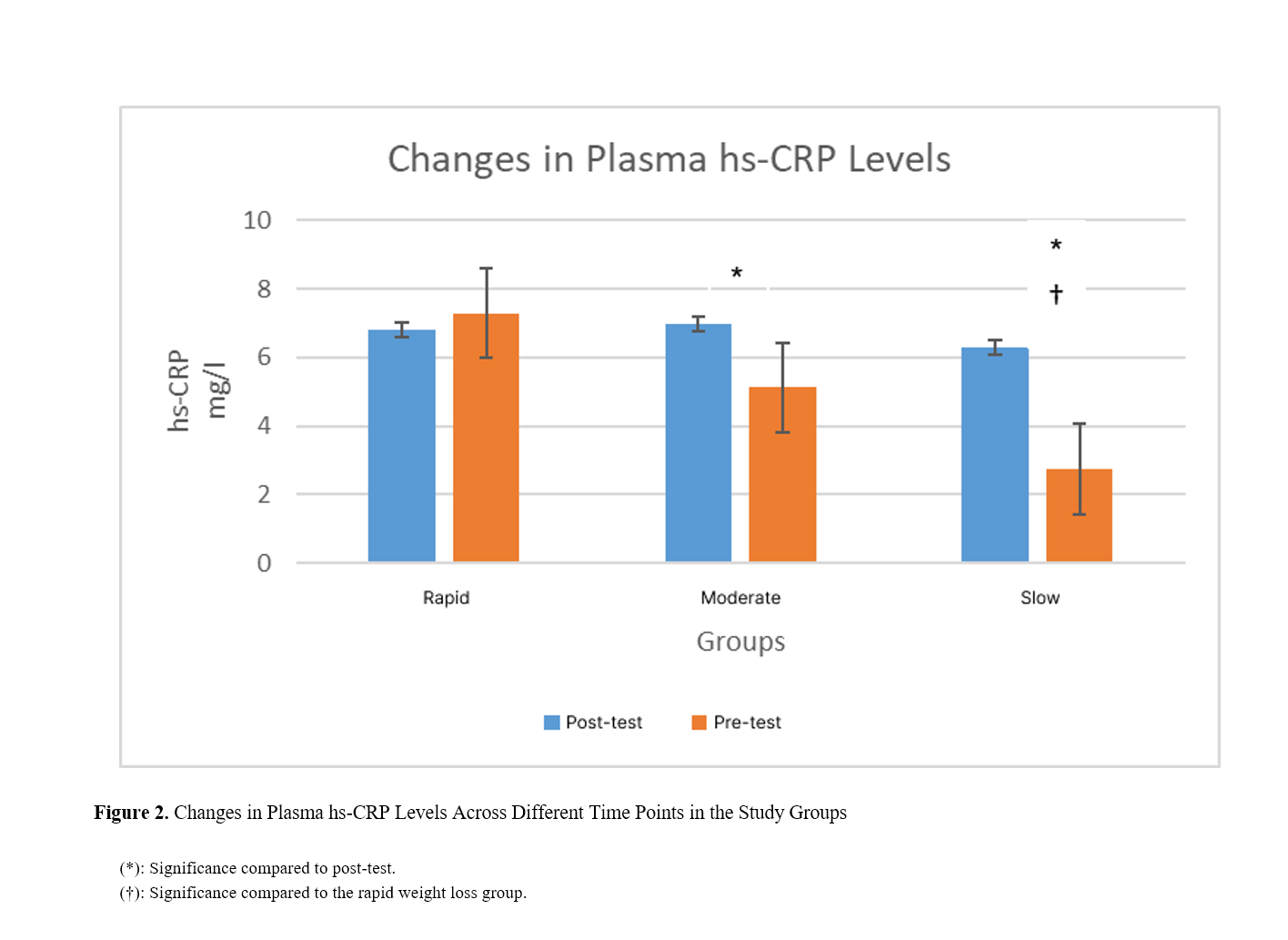
Findings: Rapid, moderate, and slow weight loss combined with a low-calorie diet and physical activity did not have a significant effect on plasma IL-1 levels in obese women. However, significant differences were observed between the rapid weight loss group and the moderate and slow weight loss groups. Specifically, a 22.66% reduction in IL-1 levels was noted in the moderate weight loss group compared to the rapid weight loss group, and a 39.59% reduction was observed in the slow weight loss group compared to the rapid weight loss group. No significant difference was found between the moderate and slow weight loss groups. Similarly, rapid, moderate, and slow weight loss combined with a low-calorie diet and physical activity did not significantly affect plasma hs-CRP levels in obese women. However, a significant difference was observed between the rapid weight loss group and the slow weight loss group, with a 62.28% reduction in hs-CRP levels in the slow weight loss group compared to the rapid weight loss group. No significant differences were found between the other groups.
Conclusion: Rapid, moderate, and slow weight loss combined with a low-calorie diet and physical activity does not significantly impact inflammatory factors.
Downloads
References
1. Naserifar M, Seraj Khorrami N, Safarzadeh S, Heidari A. Effectiveness of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy on Lifestyle Based on Self-Efficacy and Body Valuation in Obese Women. Applied Family Therapy. 2022;3(2):467-81.
2. Gülü M, Yagin FH, Yapici H, Irandoust K, Dogan AA, Taheri M, et al. Is early or late biological maturation trigger obesity? A machine learning modeling research in Turkey boys and girls. Frontiers in Nutrition. 2023;10. [DOI]
3. Mohajan D, Mohajan H. Obesity and Its Related Diseases: A New Escalating Alarming in Global Health. Journal of Innovations in Medical Research. 2023;2:12-23. [DOI]
4. Naghavi N, Taheri M, Irandoust K. Psychophysiological Responses to Cognitive and Physical Training in Obese Elderly. Int J Sport Stud Health. 2018;1(3):e83935. [DOI]
5. Seghatoleslami A, Hemmati Afif A, Irandoust K, Taheri M. Effect of Pilates Exercises on Motor Performance and Low Back Pain in Elderly Women With Abdominal Obesity. Salmand: Iranian Journal of Ageing. 2018;13(3):396-404. [DOI]
6. Karczewski J, Śledzińska E, Baturo A, Jończyk I, Maleszko A, Samborski P, et al. Obesity and inflammation. European cytokine network. 2018;29:83-94. [DOI]
7. Hajiebrahim Araghi B, Rahmani MA, Rahimaghaee F. Examining the Mediating Role of Body Esteem in the Relationship Between Social Body Anxiety and Health-Oriented Lifestyle in Women with Obesity. Psychology of Woman Journal. 2024;5(3):97-105. [DOI]
8. Jalali Farahani M, Jadidi M, Mirzaian B. The Effectiveness of Acceptance and Commitment Group Therapy on Cognitive Fusion, Mindfulness, and Body Mass Index in Women with Obesity. Journal of Adolescent and Youth Psychological Studies (JAYPS). 2024;5(9):34-41. [DOI]
9. Rezaei M, Taheri M, Irandoust K, Bragazzi NL. Combining Aerobic Exercise with Fasting Protocols for Effective Obesity Control in Women. International Journal of Sport Studies for Health. 2024;7(4):40-50. [DOI]
10. Stienstra R, Duval C, Müller M, Kersten S. PPARs, obesity, and inflammation. PPAR Research. 2007. [DOI]
11. Vatanpanah S, Khalatbari J, Tayyebi A, Sabet M. The effectiveness of compassion-focused therapy on emotional eating behavior, emotional dysregulation, perceived stress and rumination in women with chronic obesity. Applied Family Therapy Journal (AFTJ). 2023;4(2):115-28. [DOI]
12. Vatanpanah S, Khalatbari J, Tayyebi A, Sabet M. Effectiveness of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy on Emotional Eating Behavior, Emotion dysregulation, Perceived Stress, and Rumination in Women with Chronic Obesity. Journal of Adolescent and Youth Psychological Studies (JAYPS). 2024;5(1):8-18. [DOI]
13. Ding Y, Xu X. Anti-inflammatory effect of exercise training through reducing inflammasome activation-related inflammatory cytokine levels in overweight/obese populations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice. 2022;49:101656. [DOI]
14. Beigrezaei S, Yazdanpanah Z, Soltani S, Rajaie SH, Mohseni-Takalloo S, Zohrabi T, et al. The addition of exercise to a weight loss diet on inflammatory markers: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 2023;63(19):4175-87. [DOI]
15. Mohammadian Amiri A, Hassanzadeh R, Heydari S. Comparison of the Effectiveness of Schema Therapy and Life Therapy on Emotion Regulation and Attitudes Towards Eating in Women with Obesity. Health Nexus. 2024;2(2):68-76. [DOI]
16. Sadeghzadeh R, Sheibeh Z, Solat F, Naeiji MR, Mirzai F, Damavandi M. Effectiveness of Emotional Regulation Training on Parenting Style Related to Parental Obesity and Weight Management in Adolescents with Bulimia Nervosa. Journal of Assessment and Research in Applied Counseling (JARAC). 2023;5(5):85-92. [DOI]
17. Bianchi VE. Weight loss is a critical factor to reduce inflammation. Clinical Nutrition ESPEN. 2018;28:21-35. [DOI]
18. Irandoust K, Parsakia K, Estifa A, Zoormand G, Knechtle B, Rosemann T, et al. Predicting and comparing the long-term impact of lifestyle interventions on individuals with eating disorders in active population: a machine learning evaluation. Frontiers in Nutrition. 2024;11. [DOI]
19. Şahin A, Soylu D. Patient Perspectives on Lifestyle Changes Following a Diabetes Diagnosis. KMAN Counseling & Psychology Nexus. 2024;2(1):56-62. [DOI]
20. Hu FB. Diet strategies for promoting healthy aging and longevity: An epidemiological perspective. Journal of Internal Medicine. 2024;295(4):508-31. [DOI]
21. Mehta R, Neupane A, Wang L, Goodman Z, Baranova A, Younossi ZM. Expression of NALPs in adipose and the fibrotic progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obese subjects. BMC Gastroenterology. 2014;14(1):1-10. [DOI]
22. Moradian H, Delavar HP, Zabet. The effect of eight weeks of circuit resistance training on interleukin-1 beta, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and blood pressure in obese women with prehypertension. Journal of Sport Biosciences. 2022;14(1):67-84. [DOI]
23. Gielen S, Adams V, Möbius-Winkler S, Linke A, Erbs S, Yu J, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of exercise training in the skeletal muscle of patients with chronic heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;42(5):861-8. [DOI]
24. Najafi S, S A, Afrondeh. The effects of different intensities of interval resistance training on inflammatory markers in obese men. Feiz Journal of Medical Sciences. 2023.
25. Balducci S, Zanuso S, Nicolucci A, Fernando F, Cavallo S, Cardelli P, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of exercise training in subjects with type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome is dependent on exercise modalities and independent of weight loss. Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases. 2010;20(8):608-17. [DOI]
26. Justice BD. EFFECT OF WEIGHT LOSS ON INFLAMMATORY MARKERS IN SEVERELY OBESE ADULTS: University of Pittsburgh; 2011.
27. Reljic D, Dieterich W, Herrmann HJ, Neurath MF, Zopf Y. "HIIT the Inflammation": Comparative effects of low-volume interval training and resistance exercises on inflammatory indices in obese metabolic syndrome patients undergoing caloric restriction. Nutrients. 2022;14(10):1996. [DOI]
28. Kasraei H, Kargaefard M, Nazarali P, Nobari H, Zare A. The Effects Of Combined Exercise With And Without Diet On Plasma Inflammatory Biomarkers And Endothelial Dysfunction In Elderly Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Iranian Journal of Diabetes and Metabolism. 2019;18(4):207-20.
29. McLaughlin T, Abbasi F, Lamendola C, Liang L, Reaven G, Schaaf P, et al. Differentiation between obesity and insulin resistance in the association with C-reactive protein. Circulation. 2002;106(23):2908-12. [DOI]
30. Selvin E, Paynter NP, Erlinger TP. The effect of weight loss on C-reactive protein: a systematic review. Archives of internal medicine. 2007;167(1):31-9. [DOI]
31. Oh EG, Bang SY, Kim SH, Hyun SS, Chu SH, Jeon JY, et al. Therapeutic lifestyle modification program reduces plasma levels of the chemokines CRP and MCP-1 in subjects with metabolic syndrome. Biol Res Nurs. 2013;15(1):48-55. [DOI]
32. Ordonez FJ, Rosety MA, Camacho A, Rosety I, Diaz AJ, Fornieles G, et al. Aerobic training improved low-grade inflammation in obese women with intellectual disability. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2014;58(6):583-90. [DOI]
33. Brunelli DT, Chacon-Mikahil MP, Gáspari AF, Lopes WA, Bonganha V, Bonfante IL, et al. Combined Training Reduces Subclinical Inflammation in Obese Middle-Age Men. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015;47(10):2207-15. [DOI]
34. Lopes WA, Leite N, da Silva LR, Brunelli DT, Gaspari AF, Radominski RB, et al. Effects of 12 weeks of combined training without caloric restriction on inflammatory markers in overweight girls. Journal of Sports Sciences. 2016;34(20):1902-12. [DOI]
35. Shariatzadeh M, Moghadam Z, Maleki L, Keshavarz E, Hedayati M. The short-term effects of two types of high-intensity interval training on plasma levels of TNF-α, IL-6, CRP, and lipid profile in overweight women. Journal of Sport Biosciences. 2017;9(2):195-207.
36. Varady KA, Tussing L, Bhutani S, Braunschweig CL. Degree of weight loss required to improve adipokine concentrations and decrease fat cell size in severely obese women. Metabolism. 2009;58(8):1096-101. [DOI]
37. Alemán JO, Iyengar NM, Walker JM, Milne GL, Da Rosa JC, Liang Y, et al. Effects of rapid weight loss on systemic and adipose tissue inflammation and metabolism in obese postmenopausal women. Journal of the Endocrine Society. 2017;1(6):625-37. [DOI]
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Fatemeh Doroodian (Author); Nicola Luigi Bragazzi (Corresponding Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







