The Guided School Fitness Model: Confidence (CAPL-2) as the Mediator of Behaviour Change in Inactive Schoolchildren
Abstract
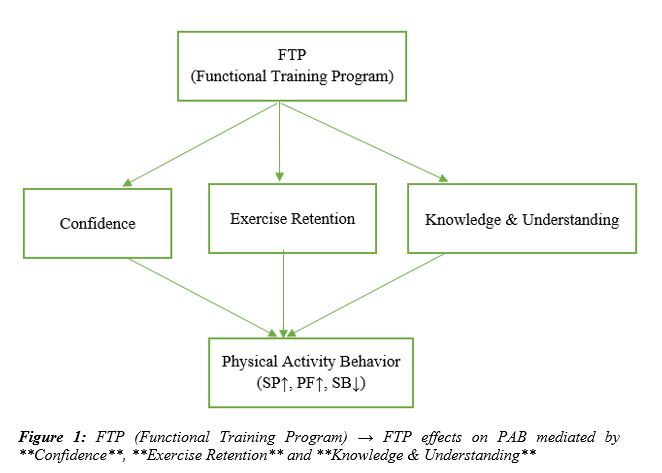
Objective: This study aims to examine the Guided School Fitness Model, especially the Functional Training Program (FTP).
Methods and Materials: Functional Training Program (FTP) used as an intervention to increase physical activity behavior (PAB) in inactive schoolchildren. Based on Self-determination Theory (SDT), the authors hypothesized that FTP's effect on PAB would be mediated through changes in schoolchildren's confidence, exercise retention, and knowledge & understanding.
Results: The FTP had a significant positive effect on confidence (β=0.624), exercise retention (β=0.755), and knowledge & understanding (β=0.684). All three mediators positively influenced PAB: confidence (β=0.543), exercise retention (β=0.498), and knowledge & understanding (β=0.571) improved physical activity behavior. Importantly, the mediation analysis confirmed that the FTP's effect on PAB is mediated by these three variables. The indirect effect from the mediation analysis via confidence (β=0.486), exercise retention (β=0.522), and knowledge & understanding (β=0.448) were all statistically significant, demonstrating specific pathways of behavior change. It also demonstrated that the model significantly explained a portion of the variance in PAB, indicating high predictive strength.
Conclusion: These findings indicate that successful interventions need to be holistic and address not only physical activity but also aspects such as confidence, long-term participation, and health literacy to achieve sustainable behavior change in inactive children.
Downloads
References
1. Akbar Z, Naeem S, Javed S, Akhtar Z, Ashfaq Z, Ismail WU, et al. Risk factors of overweight and obesity in childhood and adolescence in Pakistan, a systematic review. Discover Public Health. 2025;22 (1):75. [DOI]
2. Tanveer M, Batrakoulis A, Asghar E, Hohmann A, Brand S, de Sousa Fernandes MS, et al. Association of sleep duration with overweight and obesity among school-aged children and adolescents in Pakistan—An empirical cross-sectional study. Journal of Education and Health Promotion. 2025;14 (1):43. [PMID: 40104364] [PMCID: PMC11918329] [DOI]
3. Federation WO. Atlas of childhood obesity. Atlas of Childhood Obesity. 2019.
4. Yan W, Yan X, Mubarik S, Nawsherwan. Epidemiological trend and age-period-cohort effects on cardiovascular disease mortality and disability-adjusted life years attributable to dietary risks and high body mass index at the regional and country level across China and Pakistan. Frontiers in nutrition. 2023;10:1158769. [PMID: 37346907] [PMCID: PMC10280070] [DOI]
5. Tanveer M, Asghar E, Tanveer U, Roy N, Zeba A, Al-Mhanna SB, et al. Association of nutrition behavior and food intake with overweight and obesity among school-aged children and adolescents in Pakistan: a cross-sectional study. AIMS Public Health. 2024;11 (3):803. [PMID: 39416903] [PMCID: PMC11474325] [DOI]
6. Liao T, Duhig SJ, Du G, Luo B, Wang YT. The effect of a functional strength training intervention on movement quality and physical fitness in adolescents. Perceptual and Motor Skills. 2022;129 (1):176-94. [PMID: 34784820] [DOI]
7. Zhang D, Geok SK, Chan YM, Zaremohzzabieh Z, Lam SK, He S. Exploring the effects of a 12-week functional training program on fundamental motor skills for primary school children aged 6–7. Children and Youth Services Review. 2024;167:108008. [DOI]
8. Gavanda S, Isenmann E, Geisler S, Faigenbaum A, Zinner C. The effects of high-intensity functional training compared with traditional strength or endurance training on physical performance in adolescents: a randomized controlled trial. The Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research. 2022;36 (3):624-32. [PMID: 35180184] [DOI]
9. Jerebine A, Arundell L, Watson-Mackie K, Keegan R, Jurić P, Dudley D, et al. Effects of holistically conceptualised school-based interventions on children’s physical literacy, physical activity, and other outcomes: a systematic review. Sports medicine-open. 2024;10 (1):105. [PMID: 39333343] [PMCID: PMC11436493] [DOI]
10. Carl J, Barratt J, Wanner P, Toepfer C, Cairney J, Pfeifer K. The effectiveness of physical literacy interventions: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Sports medicine. 2022;52 (12):2965-99. [PMID: 35994237] [PMCID: PMC9691485] [DOI]
11. Ma JK, Floegel TA, Li LC, Leese J, De Vera MA, Beauchamp MR, et al. Tailored physical activity behavior change interventions: challenges and opportunities. Translational Behavioral Medicine. 2021;11 (12):2174-81. [PMID: 34424344] [PMCID: PMC8672936] [DOI]
12. Lubans D, Richards J, Hillman C, Faulkner G, Beauchamp M, Nilsson M, et al. Physical activity for cognitive and mental health in youth: a systematic review of mechanisms. Pediatrics. 2016;138 (3):e20161642. [PMID: 27542849] [DOI]
13. Moeller NC, Oestergaard L, Rasmussen MGB, Schmidt-Persson J, Larsen KT, Juhl CB. How to get children moving? The effectiveness of school-based interventions promoting physical activity in children and adolescents–A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled-and controlled studies. Health & place. 2024;89:103333. [PMID: 39163765] [DOI]
14. Xie C, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Li Y, Shi P, Wang S. Effects of interventions on physical activity behavior change in children and adolescents based on a trans-theoretical model: a systematic review. BMC Public Health. 2025;25 (1):657. [PMID: 39966763] [PMCID: PMC11834675] [DOI]
15. Ryan RM, Duineveld JJ, Di Domenico SI, Ryan WS, Steward BA, Bradshaw EL. We know this much is (meta-analytically) true: A meta-review of meta-analytic findings evaluating self-determination theory. Psychological Bulletin. 2022;148 (11-12):813. [DOI]
16. Ryan RM. The Oxford handbook of self-determination theory: Oxford University Press; 2023. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordhb/9780197600047.001.0001} 3_https://doi.org/DOI}
17. Hale GE, Colquhoun L, Lancastle D, Lewis N, Tyson PJ. Physical activity interventions for the mental health and well‐being of adolescents–a systematic review. Child and adolescent mental health. 2021;26 (4):357-68. [PMID: 34105239] [DOI]
18. Recchia F, Bernal JD, Fong DY, Wong SH, Chung P-K, Chan DK, et al. Physical activity interventions to alleviate depressive symptoms in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA pediatrics. 2023;177 (2):132-40. [PMID: 36595284] [PMCID: PMC9857695] [DOI]
19. Zhang D, Soh KG, Chan YM, Feng X, Bashir M, Xiao W. Effect of functional training on fundamental motor skills among children: a systematic review. Heliyon. 2024;10 (23). [PMID: 39687180] [DOI]
20. Lasković M, Marković M, Stanković V. Functional training VS. physical education classes: the effects on physical performance in primary school girls. Facta Universitatis, Series: Physical Education and Sport. 2022:133-41. [DOI]
21. Zhang T, Zhao J, Yu L. The Effect of Fitness Apps Usage Intensity on Exercise Adherence Among Chinese College Students: Testing a Moderated Mediation Model. Psychology Research and Behavior Management. 2023;16 (null):1485-94. [PMID: 37138699] [PMCID: PMC10150761] [DOI]
22. Pulling Kuhn A, Stoepker P, Dauenhauer B, Carson RL. A systematic review of multi-component comprehensive school physical activity program (CSPAP) interventions. American Journal of Health Promotion. 2021;35 (8):1129-49. [PMID: 33955278] [DOI]
23. Fu T, Zhang D, Wang W, Geng H, Lv Y, Shen R, et al. Functional training focused on motor development enhances gross motor, physical fitness, and sensory integration in 5–6-year-old healthy Chinese children. Frontiers in Pediatrics. 2022;10:936799. [PMID: 35899135] [PMCID: PMC9309543] [DOI]
24. Bohlen LC, Emerson JA, Rhodes RE, Williams DM. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the outcome expectancy construct in physical activity research. Annals of Behavioral Medicine. 2022;56 (7):658-72. [PMID: 34491296] [PMCID: PMC9275000] [DOI]
25. Papadopoulos N, Mantilla A, Bussey K, Emonson C, Olive L, McGillivray J, et al. Understanding the benefits of brief classroom‐based physical activity interventions on primary school‐aged children's enjoyment and subjective wellbeing: A systematic review. Journal of School Health. 2022;92 (9):916-32. [PMID: 35607277] [PMCID: PMC9545911] [DOI]
26. Wei-na LIU, Cheng-lin Z, Jun SUN. Effect of Outdoor Sport Motivation on Sport Adherence in Adolescents—The Mediating Mechanism of Sport Atmosphere. China Sport Science. 2011;31 (10):41-7. [DOI]
27. Sadeghi Pour N, Marjan Baniasadi T. Mediating Role of Enjoyment in the Associations between Social Support and Participation in Physical Activity among Female Adolescents. International Journal of Sport Studies for Health. 2025;8 (3). [DOI]
28. Hu R, Lai B, Ma W, Zhang Y, Deng Y, Liu L, et al. How formal caregiver’s BPSD knowledge influences positive aspects of caregiving: the mediating role of attitude and the moderating role of self-efficacy. BMC geriatrics. 2022;22 (1):731. [PMID: 36064326] [PMCID: PMC9444087] [DOI]
29. Makepeace R, Craig M. Higher intensity exercise after encoding is more conducive to episodic memory retention than lower intensity exercise: A field study in endurance runners. PLoS One. 2024;19 (9):e0308373. [PMID: 39269940] [PMCID: PMC11398685] [DOI]
30. Ruiz JR, Castro-Piñero J, España-Romero V, Artero EG, Ortega FB, Cuenca MM, et al. Field-based fitness assessment in young people: the ALPHA health-related fitness test battery for children and adolescents. British journal of sports medicine. 2011;45 (6):518-24. [PMID: 20961915] [DOI]
31. Segura-Díaz JM, Barranco-Ruiz Y, Saucedo-Araujo RG, Aranda-Balboa MJ, Cadenas-Sanchez C, Migueles JH, et al. Feasibility and reliability of the Spanish version of the Youth Activity Profile questionnaire (YAP-Spain) in children and adolescents. Journal of sports sciences. 2021;39 (7):801-7. [PMID: 33213295] [DOI]
32. Pan SY, Cameron C, DesMeules M, Morrison H, Craig CL, Jiang X. Individual, social, environmental, and physical environmental correlates with physical activity among Canadians: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. 2009;9 (1):21. [PMID: 19149865] [PMCID: PMC2639577] [DOI]
33. Longmuir PE, Gunnell KE, Barnes JD, Belanger K, Leduc G, Woodruff SJ, et al. Canadian Assessment of Physical Literacy Second Edition: a streamlined assessment of the capacity for physical activity among children 8 to 12 years of age. BMC public health. 2018;18 (Suppl 2):1047. [PMID: 30285687] [PMCID: PMC6167760] [DOI]
34. Barrows TS. College students' knowledge and beliefs: A survey of global understanding. The final report of the global understanding project: Transaction Publishers; 1981. 3_https://doi.org/DOI}
35. Hair JF, Sarstedt M, Ringle CM, Sharma PN, Liengaard BD. Going beyond the untold facts in PLS–SEM and moving forward. European Journal of Marketing. 2024;58 (13):81-106. [DOI]
36. Dutrisac S, Bearden AG, Borgel J, Weddell R, Jones M, Oddie S. A tailored physical education program enhances elementary students' self‐efficacy, attitudes, and motivation to engage in physical activity. Psychology in the Schools. 2023;60 (9):3419-34. [DOI]
37. Jacobi S, Beynon A, Dombrowski SU, Wedderkopp N, Witherspoon R, Hebert JJ. Effectiveness of conservative nonpharmacologic therapies for pain, disability, physical capacity, and physical activity behavior in patients with degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 2021;102 (11):2247-60. e7. [PMID: 33933439] [DOI]
38. Matthews J, Hall AM, Keogh A. Evaluating the effects of behavior change training on the knowledge, confidence and skills of sport and exercise science students. BMC Sports Science, Medicine and Rehabilitation. 2020;12 (1):62. [PMID: 33042551] [PMCID: PMC7539374] [DOI]
39. McCarthy H, Potts HW, Fisher A. Physical activity behavior before, during, and after COVID-19 restrictions: longitudinal smartphone-tracking study of adults in the United Kingdom. Journal of medical Internet research. 2021;23 (2):e23701. [PMID: 33347421] [PMCID: PMC7861037] [DOI]
40. Kurnaz M, Flôres F, Altınkök M, Esen H, Silva A. A 10-week play-based after-school program to improve coordinative abilities and physical fitness capabilities among adolescents: a randomized trial. Scientific reports. 2024;14 (1):13531. [PMID: 38866795] [PMCID: PMC11169339] [DOI]
41. Radcliffe JC. Functional training for athletes at all levels: workouts for agility, speed and power: Simon and Schuster; 2023. 3_https://doi.org/DOI}
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Asia Bano (Corresponding Author); Eliza Hafiz, Sareena Hanim Hamza , Farooq Ahmed Jam (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







