Predictors of Impulsiveness: The Roles of Sleep Quality and Body Image Dissatisfaction in Physically Disabled Adolescent Girls
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.prien.2.2.5Keywords:
Adolescent girls, mild physical disabilities, impulsiveness, sleep quality, body image dissatisfaction, cross-sectional studyAbstract
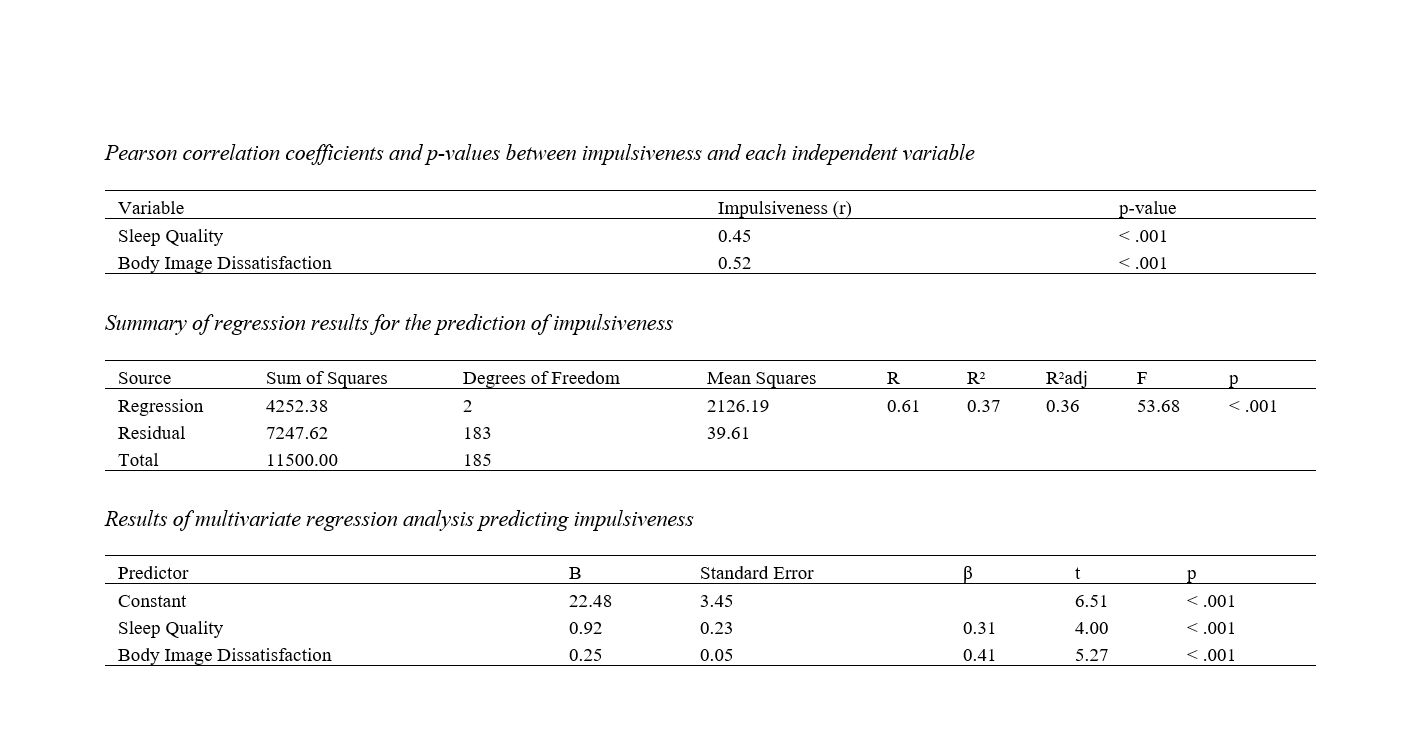
This study aimed to examine the relationships between sleep quality, body image dissatisfaction, and impulsiveness in adolescent girls with mild physical disabilities. This cross-sectional study included 186 adolescent girls with mild physical disabilities. Participants were recruited from rehabilitation centers and special schools. Impulsiveness was measured using the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale (BIS-11), sleep quality was assessed with the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), and body image dissatisfaction was evaluated using the Body Shape Questionnaire (BSQ). Pearson correlation coefficients were calculated to examine the relationships between the variables. A linear regression analysis was performed to determine the predictive value of sleep quality and body image dissatisfaction on impulsiveness, using SPSS version 27. The mean score for impulsiveness was 55.28 (SD = 10.45), sleep quality was 12.67 (SD = 3.98), and body image dissatisfaction was 87.34 (SD = 15.29). Pearson correlation analysis showed significant positive correlations between impulsiveness and sleep quality (r = 0.45, p < .001), and between impulsiveness and body image dissatisfaction (r = 0.52, p < .001). The regression model indicated that both sleep quality (B = 0.92, p < .001) and body image dissatisfaction (B = 0.25, p < .001) significantly predicted impulsiveness, explaining 37% of the variance (R² = 0.37, F(2, 183) = 53.68, p < .001). Poor sleep quality and high body image dissatisfaction are significant predictors of impulsiveness in adolescent girls with mild physical disabilities. Interventions aimed at improving sleep quality and promoting positive body image may help reduce impulsiveness and enhance overall well-being in this population.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.





