Comparison of Spinning and Resistance Training on Resistin, Visfatin, Lipid Profile, and Quality of Life in Overweight Women
Keywords:
Overweight, Resistin, Visfatin, Lipid Profile, Quality of LifeAbstract
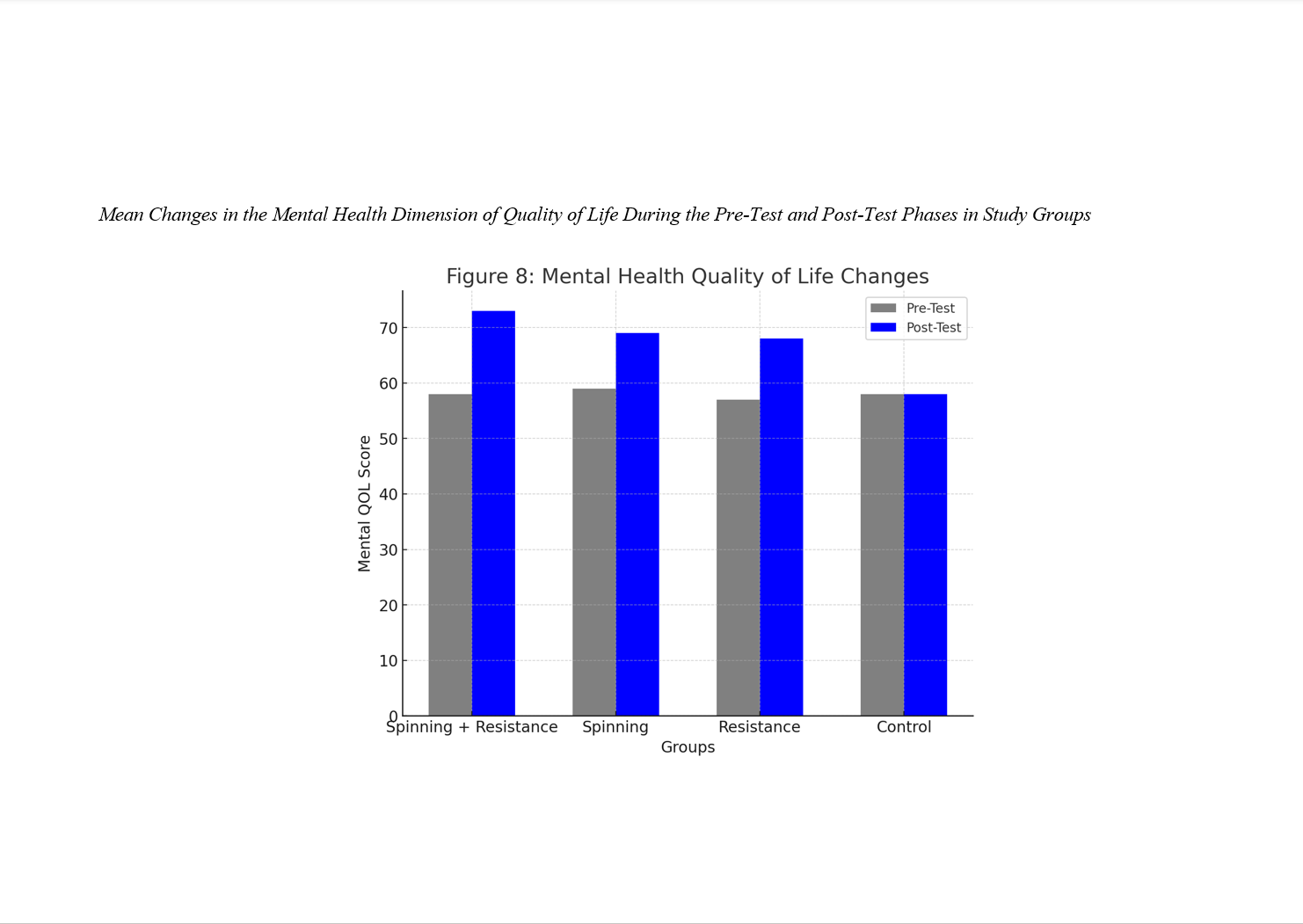
The present study aimed to compare the effects of spinning and resistance training on resistin, visfatin, lipid profile, and quality of life dimensions in overweight women. This quasi-experimental study employed a pre-test–post-test design with a control group. From all overweight women (body mass index between 25 and 29.9 kg/m²) in Najafabad, Isfahan, a total of 60 overweight women (aged 20 to 30 years) were purposively selected for participation in the study and were randomly assigned to four groups: spinning training, resistance training, combined training (spinning + resistance), and control. The study consisted of three phases: pre-test, intervention (training), and post-test. Initially, in the pre-test phase, blood sampling was performed after 12 hours of fasting, followed by the completion of the Quality of Life Questionnaire (SF-36) by the participants. After the pre-test phase, the training phase commenced. The training phase lasted for 8 weeks, with three sessions per week conducted in a gym. Forty-eight hours after the completion of the training phase, in the post-test phase, blood sampling was again performed after 12 hours of fasting, and the participants completed the Quality of Life Questionnaire (SF-36) once more. Data were analyzed using paired t-tests, analysis of covariance, and Bonferroni post hoc tests. The results indicated that spinning, resistance, and combined training (resistance combined with spinning) significantly reduced resistin and visfatin levels in overweight women. Combined training had a greater impact than the individual training modalities. Additionally, these training programs improved cholesterol, triglyceride, LDL, and HDL levels, with combined training yielding the most significant effects. The training programs also enhanced physical and psychological quality of life; however, no significant difference was observed between groups in the psychological dimension.
Downloads
References
1. Hajiebrahim Araghi B, Rahmani MA, Rahimaghaee F. Examining the Mediating Role of Body Esteem in the Relationship Between Social Body Anxiety and Health-Oriented Lifestyle in Women with Obesity. Psychology of Woman Journal. 2024;5(3):97-105. [DOI]
2. Mond JM, Gill T. Eating Disorders and Obesity. Handbook of Obesity, Two-Volume Set: CRC Press; 2024. p. 1–384
3. Abiri B, Hosseinpanah F, Banihashem S, Madinehzad SA, Valizadeh M. Mental health and quality of life in different obesity phenotypes: a systematic review. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes. 2022;20(1):63. [DOI]
4. Who. Fact sheets: obesity and overweight 2020 [Available from: https://www.who.int/en/newsroom/fact-esity-and-overweight
5. Doll HA, Petersen SE, Stewart-Brown SL. Obesity and physical and emotional well-being: associations between body mass index, chronic illness, and the physical and mental components of the SF-36 questionnaire. Obesity Research. 2020;8(2):160-70. [DOI]
6. Yamaner E, Demirkıran B, Özcan E. Effects of a Six-Week Aerobic Exercise Training Program on Lipid Profiles in Sedentary Women. International Journal of Disabilities Sports and Health Sciences. 2024;7(3):564-9. [DOI]
7. Huang WC, Chiu PC, Ho CH. The sprint-interval exercise using a spinning bike improves physical fitness and ameliorates primary dysmenorrhea symptoms through hormone and inflammation modulations: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Sports Science & Medicine. 2022;21(4):595.
8. Safarpour Z, Nayebi F, Nikofer M. The effect of 6 weeks of spinning and stationary cycling exercises on serum levels of CTRP3 and body fat percentage in obese and overweight women. Feyz. 2020;24(6):639-48.
9. Ratajczak M, Skrypnik D, Krutki P, Karolkiewicz J. Effects of an indoor cycling program on cardiometabolic factors in women with obesity vs. Normal body weight. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020;17(23):8718. [DOI]
10. Conde J, Scotece M, Gómez R, López V, Gómez-Reino JJ, Lago F, et al. Critical Review Adipokines: Biofactors from white adipose tissue. A complex hub among inflammation, metabolism, and immunity. [Journal not specified]. 2020.
11. Abdollahi Sadegh N, Norollahi Z, Sepehri Rad M, Mehrshad H. The effect of eight weeks of bodyweight resistance training on serum levels of resistin and visfatin in elderly women with metabolic syndrome. Iranian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology. 2021;5(5):107-15.
12. Bahram ME, Afrondeh R, Pourvaghar MJ, Qiyami Taklami H, Hemmati S. The effect of resistance training on serum levels of visfatin, insulin resistance, glucose, and some body composition indices in obese adolescents. Research in Physiology and Sports Management. 2022;14(1):147-59.
13. Khajeh Lendi M, Lutfali BZ, Z S. Investigating the effect of a period of Pilates exercise on serum levels of resistin, visfatin, and chemerin in overweight women. Internal Medicine, Rooz. 2020;27(1):98-113.
14. Rezaei Manesh D, Amiri Farsani P. The effect of an aquatic aerobic exercise program on plasma levels of apelin and resistin in men with type 2 diabetes. Journal of Marine Sciences and Technology. 2020;19(3):12-21.
15. Sarami A, Parastesh M, Mohammadi L. Investigating the changes in resistin levels following aerobic exercise and its relationship with fertility in male rats with type 2 diabetes. Rooz Internal Medicine. 2020;26(2):156-69. [DOI]
16. Delshad A, Dashti M. The effect of eight weeks of combined (aerobic-TRX) training and cinnamon supplementation on serum levels of leptin and visfatin in overweight inactive women. Journal of Sabzevar University of Medical Sciences. 2023;30(4):462-74.
17. Erdem G, Naharci MI, Demirtas A. Therapeutic lifestyle change intervention in metabolic syndrome decreases plasma visfatin levels. [Journal not specified]. 2024.
18. Ali Nia A, Moein A. The effect of an aerobic exercise program along with a high-fat diet on resting serum levels of resistin and the leptin-to-adiponectin ratio in male rats. Research in Medicine. 2023;47(4):33-48.
19. Montazeri A, Taghizadeh Z, Taheri S, Siahbazi S, Masoomi R. Domination of premenstrual syndrome on women's quality of life: a qualitative study. Payesh (Health Monitor) Journal. 2019;18(1):53-66.
20. Karimi Aliabad M, Najafian Razavi M, Sadeghi M, Farokhi A, Rezaei M. The Effects of Physical Activity on Key Variables That Influence the Characteristics of Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. International Journal of Sport Studies for Health. 2024;7(4):95-105. [DOI]
21. Alikhani S, Etemad Zahir Z, Azizi Beigi K. Benefits of spinning exercises and green tea on cardiovascular risk factors in overweight women. Payavard Health. 2021;15(3):212-23.
22. Ashtary-Larky D, Bagheri R, Asbaghi O, Tinsley GM, Kooti W, Abbasnezhad A, et al. Effects of resistance training combined with a ketogenic diet on body composition: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 2022;62(21):5717-32. [DOI]
23. Taheri M, Irandoust K, Ahmadi S. The effect of arginine supplementation following sleep deprivation on carbohydrate and fat metabolism, balance and fatigue index in female athlete students. Sport Sciences and Health Research. 2021;13(1):75-83. [DOI]
24. Vafaee T, Gholami M. The effect of 8 weeks of resistance training with two different intensities on plasma levels of resistin and insulin resistance in obese elderly women. Applied Studies of Biological Sciences in Sport. 2021;9(112):102-12.
25. Lee ED, Seo TB, Kim YP. Effect of resistance circuit training on health-related physical fitness, plasma lipid, and adiponectin in obese college students. Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation. 2022;18(6):382. [DOI]
26. Shang J, Chen LL, Sun H, Xiao FX. Effect of exercise on expression of visfatin of visceral fat in high-fat-diet-fed rats. China Journal of Modern Medicine. 2023;5:014.
27. Moradian H, Hosseinpour Delavar S, Zabet A. The effect of eight weeks of circular resistance training on endothelial markers, blood pressure, and lipid profile in obese women with pre-hypertension. Journal of Physiology and Physical Activity. 2022;15(2):84-94. [DOI]
28. Haji Nia M, Haghighi A, Askari R. The effect of interval and resistance training on lipid profile and body composition in middle-aged men. Journal of Torbat Heydariyeh University of Medical Sciences. 2020;8(3):61-74.
29. Pashaee Z, Jafari Afshar M, Alivand M. The effect of two types of high-intensity interval training alone and combined with resistance training on lipid profile and glucose homeostasis in overweight/obese middle-aged women. Research in Medicine. 2020;44(4):554-61.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mohadese Mohammadi (Author); Elham Eftekhari (Corresponding Author); Jamshid Banaei Borojeni, Hamid Zahedi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















