Perspective: Fröhner’s 1998 Posture Index For Lumbo-Pelvic Hip Complex
Keywords:
Posture index, lumbopelvic hip complex, syndromeAbstract
Objective: Lumbopelvic-hip complex enable to indicate force energy generation containing muscle proximal and distal end group connect abdomen and proximal low syndrome to losses of segment kinetic chain.
Methods and Materials: Rarely postural segment distortion collapses complex movement sporting events after loading stress, accordingly dynamic postural strategies reactivate spinal balance were invesitageted. Uncommon lumbopelvic hip complex evaluation is detect to young and adult individuals using Fröhner’s posture index, according to specific complex syndrome provable review were examined.
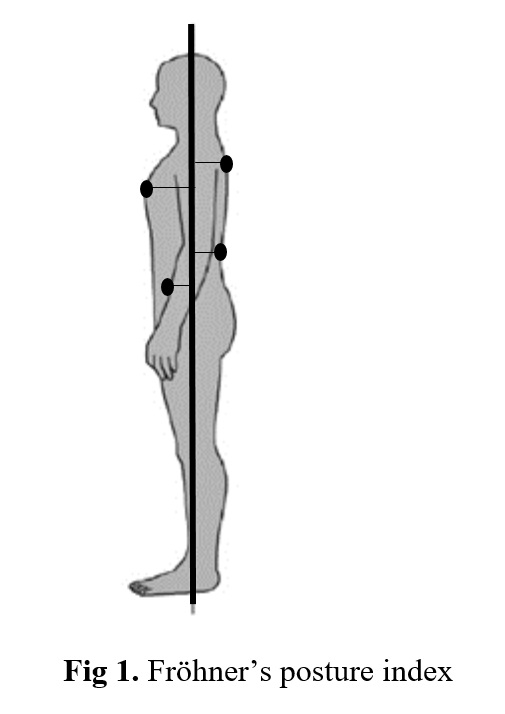
Fındings: The mechanic syndrome have been explained on compartment complex to be imbalanced musculature and myofascial dystrophy. Fröhner's posture index was explained with this perspective.
Conclusion: A new approach to the evaluation of the lumbopelvic hip complex is postural medicine research.
Keywords: Posture index, lumbopelvic hip complex, syndrome
Downloads
References
1. Mottram S, Comerford M. Stability Dysfunction and
Low Back Pain. Journal of Orthopaedic Medicine. 1998;20(2):13-
8. [DOI]
2. Chang M, Slater LV, Corbett RO, Hart JM, Hertel J.
Muscle activation patterns of the lumbo-pelvic-hip complex during
walking gait before and after exercise. Gait & Posture. 2017;52:15-
21. [PMID: 27846435] [DOI]
3. Wattananon P, Sinsurin K, Somprasong S. Association
between lumbopelvic motion and muscle activation in patients with
non-specific low back pain during forward bending task: A crosssectional study. Hong Kong Physiotherapy Journal.
2020;40(01):29-37. [PMID: 32489238] [PMCID: PMC7136525]
[DOI]
4. López-de-Celis C, Sánchez-Alfonso N, Rodríguez-Sanz
J, Romaní-Sánchez S, Labata-Lezaun N, Canet-Vintró M, et al.
Quadriceps and gluteus medius activity during stable and unstable
loading exercises in athletes. A cross-sectional study. Journal of
Orthopaedic Research. 2024;42(2):317-25. [PMID: 37593805]
[DOI]
5. Hasegawa K, Dubousset JF. Cone of Economy with
the Chain of Balance-Historical Perspective and Proof of
Concept. Spine Surgery and Related Research. 2022;6(4):337-49.
[PMID: 36051675] [PMCID: PMC9381078] [DOI]
6. Antonio S, Wolfgang G, Robert H, Fullerton B, Carla S.
The anatomical and functional relation between gluteus maximus
and fascia lata. Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies.
2013;17(4):512-7. [PMID: 24139012] [DOI]
7. Vleeming A, Pool-Goudzwaard AL, Stoeckart R, van
Wingerden J-P, Snijders CJ. The Posterior Layer of the
Thoracolumbar Fascia|Its Function in Load Transfer From Spine to
Legs. Spine. 1995;20(7). [PMID: 7701385] [DOI]
8. Kahraman Y. Postural Structure and Mechanic
Syndromes Associated with Human Movement Physiology: A
Traditional Review of Re-modelling Musculature. Turk J
Osteoporos. 2021;27(2):61-7. [DOI]
9. Fujitani R, Jiromaru T, Kida N, Nomura T. Effect of
standing postural deviations on trunk and hip muscle activity.
Journal of Physical Therapy Science. 2017;29(7):1212-5. [PMID:
28744050] [PMCID: PMC5509594] [DOI]
10. Beneck GJ, Story JW, Donald S. Postural Cueing to
Increase Lumbar Lordosis Increases Lumbar Multifidus Activation
During Trunk Stabilization Exercises: Electromyographic
Assessment Using Intramuscular Electrodes. Journal of
Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy. 2016;46(4):293-9.
[PMID: 26954268] [DOI]
11. Sasaki S, Tsuda E, Yamamoto Y, Maeda S, Kimura Y,
Fujita Y, et al. Core-Muscle Training and Neuromuscular Control
of the Lower Limb and Trunk. Journal of Athletic Training.
2019;54(9):959-69. [PMID: 31386583] [PMCID: PMC6795098]
[DOI]
12. Ludwig O, Hammes A, Kelm J, Schmitt E. Assessment
of the posture of adolescents in everyday clinical practice: Intrarater and inter-rater reliability and validity of a posture index.
Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies. 2016;20(4):761-6.
[PMID: 27814856] [DOI]
13. Ludwig O, Kelm J, Hammes A, Schmitt E, Fröhlich M.
Targeted Athletic Training Improves the Neuromuscular
Performance in Terms of Body Posture From Adolescence to
Adulthood – Long-Term Study Over 6 Years. Frontiers in
Physiology. 2018;9. [PMID: 30542291] [PMCID: PMC6277893]
[DOI]
14. Lukovic T, Cukovic S, Lukovic V, Devedzic G,
Djordjevic D. Towards a new protocol of scoliosis assessments and
monitoring in clinical practice: A pilot study. Journal of Back and
Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation. 2015;28:721-30. [PMID:
25502347] [DOI]
15. Ludwig O, Mazet C, Mazet D, Hammes A, Schmitt E.
Age-dependency of posture parameters in children and adolescents.
Journal of Physical Therapy Science. 2016;28(5):1607-10. [PMID:
27313382] [PMCID: PMC4905921] [DOI]
16. Bibrowicz K, Szurmik T, Wodarski P, Michnik R,
Mysliwiec A, Barszcz J, et al. Quality of body posture and postural
stability in people with intellectual disability playing volleyball.
Acta of bioengineering and biomechanics. 2019;21(1):23-30.
[PMID: 31197287]
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Yeliz KAHRAMAN (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







