Effects of Additional Exercise Volume on Weight Loss, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation in Young Wrestling Athletes
Keywords:
Wrestlers, Additional Exercise Volume, weight loss, inflammation, oxidative stressAbstract
Background: Maintaining an optimal weight is essential for wrestlers, given their competition in weight-classified categories. However, many wrestlers resort to unhealthy methods of rapid weight loss, such as drastic caloric restriction and dehydration, which can adversely affect their overall wellbeing.
Objective: This study aimed to examine the impact of a two-week increase in exercise volume on weight loss, serum oxidative stress, and inflammation in young wrestlers.
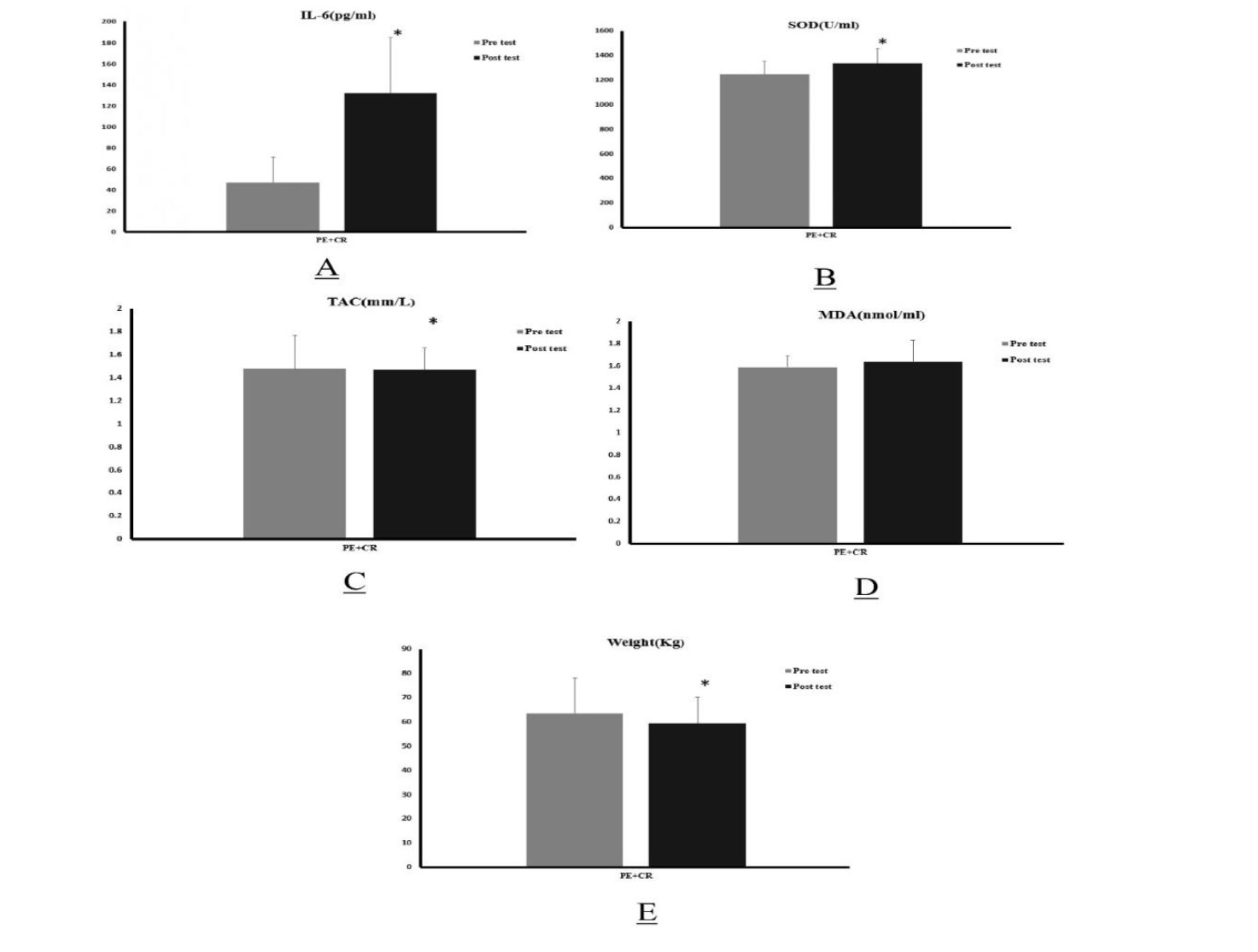
Methods and Materials: Twenty wrestlers (aged 15-19, weight 63.47 kg) participated in a 2-week exercise intervention in addition to their regular weekly wrestling drills. The intervention consisted of resistance training, high-intensity interval training, and speed training. Wrestlers weighed daily over 2-week span. The participants' superoxide dismutase (SOD), malondialdehyde (MDA), total antioxidant capacity (TAC), and serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) were measured both before and after the intervention. Data were analyzed using the paired t-test conducted through SPSS software, with a significant level set at p < 0.05.
Results: The 2-week intervention resulted in significant weight loss (p<0.001). Within group comparisons found serum levels of IL-6, SOD, and TAC significantly increased from pre-to-post testing, but MDA did not change significantly.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the present study demonstrates that a two-week increase in exercise volume can be an effective strategy for promoting weight loss and reducing oxidative stress in young wrestlers. The findings suggest that the improvement in antioxidant status is likely a result of the body's response to increased inflammation, as indicated by changes in inflammatory markers.
Downloads
References
1. Artioli GG, Franchini E, Nicastro H, Sterkowicz S, Solis
MY, Lancha AH. The need of a weight management control
program in judo: a proposal based on the successful case of
wrestling. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition.
2010;7:1-5. [PMID: 20441594] [PMCID: PMC2876998] [DOI]
2. Oppliger R, Landry G, Foster S, Lambrecht A.
WISCONSIN MINIMUM WEIGHT RULE CURTAILS WEIGHT
CUTTING PRACTICES OF HIGH SCHOOL WRESTLERS: 72.
Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise. 1995;27(5):S12. [DOI]
3. Steen SN, Brownell KD. Patterns of weight loss and
regain in wrestlers: has the tradition changed? Medicine and
science in sports and exercise. 1990;22(6):762-8. [PMID: 2287253]
[DOI]
4. Roemmich JN, Sinning WE. Weight loss and wrestling
training: effects on growth-related hormones. Journal of Applied
Physiology. 1997;82(6):1760-4. [DOI]
5. Oppligen RA, Landry GL, Foster SW, Lambrecht AC.
Bulimic behaviors among interscholastic wrestlers: a statewide
survey. Pediatrics. 1993;91(4):826-31. [DOI]
6. Ziegler PJ, San Khoo C, Kris-Etherton PM,
Jonnalagadda SS. Nutritional status of nationally ranked junior US
figure skaters. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.
1998;98(7):809. [PMID: 9664924] [DOI]
7. Sumithran P, Prendergast LA, Delbridge E, Purcell K,
Shulkes A, Kriketos A, et al. Long-term persistence of hormonal
adaptations to weight loss. New England Journal of Medicine.
2011;365(17):1597-604. [PMID: 22029981] [PMCID:
https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1105816]
8. Sundgot-Borgen J, Torstveit MK. Prevalence of eating
disorders in elite athletes is higher than in the general population.
Clinical journal of sport medicine. 2004;14(1):25-32. [PMID:
14712163] [DOI]
9. Choma CW, Sforzo GA, Keller BA. Impact of rapid
weight loss on cognitive function in collegiate wrestlers. Medicine
and science in sports and exercise. 1998;30(5):746-9. [PMID:
9588618] [DOI]
10. Yang W-H. Impact of rapid weight reduction on health
and per. 2017.
11. Nishimaki M, Tabata H, Konishi M, Pettersson S,
Sakamoto S. Effects of different periods of rapid weight loss on
dehydration and oxidative stress. Archives of budo. 2018;14:319-
27.
12. Ozkan I, Ibrahim CH. Dehydration, skeletal muscle
damage and inflammation before the competitions among the elite
wrestlers. Journal of physical therapy science. 2016;28(1):162-8.
[PMID: 26957750] [PMCID: PMC4755996] [DOI]
13. Oppliger RA, Utter AC, Scott JR, Dick RW, Klossner D.
NCAA rule change improves weight loss among national
championship wrestlers. Medicine and science in sports and
exercise. 2006;38(5):963-70. [PMID: 16672852] [DOI]
14. Donnelly JE, Hill JO, Jacobsen DJ, Potteiger J, Sullivan
DK, Johnson SL, et al. Effects of a 16-month randomized
controlled exercise trial on body weight and composition in young,
overweight men and women: the Midwest Exercise Trial. Archives
of internal medicine. 2003;163(11):1343-50. [PMID: 12796071]
[DOI]
15. Ackland TR, Lohman TG, Sundgot-Borgen J, Maughan
RJ, Meyer NL, Stewart AD, et al. Current status of body
composition assessment in sport: review and position statement on
behalf of the ad hoc research working group on body composition
health and performance, under the auspices of the IOC Medical
Commission. Sports medicine. 2012;42:227-49. [PMID:
22303996] [DOI]
16. Donnelly JE, Blair SN, Jakicic JM, Manore MM, Rankin
JW, Smith BK. Appropriate physical activity intervention
strategies for weight loss and prevention of weight regain for
adults. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise. 2009;41(2):459-
71. [PMID: 19127177] [DOI]
17. Swift DL, Johannsen NM, Lavie CJ, Earnest CP, Church
TS. The role of exercise and physical activity in weight loss and
maintenance. Progress in cardiovascular diseases. 2014;56(4):441-
7. [PMID: 24438736] [PMCID: PMC3925973] [DOI]
18. Schuenke MD, Mikat RP, McBride JM. Effect of an
acute period of resistance exercise on excess post-exercise oxygen
consumption: implications for body mass management. European
journal of applied physiology. 2002;86(5):411-7. [PMID:
11882927] [DOI]
19. Weinheimer EM, Sands LP, Campbell WW. A
systematic review of the separate and combined effects of energy
restriction and exercise on fat-free mass in middle-aged and older
adults: implications for sarcopenic obesity. Nutrition reviews.
2010;68(7):375-88. [PMID: 20591106] [DOI]
20. Rankin JW, Ocel JV, Craft LL. Effect of weight loss and
refeeding diet composition on anaerobic performance in wrestlers.
Medicine and science in sports and exercise. 1996;28(10):1292-9.
[PMID: 8897387] [DOI]
21. Çakir-Atabek H, Demir S, PinarbaSili RD, Gündüz N.
Effects of different resistance training intensity on indices of
oxidative stress. The Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research.
2010;24(9):2491-7. [PMID: 20802287] [DOI]
22. Garthe I, Raastad T, Refsnes PE, Koivisto A, SundgotBorgen J. Effect of two different weight-loss rates on body
composition and strength and power-related performance in elite
athletes. International journal of sport nutrition and exercise
metabolism. 2011;21(2):97-104. [PMID: 21558571] [DOI]
23. Azizbeigi K, Stannard SR, Atashak S, Haghighi MM.
Antioxidant enzymes and oxidative stress adaptation to exercise
training: Comparison of endurance, resistance, and concurrent
training in untrained males. Journal of exercise science & fitness.
2014;12(1):1-6. [DOI]
24. So B, Park J, Jang J, Lim W, Imdad S, Kang C. Effect of
aerobic exercise on oxidative stress and inflammatory response
during particulate matter exposure in mouse lungs. Frontiers in
Physiology. 2022;12:773539. [PMID: 35185596] [PMCID:
PMC8850364] [DOI]
25. Ramos-González E, Bitzer-Quintero O, Ortiz G,
Hernández-Cruz J, Ramírez-Jirano L. Relationship between
inflammation and oxidative stress and its effect on multiple
sclerosis. Neurologia. 2021.
26. Martínez-Aranda LM, Sanz-Matesanz M, Orozco-Durán
G, González-Fernández FT, Rodríguez-García L, Guadalupe-Grau
A. Effects of Different Rapid Weight Loss Strategies and
Percentages on Performance-Related Parameters in Combat Sports:
An Updated Systematic Review. International Journal of
Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023;20(6):5158.
[PMID: 36982067] [PMCID: PMC10048848] [DOI]
27. Yagmur R, Isik O, Kilic Y, Dogan I. Weight Loss
Methods and Effects on the Elite Cadet Greco-Roman Wrestlers.
JTRM in Kinesiology. 2019.
28. Ranisavljev M, Kuzmanovic J, Todorovic N, Roklicer R,
Dokmanac M, Baic M, et al. Rapid weight loss practices in
grapplers competing in combat sports. Frontiers in physiology.
2022;13:842992. [PMID: 35222096] [PMCID: PMC8864148]
[DOI]
29. Plowman SA, Smith DL. Exercise physiology for health
fitness and performance: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2013.
30. Hatami M, Akbari ME, Abdollahi M, Ajami M,
Jamshidinaeini Y, Davoodi SH. The relationship between intake of
macronutrients and vitamins involved in one carbon metabolism
with breast cancer risk. 2017.
31. Hiruma E, Katamoto S, Naito H. Effects of shortening
and lengthening resistance exercise with low-intensity on physical
fitness and muscular function in senior adults. MedicalExpress.
2015;2:M150105. [DOI]
32. Farzad B, Gharakhanlou R, Agha-Alinejad H, Curby DG,
Bayati M, Bahraminejad M, et al. Physiological and performance
changes from the addition of a sprint interval program to wrestling
training. The Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research.
2011;25(9):2392-9. [PMID: 21849912] [DOI]
33. Vissers D, Hens W, Taeymans J, Baeyens J-P, Poortmans
J, Van Gaal L. The effect of exercise on visceral adipose tissue in
overweight adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PloS
one. 2013;8(2):e56415. [PMID: 23409182] [PMCID:
PMC3568069] [DOI]
34. Gomez-Cabrera M-C, Domenech E, Viña J. Moderate
exercise is an antioxidant: upregulation of antioxidant genes by
training. Free radical biology and medicine. 2008;44(2):126-31.
[PMID: 18191748] [DOI]
35. Nehlsen-Cannarella S, Fagoaga O, Nieman D, Henson D,
Butterworth D, Schmitt R, et al. Carbohydrate and the cytokine
response to 2.5 h of running. Journal of Applied Physiology.
1997;82(5):1662-7. [PMID: 9134917] [DOI]
36. Bloomer RJ, Goldfarb AH, Wideman L, McKenzie MJ,
Consitt LA. Effects of acute aerobic and anaerobic exercise on
blood markers of oxidative stress. The Journal of Strength &
Conditioning Research. 2005;19(2):276-85. [PMID: 15903362]
[DOI]
37. Petersen AMW, Pedersen BK. The anti-inflammatory
effect of exercise. Journal of applied physiology. 2005;98(4):1154-
62. [PMID: 15772055] [DOI]
38. Stiegler P, Cunliffe A. The role of diet and exercise for
the maintenance of fat-free mass and resting metabolic rate during
weight loss. Sports medicine. 2006;36:239-62. [PMID: 16526835]
[DOI]
39. Donnelly JE, Blair SN, Jakicic JM, Manore MM, Rankin
JW, Smith BK. American College of Sports Medicine Position
Stand. Appropriate physical activity intervention strategies for
weight loss and prevention of weight regain for adults. Medicine
and science in sports and exercise. 2009;41(2):459-71. [PMID:
19127177] [DOI]
40. Boutcher SH. High-intensity intermittent exercise and fat
loss. Journal of obesity. 2011;2011. [PMID: 21113312 ] [PMCID:
PMC2991639] [DOI]
41. Powers SK, Jackson MJ. Exercise-induced oxidative
stress: cellular mechanisms and impact on muscle force production.
Physiological reviews. 2008;88(4):1243-76. [PMID: 18923182]
[PMCID: PMC2909187] [DOI]
42. Margaritis I, Rousseau A-S. Does physical exercise
modify antioxidant requirements? Nutrition research reviews.
2008;21(1):3-12. [PMID: 19079851] [DOI]
43. Michailidis Y, Jamurtas AZ, Nikolaidis MG, Fatouros
IG, Koutedakis Y, Papassotiriou I, et al. Sampling time is crucial
for measurement of aerobic exercise-induced oxidative stress.
Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise. 2007;39(7):1107-13.
[PMID: 17596778] [DOI]
44. Pedersen BK, Febbraio MA. Muscle as an endocrine
organ: focus on muscle-derived interleukin-6. Physiological
reviews. 2008;88(4):1379-406. [PMID: 18923185] [DOI]
45. Ropelle ER, Flores MB, Cintra DE, Rocha GZ, Pauli JR,
Morari J, et al. IL-6 and IL-10 anti-inflammatory activity links
exercise to hypothalamic insulin and leptin sensitivity through
IKKβ and ER stress inhibition. PLoS biology. 2010;8(8):e1000465.
[PMID: 20808781] [PMCID: PMC2927536] [DOI]
46. Issurin VB. Benefits and limitations of block periodized
training approaches to athletes’ preparation: a review. Sports
medicine. 2016;46:329-38. [PMID: 26573916] [DOI]
47. Moore DR, Burgomaster KA, Schofield LM, Gibala MJ,
Sale DG, Phillips SM. Neuromuscular adaptations in human
muscle following low intensity resistance training with vascular
occlusion. European journal of applied physiology. 2004;92:399-
406. [PMID: 15205956] [DOI]
48. Mastaloudis A, Leonard SW, Traber MG. Oxidative
stress in athletes during extreme endurance exercise. Free radical
biology and medicine. 2001;31(7):911-22. [PMID: 11585710]
[DOI]
49. Watson T. Antioxidant restriction and oxidative stress in
sh. 2005
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Reza Kheirandish, Ahmad Rahmani, Ali Gorzi, Ebrahim Shaabani Ezdini, Atefeh Sadeghi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







