The Effect of Continuous Aerobic and High-Intensity Interval Training on Some Physical Fitness Factors in Young Football Players
Keywords:
Speed, agility, power, long jump, shuttle run, footballAbstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of continuous aerobic and high-intensity interval training on some physical fitness factors in young football players.
Methods and Materials: For this purpose, 45 young football players from Hamadan were randomly selected and divided into three groups of 15: the continuous high-intensity aerobic training group (three sessions per week, at 90-95% of maximum heart rate), the high-intensity interval training group (three days per week, 30 minutes of high-intensity training, 30 minutes of rest), and the control group. At the beginning and after the completion of the 6-week training protocol, factors such as sprint speed test, 4x9 shuttle run agility test, and explosive leg power test were measured. The collected data were then analyzed using covariance analysis (ANCOVA) with pre-test values as the covariate and pairwise comparisons using Bonferroni post hoc test in SPSS version 26, with a significance level of less than 0.05.
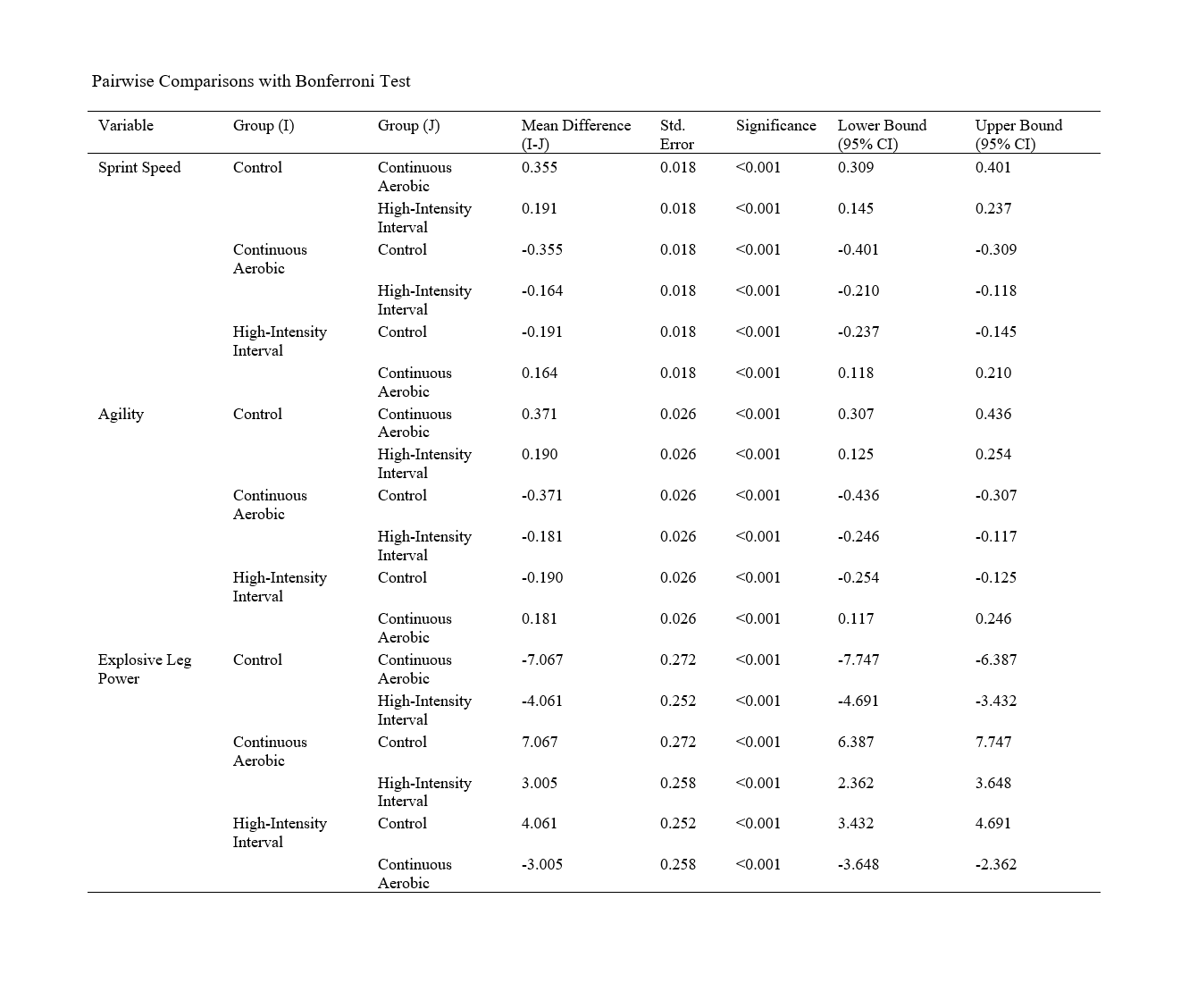
Findings: The results showed significant differences in all physical fitness factors among all groups compared to the control group and among the groups themselves.
Conclusion: The results of this study suggest that both continuous high-intensity aerobic training and high-intensity interval training likely lead to significant improvements in physical fitness factors, with continuous aerobic training potentially resulting in greater improvements. However, further research is needed for more precise examination.
Downloads
References
1. Cabrera Hernández MA, Tafur Tascón LJ, Cohen DD,
García-Corzo SA, Quiñonez Sánchez A, Povea Combariza C, et al.
Concordance between the indirect VO2max value estimated through
the distance in Yo-Yo intermittent recovery test level 1 and the direct
measurement during a treadmill protocol test in elite youth soccer
players. 2018. [DOI]
2. Parveen N, Shahid RA, Riaz L, Shaikh AS. Comparison of
Mean VO 2 max in normal Weight, Overweight and Obese Students of
a Local Medical College Using Analysis of Variance. Pakistan Journal
of Medical Research. 2019;58(1).
3. Jemni M, Prince MS, Baker JS. Assessing Cardiorespiratory
Fitness of Soccer Players: Is Test Specificity the Issue?–A Review.
Sports Medicine - Open. 2018;4(1):28. [PMID: 29923108] [PMCID:
PMC6008274] [DOI]
4. Eskandarnejhad M, Vakili J, Alezadeh R. Predicting social
anxiety and mental fitness of skilled badminton players by physical
fitness. Sociology and lifestyle management. 2021;6(16):114-30.
5. Lira FS, Dos Santos T, Caldeira RS, Inoue DS, Panissa VL,
Cabral-Santos C, et al. Short-term high-and moderate-intensity training
modifies inflammatory and metabolic factors in response to acute
exercise. Frontiers in physiology. 2017;8:290343. [PMID: 29163201]
[PMCID: PMC5671556] [DOI]
6. Eveland-Sayers BM, Farley RS, Fuller DK, Morgan DW,
Caputo JL. Physical Fitness and Academic Achievement in Elementary
School Children. Journal of Physical Activity and Health.
2009;6(1):99-104. [PMID: 19211963] [DOI]
7. Nagahvi M, Keyvan M, Ehsan A. The effects of intense
exercise alternating with ginseng on some factor supplementation on
athletic fitness. npwjm. 2017;4(13):205-12.
8. Amin Ahmadi R, Haghighi AH, Hamedinia MR. Effect of
plyometric and sprint interval training programs on performance and
some factors of physical fitness of teenager soccer players. Journal of
Applied Exercise Physiology. 2017;13(25):197-210. [DOI]
9. Bakinde ST. Educating aerobic exercise and skill-related
fitness of athletes in University of Ilorin. Indonesian Journal of
Multidiciplinary Research. 2019;2(1):195-202. [DOI]
10. Brown LE, Ferrigno, Santana. Drills for Speed, Agility and
Quickness: Human Kinetics; 2000.
11. Arslan E, Orer G, Clemente F. Running-based high-intensity
interval training vs. small-sided game training programs: effects on the
physical performance, psychophysiological responses and technical
skills in young soccer players. Biology of Sport. 2020;37(2):165-73.
[PMID: 32508384] [PMCID: PMC7249797] [DOI]
12. Chamari K, Hachana Y, Kaouech F, Jeddi R, MoussaChamari I, Wisløff U. Endurance training and testing with the ball in
young elite soccer players. British journal of sports medicine.
2005;39(1):24-8. [PMID: 15618335] [PMCID: PMC1725014] [DOI]
13. Aschendorf PF, Zinner C, Delextrat A, Engelmeyer E,
Mester J. Effects of basketball-specific high-intensity interval training
on aerobic performance and physical capacities in youth female
basketball players. The Physician and Sportsmedicine. 2019;47(1):65-
70. [DOI] [DOI]
14. Charee J, Yupaporn K, Khaothin T, Kusump S, Ashira H.
The effects of step aerobic training on muscle power and agility in
female badminton players. International Journal of Exercise Science.
2022;15(6):1317.
15. Moghadam Naghavi A, Moradian K, Amiri E. The effects of
intense exercise alternating with ginseng on some factor
supplementation on athletic fitness. NPWJM. 2017;4(13):205-12.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







