Mediating Role of Enjoyment in the Associations between Social Support and Participation in Physical Activity among Female Adolescents
Keywords:
Adolescent, Girl, Exercise, Social Support, EnjoymentAbstract
Objective: This study focused on examining the connections between social support and physical activity participation, with enjoyment identified as a mediating variable.
Methods and Materials: This research employed a descriptive-correlational approach utilizing structural equation modeling. A sample of 384 adolescent girls was selected through convenience sampling. Standardized assessment tools were used to measure the research variables, and the data analysis was performed using Smart PLS statistical software version 4, with a significance threshold set at 0.05.
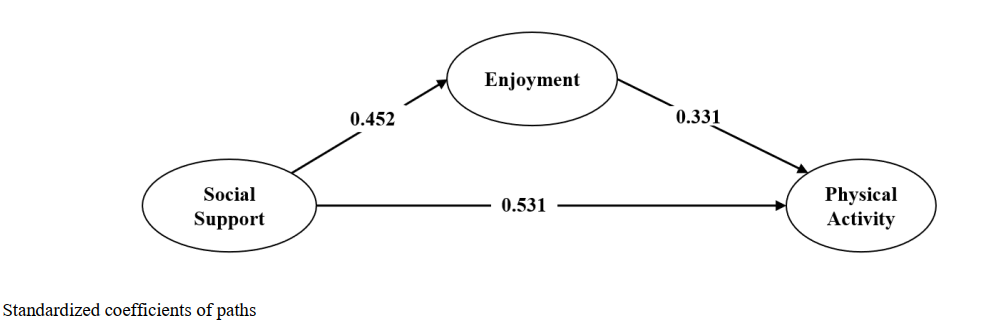
Findings: The path analysis results indicate a significant positive structural relationship between physical activity (P=0.000, T=8.54, b=0.53) and enjoyment (P=0.000, T=10.23, b=0.45) in relation to social support. Additionally, a significant positive structural relationship exists between the enjoyment and physical activity (P=0.000, T=6.84, b=0.33). In addition, enjoyment serves as a significant mediating factor in the relationship between the social support and physical activity, with a p-value of 0.000, a t-value of 4.58, and a b coefficient of 0.16.
Conclusion: The findings of this study highlight the profound influence of the home and family environment on the physical activity trajectories of children and adolescents, emphasizing that parental support plays a vital role in establishing an active lifestyle that can predict future levels of physical activity.
Downloads
References
1. Alotaibi T, Almuhanna R, Alhassan J, Alqadhib E, Mortada E, Alwhaibi R. The Relationship between Technology Use and Physical Activity among Typically-Developing Children. Healthcare (Basel). 2020;8(4):488. [DOI]
2. Woessner MN, Tacey A, Levinger-Limor A, Parker AG, Levinger P, Levinger I. The Evolution of Technology and Physical Inactivity: The Good, the Bad, and the Way Forward. Front Public Health. 2021;9:655491. [DOI]
3. Marquez DX, Aguiñaga S, Vásquez PM, Conroy DE, Erickson KI, Hillman C, et al. A systematic review of physical activity and quality of life and well-being. Transl Behav Med. 2020;10(5):1098-109. [DOI]
4. Roychowdhury D. Using Physical Activity to Enhance Health Outcomes Across the Life Span. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2020;5(1):2. [DOI]
5. Goyal J, Rakhra G. Sedentarism and Chronic Health Problems. Korean J Fam Med. 2024;45(5):239-57. [DOI]
6. Lee IM, Shiroma EJ, Lobelo F, Puska P, Blair SN, Katzmarzyk PT, et al. Effect of physical inactivity on major non-communicable diseases worldwide: an analysis of burden of disease and life expectancy. Lancet. 2012;380(9838):219-29. [DOI]
7. Bull FC, Al-Ansari SS, Biddle S, Borodulin K, Buman MP, Cardon G, et al. World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Br J Sports Med. 2020;54(24):1451-62. [DOI]
8. Esteban-Cornejo I, Hallal PC, Mielke GI, Menezes AM, Gonçalves H, Wehrmeister F, et al. Physical Activity throughout Adolescence and Cognitive Performance at 18 Years of Age. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015;47(12):2552-7. [DOI]
9. Patrick H, Williams GC. Self-determination theory: its application to health behavior and complementarity with motivational interviewing. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2012;9:18. [DOI]
10. Ryan RM, Deci EL. Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. Am Psychol. 2000;55(1):68-78. [DOI]
11. Feeney BC, Collins NL. A new look at social support: a theoretical perspective on thriving through relationships. Pers Soc Psychol Rev. 2015;19(2):113-47. [DOI]
12. Umberson D, Montez JK. Social relationships and health: a flashpoint for health policy. J Health Soc Behav. 2010;51(Suppl):S54-66. [DOI]
13. Hallal PC, Dumith SC, Reichert FF, Menezes AM, Araújo CL, Wells JC, et al. Cross-sectional and longitudinal associations between physical activity and blood pressure in adolescence: birth cohort study. J Phys Act Health. 2011;8(4):468-74. [DOI]
14. Mendonça G, Cheng LA, Mélo EN, de Farias Júnior JC. Physical activity and social support in adolescents: a systematic review. Health Educ Res. 2014;29(5):822-39. [DOI]
15. Zhang M, Jiang J, Peng W, Yang R, Liu Q, Li S, et al. A cross-sectional study of the association between physical activity and depressive symptoms among adolescents in southwest China stratified by parental absence: the mediating role of insomnia and the moderating role of resilience. BMJ Open. 2024;14(9):e079531. [DOI]
16. Lian Y, Peijie C, Kun W, Tingran Z, Hengxu L, Jinxin Y, et al. The Influence of Family Sports Attitude on Children's Sports Participation, Screen Time, and Body Mass Index. Front Psychol. 2021;12:697358. [DOI]
17. Rhodes RE, Guerrero MD, Vanderloo LM, Barbeau K, Birken CS, Chaput JP, et al. Development of a consensus statement on the role of the family in the physical activity, sedentary, and sleep behaviours of children and youth. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2020;17(1):74. [DOI]
18. Su DLY, Tang TCW, Chung JSK, Lee ASY, Capio CM, Chan DKC. Parental Influence on Child and Adolescent Physical Activity Level: A Meta-Analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(24):16861. [DOI]
19. Tong P, An IS. Review of studies applying Bronfenbrenner's bioecological theory in international and intercultural education research. Front Psychol. 2024;14:1233925. [DOI]
20. Lee Y, Park S. Understanding of Physical Activity in Social Ecological Perspective: Application of Multilevel Model. Front Psychol. 2021;12:622929. [DOI]
21. Liao Y, Cheng X, Li Z, Li Y. The mediating role of physical activity and health status between a health-supportive environment and well-being: a cross-sectional study. Front Public Health. 2023;11:1233970. [DOI]
22. Roh SY, Chang IY. The ecological system's influence on physical activities of older adults: comparison between older men and women. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024;37(1):16. [DOI]
23. Cozett C, Roman NV. Recommendations to Enhance Parental Involvement and Adolescent Participation in Physical Activity. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(3):1333. [DOI]
24. Lippold MA, Glatz T, Fosco GM, Feinberg ME. Parental Perceived Control and Social Support: Linkages to Change in Parenting Behaviors During Early Adolescence. Fam Process. 2018;57(2):432-47. [DOI]
25. Zecevic CA, Tremblay L, Lovsin T, Michel L. Parental Influence on Young Children's Physical Activity. Int J Pediatr. 2010;2010:468526. [DOI]
26. Anderson CB, Hughes SO, Fuemmeler BF. Parent-child attitude congruence on type and intensity of physical activity: testing multiple mediators of sedentary behavior in older children. Health Psychol. 2009;28(4):428-38. [DOI]
27. Kamionka A, Lipowska M, Lizińczyk S, Lipowski M. The impact of parents' physical activity goals and parental attitudes on physical activity during leisure time among children in middle childhood. Front Public Health. 2023;11:1170413. [DOI]
28. Gao Z, Chee CS, Norjali Wazir MRW, Wang J, Zheng X, Wang T. The role of parents in the motivation of young athletes: a systematic review. Front Psychol. 2024;14:1291711. [DOI]
29. Sánchez-Miguel PA, Leo FM, Sánchez-Oliva D, Amado D, García-Calvo T. The Importance of Parents' Behavior in their Children's Enjoyment and Amotivation in Sports. J Hum Kinet. 2013;36:169-77. [DOI]
30. Danioni F, Barni D. Parents' Sport Socialization Values, Perceived Motivational Climate and Adolescents' Antisocial Behaviors. Eur J Psychol. 2019;15(4):754-72. [DOI]
31. Visek AJ, Achrati SM, Mannix H, McDonnell K, Harris BS, DiPietro L. The fun integration theory: toward sustaining children and adolescents sport participation. J Phys Act Health. 2015;12(3):424-33. [DOI]
32. Golaszewski NM, Bartholomew JB. The Development of the Physical Activity and Social Support Scale. J Sport Exerc Psychol. 2019;41(4):215-29. [DOI]
33. Andarge E, Trevethan R, Fikadu T. Assessing the Physical Activity Questionnaire for Adolescents (PAQ-A): Specific and General Insights from an Ethiopian Context. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:5511728. [DOI]
34. Chen C, Weyland S, Fritsch J, Woll A, Niessner C, Burchartz A, et al. A Short Version of the Physical Activity Enjoyment Scale: Development and Psychometric Properties. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(21):11035. [DOI]
35. Dubow EF, Huesmann LR, Boxer P. A social-cognitive-ecological framework for understanding the impact of exposure to persistent ethnic-political violence on children's psychosocial adjustment. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev. 2009;12(2):113-26. [DOI]
36. Xu Z, Xu J, Liu T, Gu Z, Hu D. The pathway of social support in enhancing adolescents' physical fitness: The mediating roles of physical activity and self-efficacy. PLoS One. 2024;19(9):e0308864. [DOI]
37. Laird Y, Fawkner S, Niven A. A grounded theory of how social support influences physical activity in adolescent girls. Int J Qual Stud Health Well-being. 2018;13(1):1435099. [DOI]
38. Qi Y, Yin Y, Wang X, Zou Y, Liu B. Autonomous motivation, social support, and physical activity in school children: moderating effects of school-based rope skipping sports participation. Front Public Health. 2024;12:1295924. [DOI]
39. Zhang Y, Hasibagen, Zhang C. The influence of social support on the physical exercise behavior of college students: The mediating role of self-efficacy. Front Psychol. 2022;13:1037518. [DOI]
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Niki Sadeghi Pour (Author); Tayebeh Baniasadi (Corresponding Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







