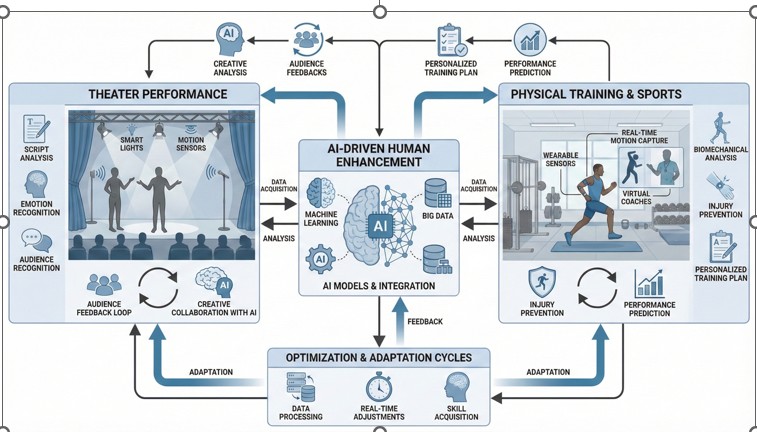
Artificial Intelligence in Theater Performance and Physical Training: A Review of Technologies Optimizing Performer Development and Artistic Execution
Keywords:
artificial intelligence, choreography, computer vision, machine learning, movement analysis, performing arts, physical training, pose estimation , technology, theaterAbstract
Objective: Theater performance demands substantial physical capabilities requiring systematic training comparable to athletic preparation. Professional performers engage in cardiovascular conditioning, strength development, and movement technique refinement to meet performance demands. Artificial intelligence technologies, including computer vision, machine learning, and generative modeling, have enabled practical applications in movement analysis, personalized training design, and performance feedback delivery. These advances address accessibility barriers, objective assessment challenges, and individualized program adaptation needs characteristic of theatrical training contexts. This review aimed to (i) examine AI technologies applied in theater performance and physical training contexts, (ii) analyze implementation challenges and limitations across applications, and (iii) identify critical research priorities requiring empirical investigation.
Methods: We searched PubMed, IEEE Xplore, ACM Digital Library, Web of Science, and Google Scholar for studies published 2014-2025. Inclusion criteria required empirical AI applications in theater performance, performing arts training, or physical conditioning relevant to theatrical demands. We extracted data on technologies employed, application contexts, reported outcomes, and identified limitations. Quality assessment examined validation methodology, sample characteristics, and outcome measurement approaches.
Results: Computer vision systems demonstrated validation accuracies with mean errors of 20-30mm in controlled laboratory environments and 50-80 mm in theatrical settings with challenging lighting and costume conditions. Generative choreography systems produced technically coherent movement sequences, receiving mixed artistic evaluations from expert practitioners. Natural language processing achieved 85-92% accuracy for surface-level script sentiment analysis while demonstrating poor performance on dramatic subtext interpretation tasks. AI fitness applications reported initial user engagement improvements, though sustained adherence declined substantially beyond six months across multiple studies. Theater practitioners demonstrated high acceptance (85%) for technical production support applications while expressing concerns (62%) regarding creative process involvement. Research examining long-term effectiveness beyond six months remained critically scarce across all application domains examined.
Conclusion: AI technologies demonstrate potential for technical support and objective assessment in theater and physical training contexts. Successful implementation requires domain-specific design approaches, preservation of human creative agency, and realistic technological capability assessment. Critical research priorities include longitudinal effectiveness validation, diverse population testing, cultural inclusivity in training datasets, and ethical framework development for responsible AI deployment in creative domains.
Downloads
References
1. Koutedakis Y JA. The dancer as a performing athlete: physiological considerations. Sports Med. 2004;34(10):651-61. [PMID: 15335242] [DOI]
2. M. W. Preparing to perform: periodization and dance. . J Dance Med Sci. 2010;14(2):67-72. [PMID: 23759480] [DOI]
3. Cohen JL SK, Witriol I, McArdle WD. . Cardiorespiratory responses to ballet exercise and the VO2max of elite ballet dancers. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1982;14(3):212-7. [DOI]
4. S. R. Considerations for integrating fitness into dance training. J Dance Med Sci. 2010;14(2):45-9. [DOI]
5. Koutedakis Y ML, Soulas D, Papapostolou V, Sullivan I, Sharp NC. . The effects of rest and subsequent training on selected physiological parameters in professional female classical dancers. Int J Sports Med. 1999;20(3):379-83. [PMID: 10496117] [DOI]
6. Liederbach M CJ. Psychological aspects of fatigue-related injuries in dancers. . J Dance Med Sci 2001;5(4):116-20. [DOI]
7. Dergaa I SH, Glenn JM, El Omri A, Washif J, Guelmami N, et al. . Using artificial intelligence for exercise prescription in personalised health promotion: a critical evaluation of OpenAI's GPT-4 model. . Biol Sport. 2024;41(2):221-41. [PMID: 38524814] [PMCID: PMC10955739] [DOI]
8. Angioi M MG, Twitchett E, Koutedakis Y, Wyon M. . Effects of supplemental training on fitness and aesthetic competence parameters in contemporary dance: a randomised controlled trial. Medical Problems of Performing Artists. 2012;27(1):3-8. [PMCID: 22543316] [DOI]
9. Cao Z HG, Simon T, Wei SE, Sheikh Y. . OpenPose: realtime multi-person 2D pose estimation using part affinity fields. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2021;46(1):172-86. [PMID: 31331883] [DOI]
10. Sutton RS BA. Reinforcement learning: an introduction. : MIT Press; 2018.
11. Goodfellow I P-AJ, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, et al. . Generative adversarial nets. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 2014;27. [DOI]
12. Devlin J CM, Lee K, Toutanova K. BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. NAACL-HLT. 2019;1:4171-86. [DOI]
13. Vaswani A SN, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez AN, et al. Attention is all you need. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst. 2017;30.
14. Bazarevsky V GI, Raveendran K, Zhu T, Zhang F, Grundmann M. . BlazePose: On-device Real-time Body Pose tracking. ArXiv. 2020;abs/2006.10204.
15. Lugaresi C TJ, Nash H, McClanahan C, Uboweja E, Hays M, et al. . MediaPipe: a framework for building perception pipelines. ArXiv. 2019;abs/1906.08172.
16. S. P. AI, AR, and VR in theatre and performance: technology in the present and future of live creative arts: Routledge; 2024.
17. Wyon MA KY. Muscular fatigue: considerations for dance. J Dance Med Sci 2013;17(2):63-9. [PMID: 23759480] [DOI]
18. WR. T. Worldwide survey of fitness trends for 2020. ACSM'S Health & Fitness Journal. 2019;23(6):10-8. [DOI]
19. Allen N WM. Dance medicine: artist or athlete? SportEX Med. 2008;35:6-9.
20. Dergaa I CK, Zmijewski P, Saad HB. . From human writing to artificial intelligence generated text: examining the prospects and potential threats of ChatGPT in academic writing. Biol Sport. 2023;40(2):615-22. [PMID: 37077800] [PMCID: PMC10108763] [DOI]
21. Washif J PJ, James C, Dergaa I, Beaven C. Artificial intelligence in sport: exploring the potential of using ChatGPT in resistance training prescription. Biol Sport. 2024;41(2):209-20. [PMID: 38524820] [PMCID: PMC10955742] [DOI]
22. Colyer SL EM, Cosker DP, Salo AIT. A review of the evolution of vision-based motion analysis and the integration of advanced computer vision methods. Sports Med Open. 2018;4(1:24). [PMID: 29869300 ] [PMCID: PMC5986692] [DOI]
23. Nogueira MR, Menezes, P., & Maçãs de Carvalho, J. Exploring the impact of machine learning on dance performance: a systematic review. . International Journal of Performance Arts and Digital Media. 2024;20(1):60–109 [DOI]
24. Nadia A. Visual Discourse and Theatrical and Cinematic Scenography
International Journal of Early Childhood Special Education (INT-JECSE). 2025;17(01). [DOI]
25. Abello J, Broadwell, P., & Tangherlini, T. R. Computational folkloristics Communications of the ACM. 2012;55(7):60-70. [DOI]
26. Yimeng Liu MS. DanceGen: Supporting Choreography Ideation and Prototyping with Generative AI. Proceedings of the 2024 ACM Designing Interactive Systems Conference; Copenhagen, Denmark: Association for Computing Machinery; 2024. p. 920–38. [DOI]
27. Alaoui SF CB, Serrano M, Bevilacqua F. , editor Movement qualities as interaction modality. Proc Conf Designing Interact Syst; 2012. [DOI]
28. Średniawa M. AI in theater. Witkacy case study. Preprints of Communication Papers of the 20th Conference on Computer Science and Intelligence Systems (FedCSIS) 2025. p. 167–74. [DOI]
29. Yuhui T, Md Dawam, Z. A., & Zainal, S. . Immersive Theatre: A Comprehensive Review and Future Direction. Pakistan Journal of Life & Social Sciences. 2024;22(2):3767-75 [DOI]
30. Guthold R SG, Riley LM, Bull FC. . Worldwide trends in insufficient physical activity from 2001 to 2016: a pooled analysis of 358 population-based surveys. Lancet Glob Health. 2018;6(10):e1077-e86. [PMID: 30193830] [DOI]
31. Teixeira PJ CE, Markland D, Silva MN, Ryan RM. Exercise, physical activity, and self-determination theory: a systematic review. . Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2012;9(78). [PMID: 22726453] [PMCID: PMC3441783] [DOI]
32. Jobin A IM, Vayena E. . The global landscape of AI ethics guidelines. . Nature Machine Intelligence. 2019;1(9):389-99. [DOI]
33. Mittelstadt BD FL. The ethics of big data: current and foreseeable issues in biomedical contexts. Sci Eng Ethics. 2016;22(2):303-41. [PMID: 26002496] [DOI]
34. Simon T JH, Matthews I, Sheikh Y. , editor Hand keypoint detection in single images using multiview bootstrapping. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR); 2017. [DOI]
35. Grishchenko I AA, Kartynnik Y, Raveendran K, Grundmann M. . Attention mesh: high-fidelity face mesh prediction in real-time. arXiv. 2020;2006.10962 [DOI]
36. Zhang F BV, Vakunov A, Tkachenka A, Sung G, Chang CL, et al. MediaPipe hands: on-device real-time hand tracking. arXiv. 2020;2006.10214. [DOI]
37. Stenum J, Rossi C, Roemmich RT. Two-dimensional video-based analysis of human gait using pose estimation. PLoS computational biology. 2021;17(4):e1008935. [PMID: 33891585] [PMCID: PMC8099131] [DOI]
38. Nakano N ST, Ueda K, Omura L, Kimura A, Iino Y, Fukashiro S, Yoshioka S. Evaluation of 3D markerless motion capture accuracy using OpenPose with multiple video cameras. Front Sports Act Living. 2020;2(50). [PMID: 33345042] [PMCID: PMC7739760] [DOI]
39. Dergaa I, Fekih-Romdhane F, Hallit S, Loch AA, Glenn JM, Fessi MS, et al. ChatGPT is not ready yet for use in providing mental health assessment and interventions. Frontiers in Psychiatry. 2024;14:1277756. [PMID: 38239905] [PMCID: PMC10794665] [DOI]
40. Mimno D, Broadwell PM, Tangherlini TR, editors. The Telltale Hat: LDA and Classification Problems in a Large Folklore Corpus. DH; 2014.
41. Dergaa I, Zakhama L, Dziri C, Ben Saad H. Enhancing scholarly discourse in the age of artificial intelligence: A guided approach to effective peer review process. La Tunisie Medicale. 2023;101(10):721-6.
42. Bench H. Dancing in digital archives: circulation, pedagogy, performance. Transmission in Motion: Routledge; 2016. p. 179-91. [DOI]
43. Velloso E, Bulling A, Gellersen H, Ugulino W, Fuks H, editors. Qualitative activity recognition of weight lifting exercises. Proceedings of the 4th Augmented Human International Conference; 2013. [DOI]
44. O’Reilly M, Caulfield B, Ward T, Johnston W, Doherty C. Wearable inertial sensor systems for lower limb exercise detection and evaluation: a systematic review. Sports Medicine. 2018;48(5):1221-46. [PMID: 29476427]
45. Beber R. Effects of Ankle Bracing on Knee Biomechanics During a Cut Maneuver: California State University, Fullerton; 2020.
46. Kainz H, Graham D, Edwards J, Walsh HP, Maine S, Boyd RN, et al. Reliability of four models for clinical gait analysis. Gait & posture. 2017;54:325-31. [PMID: 28411552] [DOI]
47. Mündermann L, Corazza S, Andriacchi TP. The evolution of methods for the capture of human movement leading to markerless motion capture for biomechanical applications. Journal of neuroengineering and rehabilitation. 2006;3(1):6. [PMID: 16539701] [PMCID: PMC1513229] [DOI]
48. Koutedakis Y, Sharp NC. Thigh-muscles strength training, dance exercise, dynamometry, and anthropometry in professional ballerinas. The Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research. 2004;18(4):714-8. [PMID: 15574072] [DOI]
49. Li W, Chen X, Li P, Sorkine-Hornung O, Chen B. Example-based motion synthesis via generative motion matching. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG). 2023;42(4):1-12. [DOI]
50. Crnkovic-Friis L, Crnkovic-Friis L. Generative choreography using deep learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:160506921. 2016.
51. Tang T, Jia J, Mao H, editors. Dance with melody: An lstm-autoencoder approach to music-oriented dance synthesis. Proceedings of the 26th ACM international conference on Multimedia; 2018. [DOI]
52. Lee H-Y, Yang X, Liu M-Y, Wang T-C, Lu Y-D, Yang M-H, et al. Dancing to music. Advances in neural information processing systems. 2019;32.
53. Dorsen A. The Dangers of AI Intoxication. American Theatre. 2023;30.
54. Maiti A. From Strings to Sensors: Movement Representation in AI Theatre. Moveable Type. 2024;15(1). [DOI]
55. Horváth D. Curtain call for AI: Transforming theatre through technology. Sustainable Futures. 2025:100747. [DOI]
56. Brown T, Mann B, Ryder N, Subbiah M, Kaplan JD, Dhariwal P, et al. Language models are few-shot learners. Advances in neural information processing systems. 2020;33:1877-901.
57. Ouyang L, Wu J, Jiang X, Almeida D, Wainwright C, Mishkin P, et al. Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. Advances in neural information processing systems. 2022;35:27730-44.
58. Rosa R, Dušek O, Kocmi T, Mareček D, Musil T, Schmidtová P, et al. THEaiTRE: Artificial intelligence to write a theatre play. arXiv preprint arXiv:200614668. 2020.
59. Mirowski P, Mathewson KW, Pittman J, Evans R, editors. Co-writing screenplays and theatre scripts with language models: Evaluation by industry professionals. Proceedings of the 2023 CHI conference on human factors in computing systems; 2023. [DOI]
60. Dergaa I. Artificial intelligence and promoting open access in academic publishing. La Tunisie medicale. 2023;101(6):533-6.
61. Martin JH, Jurafsky D. Speech and language processing: An introduction to natural language processing, computational linguistics, and speech recognition: Pearson/Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River; 2009.
62. Christopher DM, Prabhakar R, Hinrich S. Introduction to information retrieval. Cambridge University Press; 2008.
63. Silver D, Huang A, Maddison CJ, Guez A, Sifre L, Van Den Driessche G, et al. Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search. nature. 2016;529(7587):484-9. [PMID: 26819042] [DOI]
64. Schoeppe S, Alley S, Van Lippevelde W, Bray NA, Williams SL, Duncan MJ, et al. Efficacy of interventions that use apps to improve diet, physical activity and sedentary behaviour: a systematic review. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity. 2016;13(1):127. [PMID: 27927218] [PMCID: PMC5142356] [DOI]
65. Romeo A, Edney S, Plotnikoff R, Curtis R, Ryan J, Sanders I, et al. Can smartphone apps increase physical activity? Systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of medical Internet research. 2019;21(3):e12053. [PMID: 30888321] [PMCID: PMC6444212] [DOI]
66. Twitchett E, Angioi M, Koutedakis Y, Wyon M. Video analysis of classical ballet performance. Journal of Dance Medicine & Science. 2009;13(4):124-8. [DOI]
67. Zhang Z, Song Y, Qi H, editors. Age progression/regression by conditional adversarial autoencoder. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2017. [DOI]
68. Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, et al. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014.
69. Garner SB. Watching Movement: Phenomenology, cognition, performance: Routledge; 2018. 203-15 p. [PMID: 30044493] [DOI]
70. Mathis A, Mamidanna P, Cury KM, Abe T, Murthy VN, Mathis MW, et al. DeepLabCut: markerless pose estimation of user-defined body parts with deep learning. Nature neuroscience. 2018;21(9):1281-9. [PMID: 30127430] [DOI]
71. Chen Y, Tian Y, He M. Monocular human pose estimation: A survey of deep learning-based methods. Computer vision and image understanding. 2020;192:102897. [DOI]
72. Fukushima T BP, Russomanno TG, Lames M. . The potential of human pose estimation for motion capture in sports: a validation study. Sports Engineering 2024;27(19). [DOI]
73. Song J, & Ding, L. Reconstructing dance movements using a mathematical model based on optimized nature-inspired machine learning. Artificial Intelligence Review. 2025;58(5):147. [DOI]
74. Aristidou A, Stavrakis, E., Papaefthimiou, M., Papagiannakis, G., & Chrysanthou, Y. . Style-based motion analysis for dance composition. The visual computer. 2018;34(12):1725-37. [DOI]
75. Le N, Pham, T., Do, T., Tjiputra, E., Tran, Q. D., & Nguyen, A., editor Music-driven group choreography. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2023. [DOI]
76. Aristidou A, Charalambous, P., & Chrysanthou, Y. Emotion analysis and classification: understanding the performers' emotions using the LMA entities. Computer Graphics Forum. 2015;34(6):262-76. [DOI]
77. Alemi O, Françoise, J., & Pasquier, P. . GrooveNet: Real-time music-driven dance movement generation using artificial neural networks. networks. 2017;8(17):26.
78. Cini K, & Abela, J. Forecasting film audience ratings: A natural language processing approach to script and production data. Entertainment Computing. 2025;55:101043. [DOI]
79. Mohammad SM, & Turney, P. D. Crowdsourcing a word–emotion association lexicon. Computational intelligence. 2013;29(3):436-65. [DOI]
80. Ferguson T, Olds, T., Curtis, R., Blake, H., Crozier, A. J., Dankiw, K., ... & Maher, C. Effectiveness of wearable activity trackers to increase physical activity and improve health: a systematic review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. The Lancet Digital Health. 2022;4(8):e615-e26. [PMID: 35868813] [DOI]
81. Eysenbach G. The law of attrition. . Journal of medical Internet research. 2005;7(1):e11. [PMID: 15829473] [PMCID: PMC1550631] [DOI]
82. Lister C, West, J. H., Cannon, B., Sax, T., & Brodegard, D. . Just a fad? Gamification in health and fitness apps. JMIR serious games. 2014;2(2):e3413. [PMID: 25654660] [PMCID: PMC4307823] [DOI]
83. Thompson WR. Worldwide survey of fitness trends for 2022. ACSM'S Health & Fitness Journal. 2022;26(11):11-20. [DOI]
84. Bort-Roig J, Gilson, N. D., Puig-Ribera, A., Contreras, R. S., & Trost, S. G. . Measuring and influencing physical activity with smartphone technology: a systematic review. Sports medicine. 2014;44(5):671-86. [PMID: 24497157] [DOI]
85. Direito A, Carraça, E., Rawstorn, J., Whittaker, R., & Maddison, R. . mHealth technologies to influence physical activity and sedentary behaviors: behavior change techniques, systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Annals of behavioral medicine. 2017;51(2): 226-39. [PMID: 27757789] [DOI]
86. Müller AM, Maher, C. A., Vandelanotte, C., Hingle, M., Middelweerd, A., Lopez, M. L., ... & Wark, P. A. Physical activity, sedentary behavior, and diet-related eHealth and mHealth research: bibliometric analysis. . Journal of medical Internet research. 2018;20(4):e8954. [DOI]
87. Wyon M, Allen, N., Angioi, M., Nevill, A., & Twitchett, E. . Anthropometric factors affecting vertical jump height in ballet dancers. Journal of dance medicine & Science. 2006;10(3-4):106-10. [DOI]
88. Klimova LP, Marina Actual trends of architectural forms and graphics in the costume design context. E3S Web of Conferences. 2020. [DOI]
89. Chen D. Basic characteristics and body aesthetics analysis of modern dance. Frontiers in Art Research. 2024;6(4):47-50. [DOI]
90. Gebru T, Morgenstern, J., Vecchione, B., Vaughan, J. W., Wallach, H., Iii, H. D., & Crawford, K. Datasheets for datasets. Communications of the ACM. 2021;64(12):86-92. [DOI]
91. El Raheb K, Papapetrou, N., Katifori, V., & Ioannidis, Y., editor Balonse: Ballet ontology for annotating and searching video performances. Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Movement and Computing 2016. [DOI]
92. Xie K, Wang, T., Iqbal, U., Guo, Y., Fidler, S., & Shkurti, F., editor Physics-based human motion estimation and synthesis from videos. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision; 2021. [DOI]
93. Fernandes A. The Replacement of What? Artificial Intelligence, Creativity and (More-than-) Humanness. Journal of Creative Communications. 2025;20(1):11-22. [DOI]
94. Yang Q, Steinfeld, A., Rosé, C., & Zimmerman, J. , editor Re-examining whether, why, and how human-AI interaction is uniquely difficult to design. Proceedings of the 2020 chi conference on human factors in computing systems 2020. [DOI]
95. B. S. Human-centered artificial intelligence: reliable, safe and trustworthy. . Int J Hum Comput Interact. 2020;36(6):495-504. [DOI]
96. Brickwood KJ WG, O'Brien J, Williams AD. Consumer-based wearable activity trackers increase physical activity participation: systematic review and meta-analysis. . JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019;7(4):e11819. [PMID: 30977740] [PMCID: PMC6484266] [DOI]
97. Kosma M, Erickson, N., & Gremillion, A. The embodied nature of physical theater: artistic expression, emotions, interactions. Research in Dance Education. 2024:1-26. [DOI]
98. Koutedakis Y, Khaloula, M., Pacy, P. J., Murphy, M., & Dunbar, G. M. J. . Thigh peak torques and lower-body injuries in dancers. Journal of Dance Medicine & Science. 1997;1(1):12-5. [DOI]
99. Li B. The Return of Spiritual Body: a Study of the Practice and Theory of the Actor’s Body in Training and Performance: University of East Anglia; 2025.
100. Cohen G. Missing, Biased, and Unrepresentative: The Quantitative Analysis of Multisource Biographical Data. Historical Methods. A Journal of Quantitative and Interdisciplinary History. 2002;35(4):166-76. [DOI]
101. Niewiadomski R, Mancini, M., Piana, S., Alborno, P., Volpe, G., & Camurri, A., editor Low-intrusive recognition of expressive movement qualities. Proceedings of the 19th ACM international conference on multimodal interaction 2017. [DOI]
102. Halprin D. The expressive body in life, art, and therapy: Working with movement, metaphor and meaning.: Jessica Kingsley Publishers; 2002.
103. Stadlmann C, & Zehetner, A., editor Human intelligence versus artificial intelligence: A comparison of traditional and AI-based methods for prospect generation. Marketing and smart technologies: Proceedings of ICMarkTech 2020; 2021; Singapore: Springer Singapore. [DOI]
104. Bauer MS, Damschroder, L., Hagedorn, H., Smith, J., & Kilbourne, A. M. . An introduction to implementation science for the non-specialist. BMC psychology. 2015;3(32). [PMID: 26376626] [PMCID: PMC4573926] [DOI]
105. Drummond MF SM, Claxton K, Stoddart GL, Torrance GW. . Methods for the economic evaluation of health care programmes. : Oxford Univ Press. ; 2015.
106. Johnson M, Schuster, M., Le, Q., Krikun, M., Wu, Y., Chen, Z., ... & Dean, J. . Google’s multilingual neural machine translation system: Enabling zero-shot translation. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics. 2017;2:339-51. [DOI]
107. Neff G NP. Automation, algorithms, and politics: talking to bots. International Journal of Communication. 2016;10:4915–31. [DOI]
108. Young JE, Igarashi, T., Sharlin, E., Sakamoto, D., & Allen, J. Design and evaluation techniques for authoring interactive and stylistic behaviors. ACM Transactions on Interactive Intelligent Systems (TiiS). 2014;3(4):1-36. [DOI]