A Combined Parenting Model for Children’s Oppositional Defiance: A Qualitative Study
Keywords:
combined parenting, joint problem-solving, effective parent–child interaction, parental management, positive parenting stabilization, emotional and supportive skills, oppositional defianceAbstract
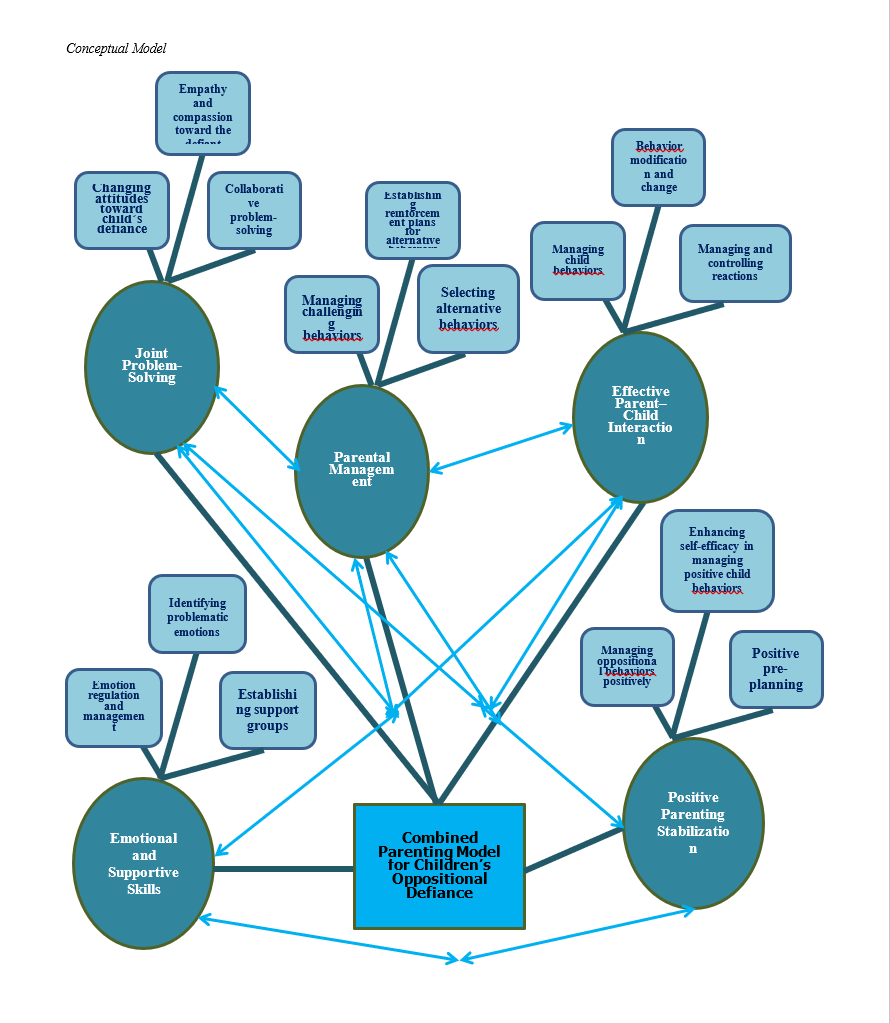
The combined parenting model for children’s oppositional defiance has received little attention in previous studies. Accordingly, this research was conducted with the aim of discovering a combined parenting model for children exhibiting oppositional defiant behavior. The present study employed a qualitative design using a deductive thematic network analysis approach. The research context and sample consisted of 48 scientific sources, including books, articles, and dissertations. A thematic analysis result-recording form was used to extract the identified dimensions of the combined parenting construct in the study. The textual data were analyzed through thematic network analysis based on the approach of Attride-Stirling et al. (2001), followed by conventional thematic analysis and subsequent calculation of the Content Validity Index (CVI) and Content Validity Ratio (CVR). The results indicated that the combined parenting model for children’s oppositional defiance includes five main and final thematic categories: joint problem-solving training, effective parent–child interaction training, parental management training, positive parenting stabilization, and emotional and supportive skills training. Each of these five major themes also comprises a diverse range of essential subthemes. Based on the findings, it is suggested that the combined parenting model for children’s oppositional defiance be considered in future research as the foundation for psychometric studies (such as developing a measurement instrument for combined parenting) and for designing comprehensive psychological training programs.
Downloads
References
Amini Naghani, S., Najarpourian, S., & Samavi, S. A. (2020). Comparing the effectiveness of the triple p-positive parenting program and parenting program of acceptance and commitment therapy on parent-child relationship and self-efficacy of mothers with oppositional defiant disorder children. Journal of Research & Health, 10(2), 111-122. https://doi.org/10.32598/JRH.10.2.7
Attride-Stirling, J., Davis, H., Markless, G., Sclare, I., & Day, C. (2001). 'Someone to talk to who'll listen': Addressing the psychosocial needs of children and families. Journal of Community & Applied Social Psychology, 11(3), 179-191. https://doi.org/10.1002/casp.613
Costin, J., Lichte, C., Hill-Smith, A., Vance, A., & Luk, E. (2004). Parent group treatments for children with oppositional defiant disorder. Australian e-Journal for the advancement of mental health, 3(1), 36-43. https://doi.org/10.5172/jamh.3.1.36
Dashtbanzadeh, S., Neshat Doost, H. T., Akrami, N., & Mehrabi, H. A. (2024). Comparison of the effectiveness of the treatment package of oppositional defiant disorder based on biological parental experiences and parent-child relationship-based play therapy on the quality of parent-child interaction and symptoms of children with ODD. Clinical Psychology Studies, 15(55), 61-75. https://journals.atu.ac.ir/article_17468_47451596c8a2ca59f1eabeaf80ee84c9.pdf
Eskander, N. (2020). The psychosocial outcome of conduct and oppositional defiant disorder in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Cureus, 12(8), e9521. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.9521
Fooladvand, M., Nadi, M. A., Abedi, A., & Sajjadian, I. (2021). Parenting styles for children with oppositional defiant disorder: Scope review. Journal of education and health promotion, 10, 21. https://doi.org/10.4103/jehp.jehp_566_19
Fucà, E., Cirillo, F., Celestini, L., Alfieri, P., Valentini, D., Costanzo, F., & Vicari, S. (2023). Assessment of oppositional defiant disorder and oppositional behavior in children and adolescents with Down syndrome. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 13, 1062201. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1062201
Ghosh, A., Ray, A., & Basu, A. (2017). Oppositional defiant disorder: current insight. Psychology research and behavior management, 10, 353-367. https://doi.org/10.2147/PRBM.S120582
Gubbels, J., van der Put, C. E., & Assink, M. (2019). The effectiveness of parent training programs for child maltreatment and their components: A meta-analysis. International journal of environmental research and public health, 16(13), 2404. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16132404
Hawes, D. J., Gardner, F., Dadds, M. R., Frick, P. J., Kimonis, E. R., Burke, J. D., & Fairchild, G. (2023). Oppositional defiant disorder. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 9(1), 31. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-023-00441-6
Helander, M., Enebrink, P., Hellner, C., & Ahlen, J. (2023). Parent Management Training Combined with Group-CBT Compared to Parent Management Training Only for Oppositional Defiant Disorder Symptoms: 2-Year Follow-Up of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 54(4), 1112-1126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-021-01306-3
Kaur, M., Floyd, A., & Balta, A. M. (2022). Oppositional defiant disorder: Evidence-based review of behavioral treatment programs. Annals of Clinical Psychiatry, 34(1), 44-58. https://doi.org/10.12788/acp.0056
Klos, S., Thöne, A. K., Döpfner, M., & Görtz-Dorten, A. (2025). Self-rated symptoms of oppositional defiant disorder and conduct disorder: Factor structure, reliability, and validity in a clinical sample of adolescents. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 56(4), 1147-1160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-024-01802-2https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-025-01821-7
Masiran, R., Tan, K. A., Ismanizan, M. A., Roslee, N. A., & Prabaharan, P. (2025). Prevalence of children's emotional and behavioural problems and parents' psychological distress in child and adolescent psychiatric clinic Hospital Sultan Abdul Aziz Shah. International Journal of Psychiatry in Clinical Practice, 29(2), 91-95. https://doi.org/10.1080/13651501.2025.2500543
Muratori, P., Conversano, C., Levantini, V., Masi, G., Milone, A., Villani, S., Bögels, S., & Gemignani, A. (2021). Exploring the efficacy of a mindfulness program for boys with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and oppositional defiant disorder. Journal of Attention Disorders, 25(11), 1544-1553. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054720915256
Nobakht, H. N., Steinsbekk, S., & Wichstrøm, L. (2024). Development of symptoms of oppositional defiant disorder from preschool to adolescence: the role of bullying victimization and emotion regulation. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines, 65(3), 343-353. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.13845
Sacco, R., Camilleri, N., & Umla-Runge, K. (2021). The prevalence of oppositional defiant disorders among young people in Europe: A systematic review and meta-analysis. European Psychiatry, 64(Suppl 1), S639-S640. https://doi.org/10.1192/j.eurpsy.2021.596https://doi.org/10.1192/j.eurpsy.2021.1842https://doi.org/10.1192/j.eurpsy.2021.1640https://doi.org/10.1192/j.eurpsy.2021.1698https://doi.org/10.1192/j.eurpsy.2021.1693