Comparison of the Effectiveness of Infinite Tomatis Sound Therapy, Vestibulo-Cerebellar Skills Training, and the Combination of Both Methods on Response Inhibition in Students with Specific Learning Disorder with Reading Impairment
Keywords:
sound therapy, vestibulo-cerebellar skills, response inhibition, learning disorderAbstract
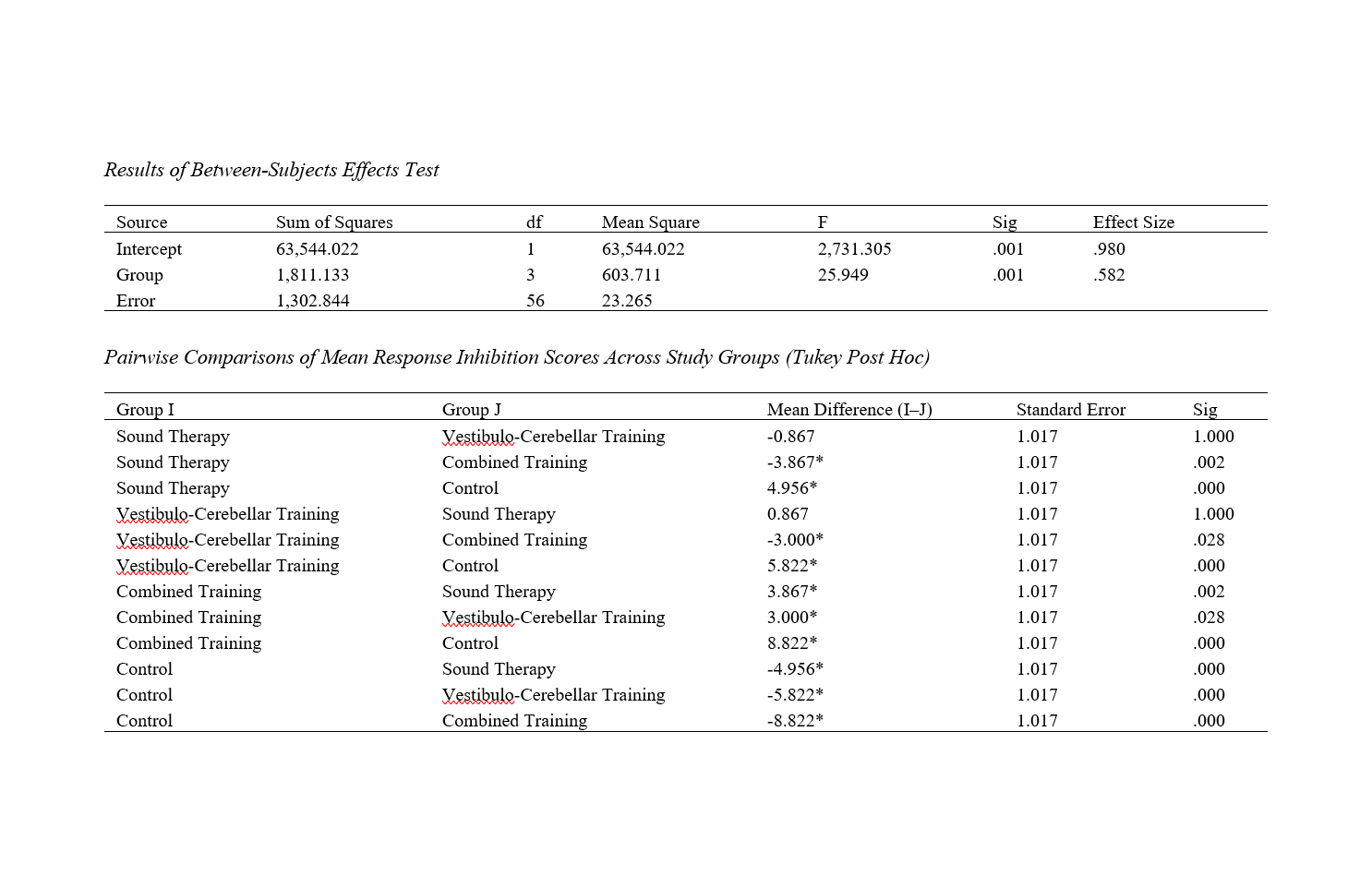
The present study aimed to compare the effectiveness of Infinite Tomatis sound therapy, vestibulo-cerebellar skills training, and the combination of both methods on response inhibition in students aged 8 to 12 years with specific learning disorder characterized by reading impairment. This research was an applied study utilizing a quasi-experimental design with pre-test, post-test, and follow-up stages accompanied by a control group. The statistical population consisted of all students with reading difficulties in Tehran in 2024 who sought treatment at counseling and rehabilitation clinics. The sample included 60 students from this population who were selected through convenience sampling and randomly assigned to four groups: Infinite Tomatis sound therapy training (n=15), vestibulo-cerebellar skills training (n=15), combined Infinite Tomatis sound therapy and vestibulo-cerebellar skills training (n=15), and a control group (n=15). After the intervention sessions, participants in all three experimental groups completed the research questionnaires again. The data were collected using the Reading and Dyslexia Test (NAMA) by Karami Nouri et al. (2008), the IVA2 Test, and the Go/No-Go Test developed by Bruner and Hoffman (1984). Data analysis was performed using repeated measures ANOVA with SPSS version 22. The findings indicated a significant difference in response inhibition scores between the combined training group and the vestibulo-cerebellar skills training group. Specifically, the response inhibition scores in the combined training group were higher than those in the vestibulo-cerebellar skills training group.
Downloads
References
Bahmerd, F., Esteki, M., & Shahriari Ahmadi, M. (2021). The Effect of Cerebellar Training on Improving the Reading and Motor Skills of Students with Dyslexia. https://journals.iau.ir/article_689714.html?lang=en
Brbić, I., & Tomić, L. (2020). An integrative review of the effectiveness of the tomatis method in children with autism spectrum disorder. RAD CASA-Medical Sciences, 543, 49-56. https://hrcak.srce.hr/clanak/354581
Cainelli, E., Vedovelli, L., Carretti, B., & Bisiacchi, P. (2023). EEG correlates of developmental dyslexia: a systematic review. Annals of Dyslexia, 73(2), 184-213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-022-00273-1
Crisci, G., Caviola, S., Cardillo, R., & Mammarella, I. C. (2021). Executive functions in neurodevelopmental disorders: Comorbidity overlaps between attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder and specific learning disorders. Frontiers in human neuroscience, 15, 594234. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2021.594234
Dado, Z., & Emadian, S. A. (2024). The effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral play therapy on executive functions in elementary school students with specific reading disorder. The First International Conference on Health, Hygiene, and Education, Sari,
El-Tellawy, M. M., Ahmad, A. R., Saad, K., Alruwaili, T. A., AbdelMoneim, I. M., Shaaban, I., Alinad, A. K. M., Albulayhid, S. B. H., & Khalaf, S. M. (2022). Effect of hyperbaric oxygen therapy and tomatis sound therapy in children with autism spectrum disorder. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 113, 110457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2021.110457
Friantary, H., Afriani, Z. L., & Nopitasari, Y. (2020). The implementation of indonesian language learning for dyslexic in children at elementary schools in Bengkulu. Linguists: Journal Of Linguistics and Language Teaching, 6(2), 23-29. https://doi.org/10.29300/ling.v6i2.3950
Hemmati, A., Ahmadi, V., & Mami, S. (2022). Investigating the Mediating Role of Executive Functions in the Relationship Between Fine Motor Skills and Reading Skills in Students with Reading Disorder. Exceptional Education Journal, 167, 35-48. https://exceptionaleducation.ir/article-1-2492-en.html
Li, S., Guo, J., Zheng, K., Shi, M., & Huang, T. (2022). Is sedentary behavior associated with executive function in children and adolescents? A systematic review. Frontiers in Public Health, 10, 832845. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.832845
Liang, X., Qiu, H., Wang, P., & Sit, C. H. (2022). The impacts of a combined exercise on executive function in children with ADHD: A randomized controlled trial. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports, 32(8), 1297-1312. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.14192
Malayeri, S., & Pourgharib, J. (2022). Central Auditory Processing. Setayesh Publication.
Northern, J. L., & Downs, M. P. (2022). Hearing in children. Plural Publishing Inc. https://books.google.com/books/about/Hearing_in_Children.html?id=1CUFXsBbBgoC
Osa-Afiana, D. D. (2022). Symptom identification, assessment and management of dyslexia in children. IFE Psychologia: An International Journal, 30(2), 76-82. https://journals.co.za/doi/10.10520/ejc-ifepsyc_v30_n2_a10
Rahmani, N., Estaki, M., & Niusha, B. (2019). The Effectiveness of Sound Therapy by Tomatis Method on Executive Functions in Dyslexic Students in Academic Years 2018-19 in Tehran. Journal of Paramedical Sciences & Rehabilitation, 8(3), 34-44. https://jpsr.mums.ac.ir/article_14093.html
Rahmani, N., Esteki, M., & Beheshteh, N. (2019). The Effectiveness of Sound Therapy using the Tomatis Method on the Reading Skills and Motor Skills of Students with Reading Problems. Journal, 1(10), 68-85. https://www.ceciranj.ir/article_91930_en.html
Shahroudi, E., Hassanzadeh, R., & Emadian, S. A. (2020). Comparing the Effectiveness of Cognitive Rehabilitation and Vestibular Stimulation on the Academic Achievement of Female Students with Specific Learning Disorder. Community Health Journal.
Snowling, M. J., Nash, H. M., Gooch, D. C., Hayiou‐Thomas, M. E., Hulme, C., Wellcome, L., & Reading Project, T. (2019). Developmental outcomes for children at high risk of dyslexia and children with developmental language disorder. Child development, 90(5), e548-e564. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.13216
Stucke, N. J., Stoet, G., & Doebel, S. (2022). What are the kids doing? Exploring young children's activities at home and relations with externally cued executive function and child temperament. Developmental science, 25(5), e13226. https://doi.org/10.1111/desc.13226
Tabrizi, N., & Tabrizi, M. (2022). Treatment of Reading Disorders. Fararavan Publication.
Williams, K. J., Walker, M. A., Vaughn, S., & Wanzek, J. (2021). A Synthesis of Reading and Spelling Interventions and Their Effects on Spelling Outcomes for Students with Learning Disabilities. J Learn Disabil, 50(3), 286-297. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022219415619753
Yang, L., Li, C., Li, X., Zhai, M., An, Q., Zhang, Y., Zhao, J., & Weng, X. (2022). Prevalence of developmental dyslexia in primary school children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Sciences, 12(2), 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12020240