The Mediating Role of Attention Bias in the Relationship Between Anxiety Sensitivity and Academic Motivation in Children With Specific Learning Disorders
Keywords:
Anxiety sensitivity, Attention bias, Academic motivation, Specific learning disorders, Mediation model, Structural equation modeling.Abstract
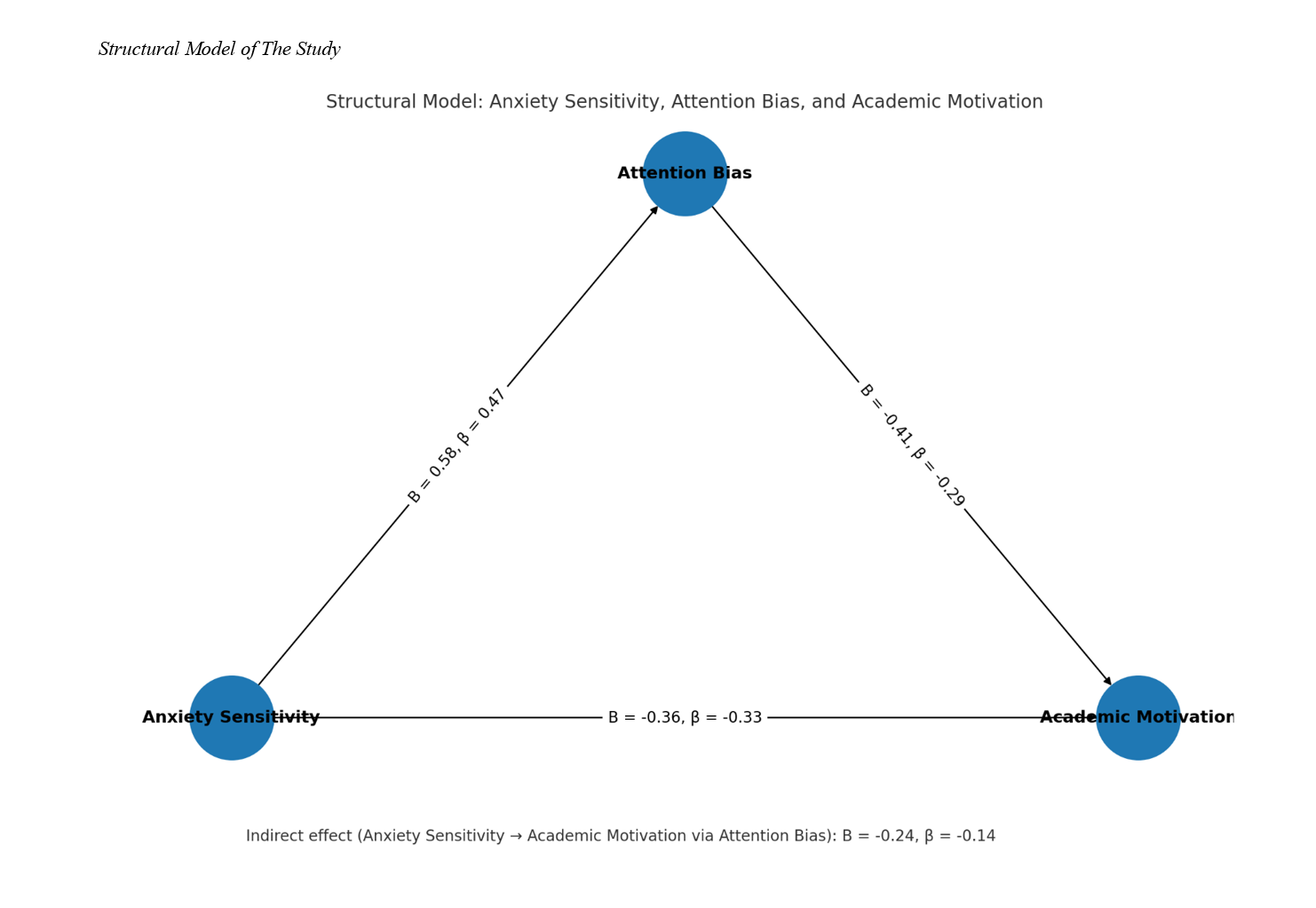
This study aimed to investigate the mediating role of attention bias in the relationship between anxiety sensitivity and academic motivation among children diagnosed with specific learning disorders (SLD). A descriptive–correlational design was used, involving 400 students with specific learning disorders enrolled in learning disability centers in Tehran during the 2024–2025 academic year. The sample size was determined using the Krejcie and Morgan table. Data were collected using three standardized instruments: the Academic Motivation Scale (AMS; Vallerand et al., 1992) to measure academic motivation, the Anxiety Sensitivity Index for Children (ASIC; Laurent et al., 1998) to assess anxiety sensitivity, and the Dot-Probe Task (MacLeod et al., 1986) to evaluate attention bias. Data analysis was performed using Pearson correlation coefficients and Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) through SPSS-27 and AMOS-21 software. Model fit was assessed using multiple indices including χ²/df, GFI, AGFI, CFI, TLI, and RMSEA. Results revealed that anxiety sensitivity was negatively correlated with academic motivation (r = −.42, p < .001) and positively correlated with attention bias (r = .47, p < .001). Attention bias was negatively correlated with academic motivation (r = −.36, p < .001). The SEM results indicated excellent model fit (χ²/df = 1.63, CFI = .97, TLI = .96, RMSEA = .039). Anxiety sensitivity significantly predicted attention bias (β = 0.47, p < .001) and academic motivation (β = −0.33, p < .001). The indirect effect of anxiety sensitivity on academic motivation through attention bias was also significant (β = −0.14, p = .002), confirming partial mediation. The findings suggest that attention bias partially mediates the relationship between anxiety sensitivity and academic motivation in children with specific learning disorders.
Downloads
References
Abdulahi Beqrabadi, G., & Heidary rad, M. (2025). The Effectiveness of Emotion Regulation Training on Academic Self-Regulation and Procrastination of Male Students with Special Learning Disorder. Rooyesh, 13(11), 193-202. https://frooyesh.ir/article-1-5571-en.html
Bulut, S., Bukhori, B., & Parsakia, K. (2024). Enhancing Selective Attention in Children with Learning Disorders: Efficacy of Executive Functions Training. KMAN Counseling & Psychology Nexus, 1(2), 86-93. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.psychnexus.1.2.14
Conant, L. L., & Miller, L. E. (2024). Intellectual developmental disorder, autism spectrum disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and specific learning disorders across the lifespan. https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2024-40079-022
Fathiazar, E., Mani, A., Adib, Y., & Sharifi, Z. N. (2020). Effectiveness of an Educational Neuroscience-Based Curriculum to Improve Academic Achievement of Elementary Students With Mathematics Learning Disabilities. Research and Development in Medical Education, 9(1), 18-18. https://doi.org/10.34172/rdme.2020.018
Gao, L., Li, S., Yue, Y., & Long, G. (2023). Maternal Age At Childbirth And The Risk Of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder And Learning Disability In Offspring. Front Public Heal, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2023.923133
Ghadampour, A., & Bawzin, F. (2021). The Effectiveness of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy System on Attention Bias in Adolescent Students with Symptoms of Social Anxiety. Psychological studies, 4, 0-2. https://ensani.ir/fa/article/495796/
Kausik, N. H., & Hussain, D. (2023). The impact of inclusive education on academic motivation, academic self-efficacy, and well-being of students with learning disability. Journal of Education, 203(2), 251-257. https://doi.org/10.1177/00220574211031957
Lievore, R. (2024). Let’s Face It! The Role of Social Anxiety and Executive Functions in Recognizing Others’ Emotions From Faces: Evidence From Autism and Specific Learning Disorders. Development and Psychopathology, 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0954579424000038
Mehrinejad, A., Farahbijari, A., & Norouzi Nargesi, M. (2016). Comparison of attention bias and emotional processing styles in female students with generalized anxiety disorder, with body dysmorphic disorder and inpatient. Clinical Psychology Studies, 6(24), 99-114. https://doi.org/10.22054/jcps.2016.6516
Mohammadlou, M., Sotoude Asl, N., Ghorbani, R., & Talepasand, S. (2024). The Effectiveness of Cognitive Rehabilitation on Improving Selective Attention, Cognitive Flexibility and Academic Progress of Students with Specific Learning Disorders. Journal of Applied Psychological Research, 15(1), 317-340. https://japr.ut.ac.ir/article_94180.html
Narimani, M., Sahebgharan Fard, M., & Nokhostin Goldoust, A. (2023). Comparing the Effectiveness of a Model Based on Achievement Motivation and Social Skills Training on Academic Self-Efficacy in Students with Learning Disabilities. Learning Disabilities, 12(3), 91-81. https://doi.org/10.22098/jld.2023.12901.2095
Nazarboland, N., Abedivzadeh, N., & Ghanbari, S. (2022). The Role of Anxiety in Executive Functions of Children With Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder and Mathematical Learning Disability Comorbidity. Journal of Neurodevelopmental Cognition, 2(1), 1-11. https://doi.org/10.52547/jncog.2022.103434
Nazari, A. (2023). Investigating hyperactivity with attention deficit and learning disorders: A case study of an 8th-grade student. Journal of Research in Persian Language and Literature Education, 2(4), 41-59. https://journals.cfu.ac.ir/article_3383.html?lang=en
Nejatifar, S., & Abedi, A. (2023). Effectiveness of Motivational Interviewing on Participation and Emotional Skills in Learning Disabled Adults. Psychological Research in Individuals with Exceptional Needs, 1(1), 32-40. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.prien.1.1.5
Nourizadeh, R., & Moslem Nejad, A. (2023). Comparing Academic Motivation and Behavioral Disorders in Students with Learning Disabilities and Normal Students. Sixteenth National Scientific-Research Conference on Psychology and Educational Sciences,
Núñez, J. C., Rodríguez, C., Herrero, E. T., Fernández, E., & Cerezo, R. (2020). Prior Academic Achievement as a Predictor of Non-Cognitive Variables and Teacher and Parent Expectations in Students With Learning Disabilities. Learning Disability Quarterly, 45(2), 121-133. https://doi.org/10.1177/0731948720925402
Pettit, J. W., Bechor, M., Rey, Y., Vasey, M. W., Abend, R., Pine, D. S., Bar‐Haim, Y., Jaccard, J., & Silverman, W. K. (2020). A Randomized Controlled Trial of Attention Bias Modification Treatment in Youth With Treatment-Resistant Anxiety Disorders. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 59(1), 157-165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2019.02.018
Raji, O., & Javaid, S. (2022). Successful Diagnosis of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Later Life of an Adult With Intellectual Disability: A Case Report. British Journal of Learning Disabilities, 50(4), 578-585. https://doi.org/10.1111/bld.12446
Saeedmanesh, M., Azizi, M., & Hematian, Z. (2020). The Effectiveness of Mindfulness and the Attention Bias Program on Attention, Inhibition and Emotional Regulation in Children with Generalized Anxiety Disorder. jcp, 8(2), 33-45. http://jcp.khu.ac.ir/article-1-3141-en.html
Shahroudi, E., Hassan Zadeh, R., & Emadian, S. A. (2020). Comparison of the Effectiveness of Cognitive Rehabilitation and Vestibular Stimulation on Academic Achievement of Girls with Specific Learning Disorders. https://chj.rums.ac.ir
Shechner, T., Britton, J. C., Pérez-Edgar, K., Bar-Haim, Y., Ernst, M., Fox, N. A., Leibenluft, E., & Pine, D. S. (2012). Attention biases, anxiety, and development: toward or away from threats or rewards? Depression and Anxiety, 29(4), 282-294. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.20914
Stahopoulou, A., & Siskou, K. (2023). Enhancing Mental Health Promotion of Students With Learning Disabilities: The Role of Motivation and Digital Technologies. GSC Advanced Research and Reviews, 16(1), 116-128. https://doi.org/10.30574/gscarr.2023.16.1.0307
Tiengsomboon, U., & Luvira, V. (2024). Family support for children with learning disabilities to attain good academic performance: A qualitative study. Malaysian Family Physician: the Official Journal of the Academy of Family Physicians of Malaysia, 19, 25. https://doi.org/10.51866/oa.529
Zuppardo, L., Serrano, F., Pirrone, C., & Rodriguez-Fuentes, A. (2023). More Than Words: Anxiety, Self-Esteem, and Behavioral Problems in Children and Adolescents With Dyslexia. Learning Disability Quarterly, 46(2), 77-91. https://doi.org/10.1177/07319487211041103