The Effectiveness of a Combined Pelvic Floor Exercise Program and Desensitization-Based Sex Therapy on Pain and Sexual Satisfaction in Female Athletes
Objective: This study evaluated the effectiveness of an integrated pelvic floor muscle training program combined with desensitization-based sex therapy on sexual pain and sexual satisfaction in female athletes.
Methods: In a randomized controlled trial, 68 sexually active female athletes (18–40 years) reporting penetration-related pain were allocated to either a combined intervention group (PFMT plus desensitization-based sex therapy; 8 weekly sessions) or an attention-matched education control group. Outcomes were assessed at baseline, post-intervention (8 weeks), and 3-month follow-up. Primary outcomes included pain during intercourse (Visual Analogue Scale, VAS) and sexual satisfaction (Female Sexual Function Index, FSFI). Secondary outcomes included sexual distress, pain catastrophizing, and pelvic floor muscle strength. Data were analyzed using intention-to-treat mixed-effects models.
Results: At post-intervention, the combined intervention group demonstrated significantly greater reductions in sexual pain compared with controls (adjusted mean difference = −1.0, 95% CI −1.6 to −0.4; p = .001; Cohen’s d = 0.60). Sexual satisfaction improved significantly in the intervention group (adjusted difference = +3.1 FSFI points, 95% CI 1.4–4.8; p < .001; d = 0.65). Improvements were largely maintained at 3-month follow-up. Significant reductions were also observed in pain catastrophizing (d = 0.70) and sexual distress (d = 0.72), alongside objective gains in pelvic floor muscle strength (p < .001).
Conclusion: A combined PFMT and desensitization-based sex therapy program is an effective, non-invasive intervention for reducing sexual pain and improving sexual satisfaction in female athletes, supporting a biopsychosocial approach to sexual rehabilitation in sports contexts.
Artificial Intelligence in Theater Performance and Physical Training: A Review of Technologies Optimizing Performer Development and Artistic Execution
Objective: Theater performance demands substantial physical capabilities requiring systematic training comparable to athletic preparation. Professional performers engage in cardiovascular conditioning, strength development, and movement technique refinement to meet performance demands. Artificial intelligence technologies including computer vision, machine learning, and generative modeling have enabled practical applications in movement analysis, personalized training design, and performance feedback delivery. These advances address accessibility barriers, objective assessment challenges, and individualized program adaptation needs characteristic of theatrical training contexts. This review aimed to (i) examine AI technologies applied in theater performance and physical training contexts, (ii) analyze implementation challenges and limitations across applications, and (iii) identify critical research priorities requiring empirical investigation.
Methods: We searched PubMed, IEEE Xplore, ACM Digital Library, Web of Science, and Google Scholar for studies published 2014-2025. Inclusion criteria required empirical AI applications in theater performance, performing arts training, or physical conditioning relevant to theatrical demands. We extracted data on technologies employed, application contexts, reported outcomes, and identified limitations. Quality assessment examined validation methodology, sample characteristics, and outcome measurement approaches.
Results: Computer vision systems demonstrated validation accuracies with mean errors of 20-30 mm in controlled laboratory environments and 50-80 mm in theatrical settings with challenging lighting and costume conditions. Generative choreography systems produced technically coherent movement sequences, receiving mixed artistic evaluations from expert practitioners. Natural language processing achieved 85-92% accuracy for surface-level script sentiment analysis while demonstrating poor performance on dramatic subtext interpretation tasks. AI fitness applications reported initial user engagement improvements though sustained adherence declined substantially beyond six months across multiple studies. Theater practitioners demonstrated high acceptance (85%) for technical production support applications while expressing concerns (62%) regarding creative process involvement. Research examining long-term effectiveness beyond six months remained critically scarce across all application domains examined.
Conclusion: AI technologies demonstrate potential for technical support and objective assessment in theater and physical training contexts. Successful implementation requires domain-specific design approaches, preservation of human creative agency, and realistic technological capability assessment. Critical research priorities include longitudinal effectiveness validation, diverse population testing, cultural inclusivity in training datasets, and ethical framework development for responsible AI deployment in creative domains.
Generative Artificial Intelligence and Large Language Models in Didactics of Sports Sciences and Physical Education: A Comprehensive Review of Pedagogical Applications, Teaching Innovations, and Research Implications
Objective: The global burden of physical inactivity contributes to 5.3 million deaths annually, exceeding smoking-related mortality in certain regions and contributing substantially to the 1.5 billion individuals worldwide living with chronic diseases. Physical education (PE) represents a critical intervention point, yet persistent challenges limit effectiveness including inadequate instructional time (80 minutes weekly versus recommended 150 minutes), insufficient specialized teacher preparation (42% of elementary PE teachers lack specialized training), and limited capacity for differentiated instruction in heterogeneous student populations. The emergence of Generative Artificial Intelligence (Gen AI), particularly Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT (launched November 2022, achieving 100 million users within two months), presents unprecedented opportunities for transforming pedagogical practices in sports sciences and PE contexts while simultaneously introducing critical challenges regarding academic integrity, cognitive development, and the preservation of embodied learning central to movement education. This comprehensive review aimed to: (i) systematically examine current applications and pedagogical affordances of Gen AI and LLMs in sports sciences and PE didactics; (ii) analyze alignment with established pedagogical principles including constructivism, social constructivism, situated learning theory, and Universal Design for Learning; (iii) critically evaluate potential benefits and risks from a didactics perspective including impacts on teacher development, student learning outcomes, curriculum design, and assessment practices; and (iv) propose evidence-informed frameworks for pedagogically sound integration emphasizing human-AI collaboration rather than replacement of essential teaching functions.
Methods: A systematic literature search was conducted following adapted PRISMA guidelines across seven databases (PubMed/MEDLINE, Web of Science, Scopus, IEEE Xplore, ERIC, SPORTDiscus, Google Scholar) covering January 2022 to November 2025. Search terms combined Gen AI/LLM terminology with pedagogical concepts in sports sciences contexts using Boolean operators. Inclusion criteria focused on peer-reviewed articles examining pedagogical applications, teaching innovations, learning outcomes, and didactic research methodologies. From 1,247 initial records, 858 titles and abstracts were screened after duplicate removal (n=389), with 247 undergoing full-text review. Final analysis included 78 studies meeting inclusion criteria. Data extraction utilized standardized forms capturing study characteristics, methodological approaches, AI technology examined, pedagogical context, theoretical framework, key findings, and practice implications. Thematic analysis employed a pedagogically-oriented framework organizing findings into four domains aligned with core didactic functions: teaching support, learning enhancement, assessment innovation, and didactic research.
Results: Analysis of 78 studies (67% published 2023-2024) revealed significant pedagogical applications across four domains with concurrent identification of critical challenges. Teaching Support domain demonstrated lesson planning time reductions of 35% to 45%, with AI-assisted lesson plan quality rated 7.3 out of 10 (SD=1.2) for curriculum alignment compared to 7.8 out of 10 (SD=0.9) for manually created plans. Educators reported 67% satisfaction with differentiated instruction materials generated through Gen AI platforms. Learning Enhancement domain revealed improved conceptual understanding when engaging with AI tutors for anatomy and biomechanics concepts, with students valuing immediate availability and scaffolded explanations. Assessment Innovation applications showed AI-generated feedback demonstrated substantial agreement with expert teacher feedback for student assignments. Didactic Research efficiency gains included literature synthesis completion substantially faster than traditional methods and qualitative coding demonstrating substantial agreement between AI and expert human coders. However, critical challenges emerged including academic integrity violations in 23% to 43% of student work, factual inaccuracies in AI-generated specialized content, cognitive atrophy concerns (AI-Chatbot Induced Cognitive Atrophy, AICICA), reduced emphasis on embodied learning in PE contexts, and equity issues affecting students with limited digital literacy or technology access.
Conclusion: Gen AI and LLMs represent transformative tools for sports sciences and PE didactics when implemented within robust pedagogical frameworks that preserve the essential embodied, social, and affective dimensions of movement education. Evidence supports specific applications including administrative efficiency, differentiated cognitive content delivery, formative assessment support, and research methodology enhancement, while simultaneously demanding critical attention to academic integrity, accuracy verification, equity considerations, and prevention of cognitive atrophy through over-reliance. A hybrid pedagogical model is recommended integrating Gen AI for cognitive content delivery, theoretical knowledge construction, and administrative tasks while rigorously preserving face-to-face instruction, kinesthetic learning experiences, immediate physical feedback, and human mentorship central to sports education. Successful integration requires comprehensive teacher professional development focusing on pedagogical decision-making rather than technical operation, explicit policies balancing academic integrity with beneficial use, critical AI literacy curriculum specific to sports sciences contexts, and ongoing empirical evaluation of long-term learning outcomes. The field requires a paradigm shift from technology-driven adoption to pedagogy-informed integration, ensuring Gen AI serves educational goals rather than dictating them.
Ramadan Fasting: Physical and Performance Maintained, Health Challenged in Elite Adolescent Football
Objectives: Adolescent Muslim athletes participating in elite sports during Ramadan Fasting (RF) face unique physiological and developmental challenges. This prospective cohort study aimed to observe the changes in body composition, hydration status, physiological performance, and hematological profiles in 20 elite Malaysian adolescent footballers (17.8 ± 0.8 years).
Methods: Measurements were taken at four phases (two weeks before Ramadan, BRF-2; mid, 2nd weeks of Ramadan, RF-2; late, 4th weeks of Ramadan, RF-4; and two weeks after Ramadan, ARF-6) using dual-time-point (morning/evening) blood and urine sampling, bioelectrical impedance, skinfolds, and the Yo-Yo Intermittent Run (YYIR) test.
Results: Results showed that energy balance, body composition, and aerobic performance (YYIR distance and HRmax) were successfully maintained throughout RF (p>0.05). However, significant dynamic fluid shifts were observed: morning measurements showed hemodilution, while late-afternoon Urine Specific Gravity was significantly higher in RF-4, indicating daily hemoconcentration and dehydration stress. Furthermore, while red blood cells (RBC) and haemoglobin (HB) showed transient morning reductions during RF, the most critical finding was the delayed post-fasting reduction in Mean Cell Volume (MCV) and persistent low Hematocrit (HCT) at ARF-6.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that elite performance is preserved through strong physiological adaptation and effective energy intake, but the RF period induced a subclinical iron deficiency stress that manifested as microcytosis post-Ramadan. Coaches and medical staff must implement rigorous post-Ramadan nutritional and detailed hematological screening to safeguard the long-term health of adolescent footballers.
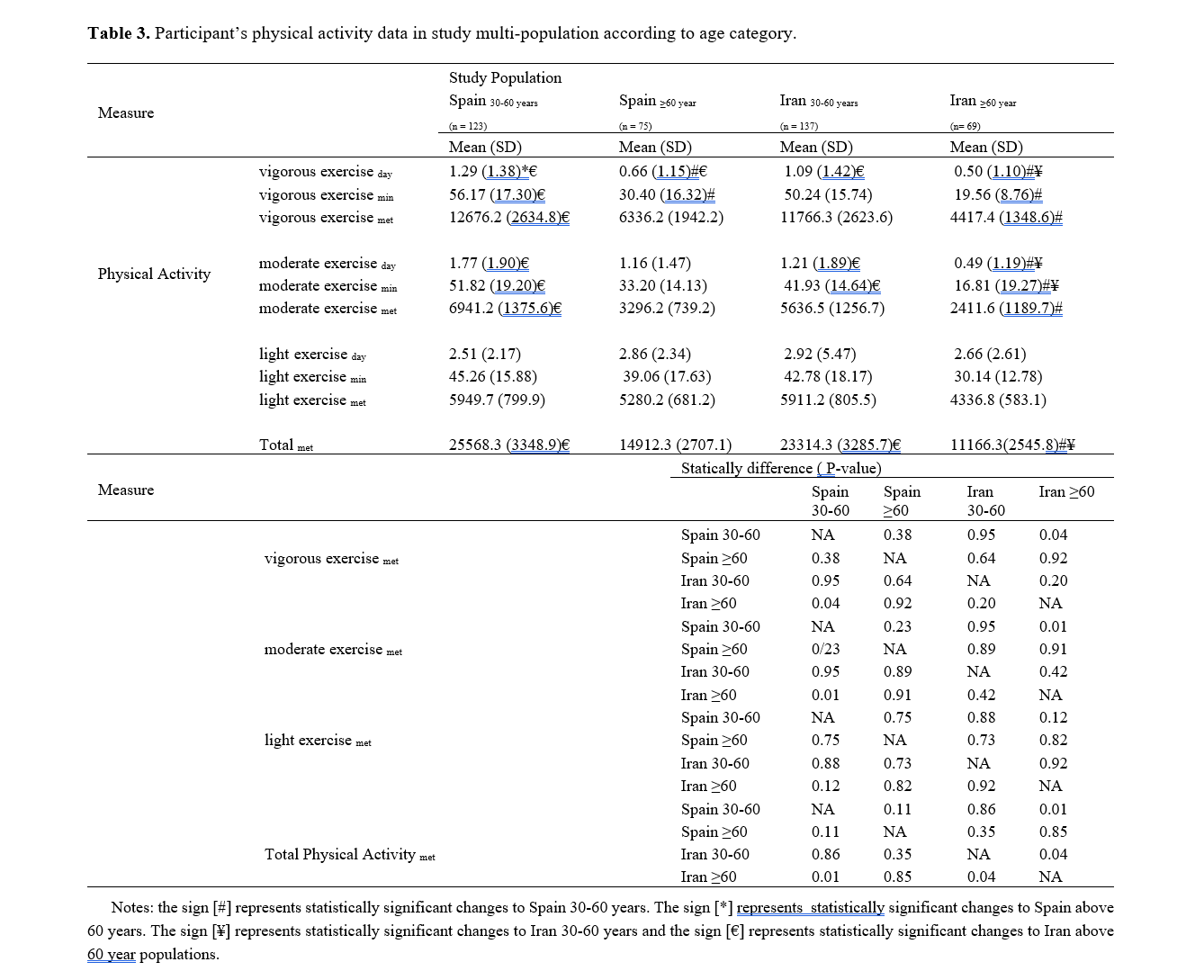
Analysis of the Use of Video Challenge Systems in Volleyball at the 2024 Paris Olympic Games
|
Objective: The use of video-assisted officiating technologies in sports competitions has created a significant transformation in referees’ decision-making processes in recent years. In particular, the Video Challenge System (VCS) in volleyball has become an important element that supports referees’ decisions and may influence teams’ strategic approaches in high-level events. In this context, the study aimed to provide a descriptive examination of data related to the use of the Video Challenge System in volleyball matches played at the 2024 Paris Olympic Games and to evaluate its implementation processes. Methods and Materials: A total of 97 challenges from 25 matches were analyzed. The analysis examined the number of challenges, their approval or rejection, and their distribution by match stage, match outcome, and country, using descriptive statistics and independent t-tests conducted in an exploratory manner. Results: The results showed that 28.87% of all challenges were upheld, while 71.13% were rejected. Winning teams submitted fewer challenges but demonstrated higher success rates in addressing them. Descriptive differences were observed across competition stages, with higher approval rates recorded in the semifinal and bronze medal matches. Variations were also observed among countries in terms of challenge frequency and outcomes. Referees rarely initiated VCS reviews, and such instances occurred infrequently across matches. Conclusion: Overall, the findings suggest that VCS use may support referee decision-making processes and may be associated with perceived fairness, while patterns of use appear to vary according to team characteristics, competition stage, and national context. These results should be interpreted as descriptive and exploratory in nature. |
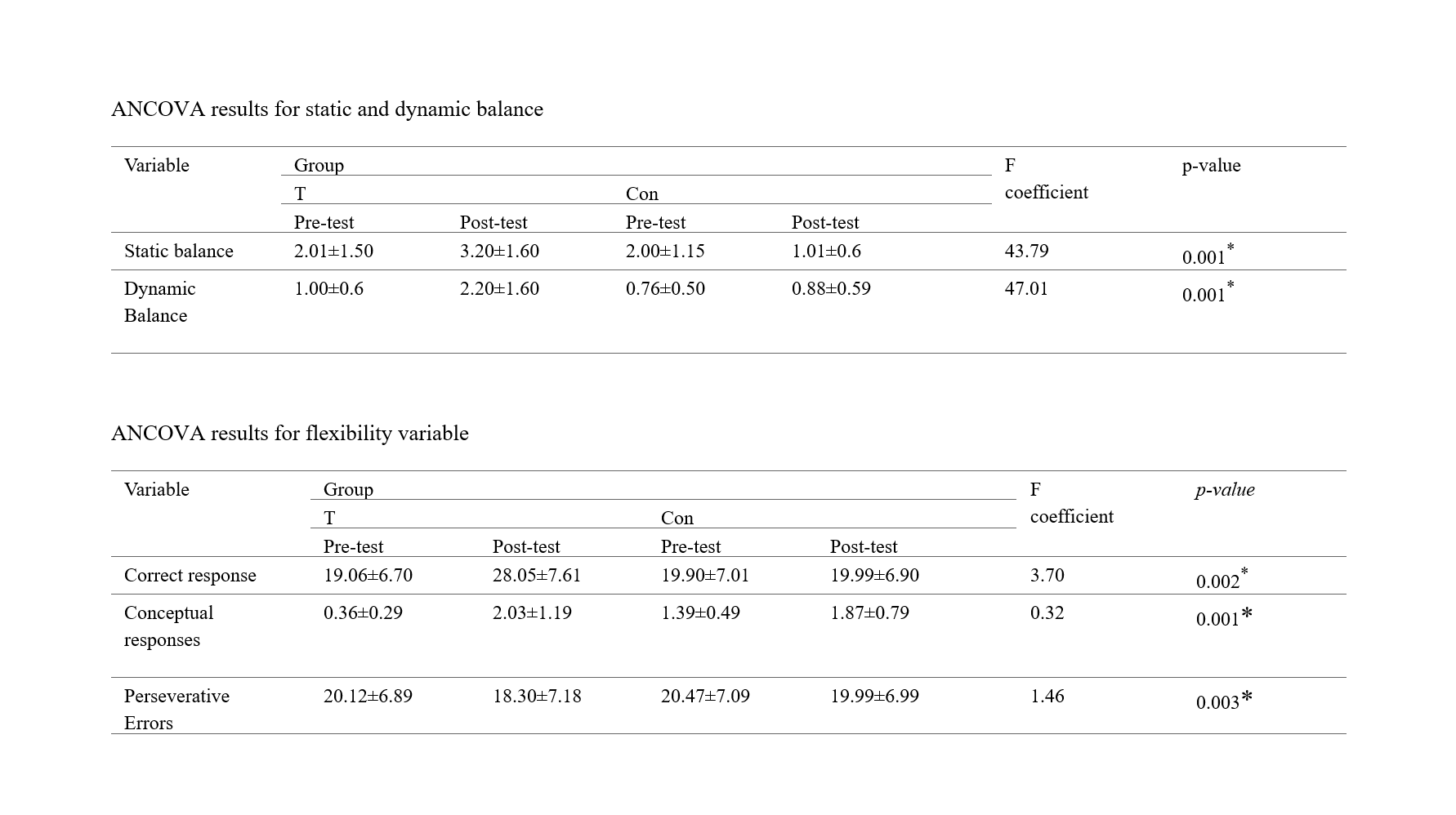
Increasing Exercise Awareness in Individuals with Intellectual Disabilities Among Sports Science Students: An Educational Application
|
Objective: The primary aim of this research is to examine the awareness levels of students studying at the Faculty of Sports Sciences regarding the importance of exercise for individuals with intellectual disabilities and to contribute to developing this awareness. Considering the physical, psychological, and social benefits of exercise programmes for individuals with intellectual disabilities, increasing this awareness is crucial both for developing students' professional knowledge and skills and for contributing to the quality of life of individuals with intellectual disabilities. Methods: The ‘Attitude Scale Towards Sports Activities of Individuals with Intellectual Disabilities’ developed by İlhan and Esentürk (2015) was administered to 68 participants studying at the Faculty of Sports Sciences in order to collect pre-test data. In the next stage, participants underwent a 120-minute training programme covering the definitions of mental disability, the characteristics of individuals with mental disabilities, and the benefits of exercise. Participants who completed the training were paired one-on-one with individuals with intellectual disabilities and underwent a 240-minute exercise programme, which was carried out over 2 days, 120 minutes per day. After the exercise programme was completed, the same attitude scale was re-administered to the participants to collect final test data. The data obtained were transferred to IBM SPSS 26 software for analysis. When evaluating the study data, the Shapiro-Wilk and Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests were used to check the normality of the numerical measurements, and the dependent samples t-test was used to examine changes over time. Findings: The results of the study revealed a statistically significant increase in the participants' pre-test and post-test mean scores on the attitude scale and sub-dimension scores regarding the sporting activities of individuals with intellectual disabilities over time. |
Conclusion: The research is significant in terms of contributing to the development of positive attitudes towards individuals with intellectual disabilities by future sports educators and the training of more conscious and equipped sports scientists in this field.
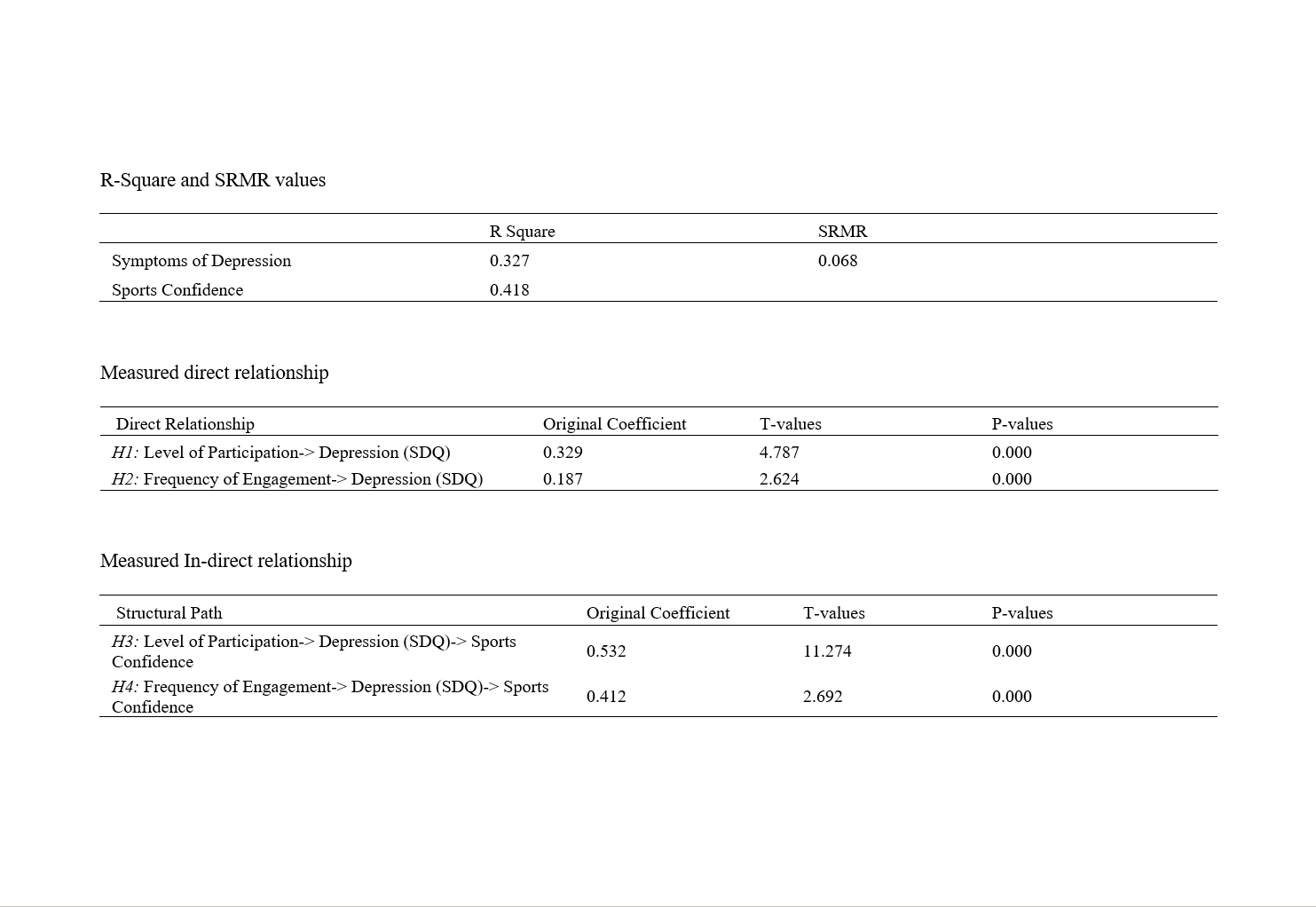
The Effect of Swimming Training on Sources of Self-Confidence in Sports and Self-Assessment of Swimming Skills
|
Objective: The aim of the study was to examine the effect of swimming training given to University students on the Swimming Skills Self-Assessment and Sources of Self-Confidence in Sports scale. Methods: Questionnaire scales were used before and after 14 weeks of swimming training with 1st and 2nd class students studying at Kocaeli University Faculty of Sports Sciences. Participants in the study were students aged 21 with the highest percentages (31.7%), male with 58.5%, students in the Sports Management Department with 52%, 1st class year students with 69.9%, students with an average height of 170-179 cm with 34.1% and students weighing 50-69 kg with 30.1%. The Swimming Skills Self-Assessment Scale and the Self-Confidence Sources Scale in Sports were applied to the students. The students' demographic characteristics and scale analyses were analyzed in the SPSS program. Findings: The study found that before swimming training, women's Swimming Skills Self-Assessment results (2.45±1.08) were lower than men's (3.17±1.01), but the difference decreased after the training. It was determined that no significant differences occurred in the Swimming Skills Self-Assessment and Sports Self-Confidence scales in terms of gender, department, and class after swimming training. The analysis results indicate that sporting activities enhance skill development and confidence. Conclusion: The study found that University Students’ Swimming Skill Self-Assessment and Self-Confidence in Sports improved after swimming instruction, and there were no differences across all variables. In conclusion, it can be said that sporting activities are important for developing skills and confidence in individuals. |
The Relationship Between Participation in Martial Arts Sports and Aggression Levels Among Students
Objective: This study examines the relationship between sports participation and aggression, with a specific focus on martial arts disciplines (taekwondo and karate), as well as gender differences.
Methods: The sample consisted of 63 licensed martial arts athletes (33 female, 30 male), each with a minimum of five years of experience in their respective sports. The primary aim was to investigate how discipline, gender, and years of experience impact various dimensions of aggression. Data were collected using the 30-item “Aggression Inventory,” developed by İpek İlter (Kiper) in 1984, whose validity and reliability were confirmed for this study. A demographic questionnaire was also administered to gather information on gender, sport discipline, years of engagement in sports, and parental background (education and occupation). Descriptive statistics, independent samples t-tests, and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) were used to analyze the data via the SPSS software package.
Results: The findings revealed no statistically significant differences in aggression levels based on the number of years of experience in sports. However, karate athletes exhibited significantly higher levels of destructive and passive aggression than taekwondo athletes, suggesting that the nature or culture of specific martial arts disciplines may differentially affect aggression levels. Additionally, gender differences were found only in assertiveness, with male athletes scoring significantly higher than female athletes. When it came to destructive or passive aggression, there were no discernible gender differences. These findings imply that gender and athletic discipline may have an impact on some aspects of aggression.
Conclusion: This study highlights how essential it is to contain behavioral and psychological knowledge in training programs for the purpose of better control and possibly lessening athletes' tendency for aggression. A more comprehensive and informed approach to athlete improvement and coaching can emerge from an understanding of the complex connection between sport, gender, and aggression.
Current Issue

Articles
-
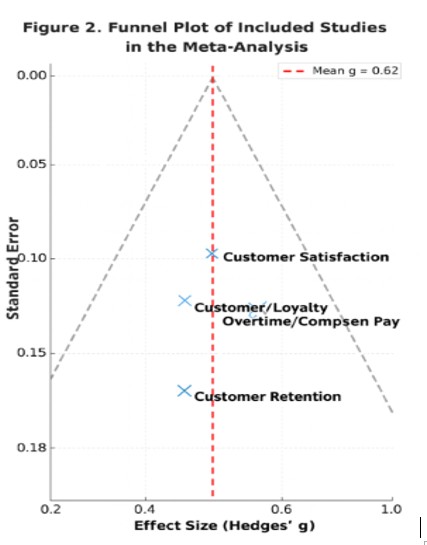
Leveraging Audiovisual Psycholinguistic Interventions to Enhance Sports Facility Income: Evidence from Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Pramusinta Putri Dewanti * ; Sumaryanti Sumaryanti, , Sigit Nugroho , Fadli Ihsan , Bekir Erhan Orhan1-10 -
Moderate and Vigorous Physical Activity as a Protective Factor against Anxiety in University Students
Roxana Abril Morales-Beltrán , Germán Hernández-Cruz , Diana Korinna Zazueta-Beltrán , Roberto Andrés González-Fimbres ; Luis Felipe Reynoso-Sánchez *1-10
Journal Bibliographic Information:
Title: International Journal of Sport Studies for Health
Abbreviated Title: Int J Sport Stud Health
Acronym: INTJSSH
Online ISSN: 2588-5782
Editor-in-Chief: Khadijeh Irandoust, Ph.D.
Publisher: KMAN Publication Inc.
Language: English
Email: intjssh@kmanpub.com