Designing an Interpretative Structural Model (ISM) of Fear Appeal Based Advertising in Selected Insurance Companies
Abstract
Objective: The performance of advertising with a fear appeal is negatively framed, warning against the non-use or application of a specific good or service, which may entail various risks including financial, social, and safety hazards for individuals.
Methodology: The objective of this study is to design an interpretive structural model of fear appeal-based advertising in selected insurance companies. The research method is descriptive and inferential. The research population includes marketing professionals, experts, elites, managers, and employees of insurance companies. The data collection tools are library research and interviews. For data analysis, the Interpretive Structural Modeling (ISM) method was utilized in the MICMAC software. This study examined the presentation of a fear appeal-based advertising model in selected insurance companies, resulting in the extraction of the final model.
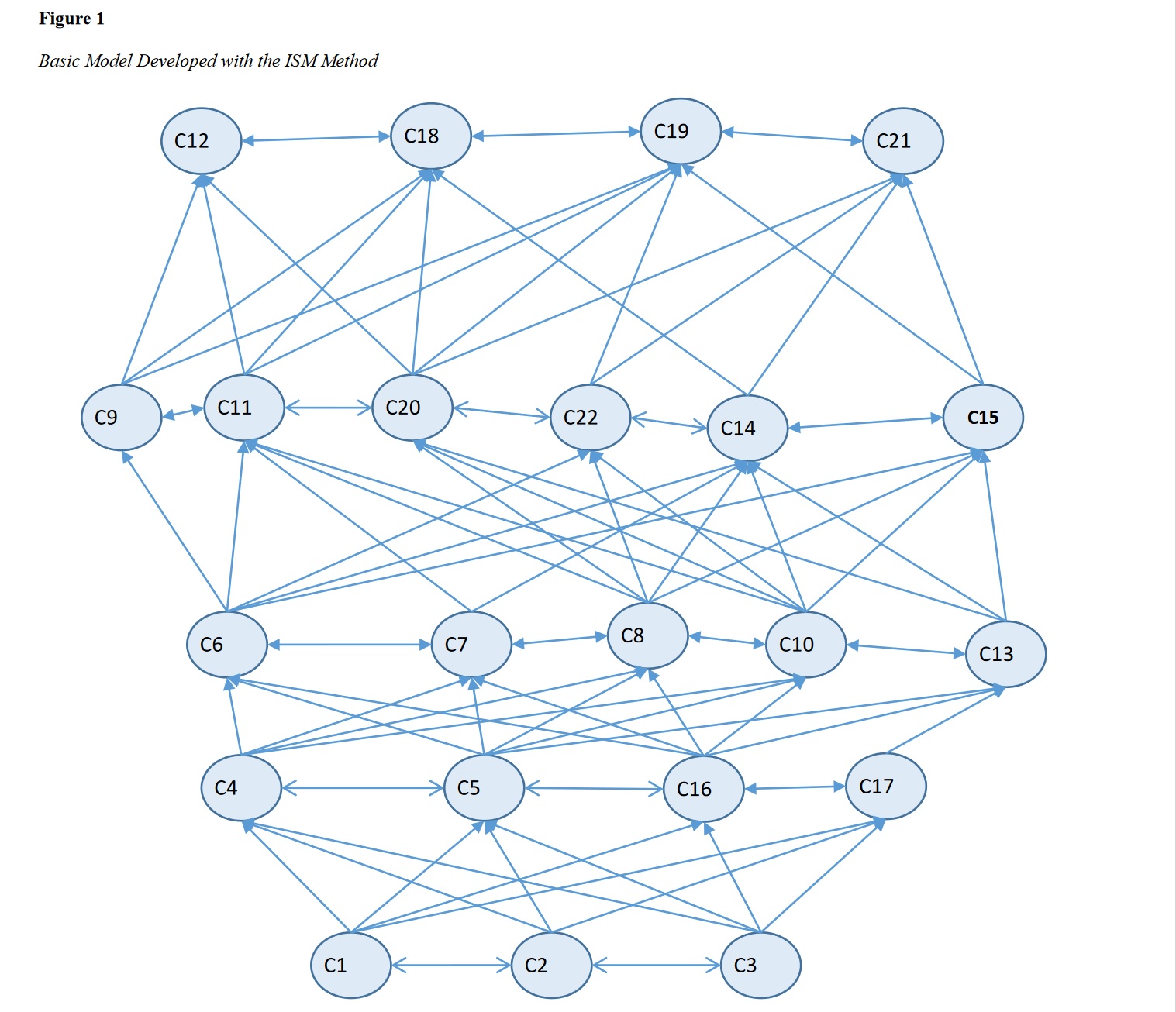
Findings: Based on the interpretive structural modeling technique, a 22-component model of fear appeal-based advertising in selected insurance companies has been designed.
Conclusion: According to the designed model, 5 consecutive levels are shown. By making changes to the variables at the lowest level, desirable results and outcomes can be observed in the upstream impact factors. Perceived benefits, peer groups, and advertising influence were identified at the lowest level and as the most influential components. Changing these three components can manage the higher level of the model and direct it towards increasing the effectiveness of marketing based on fear appeal for profitability.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Mohammad Sajad Rashidpour (Author); Alireza Pirhayati (Corresponding Author); Javad Niknafs , Mohammad Aidi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















