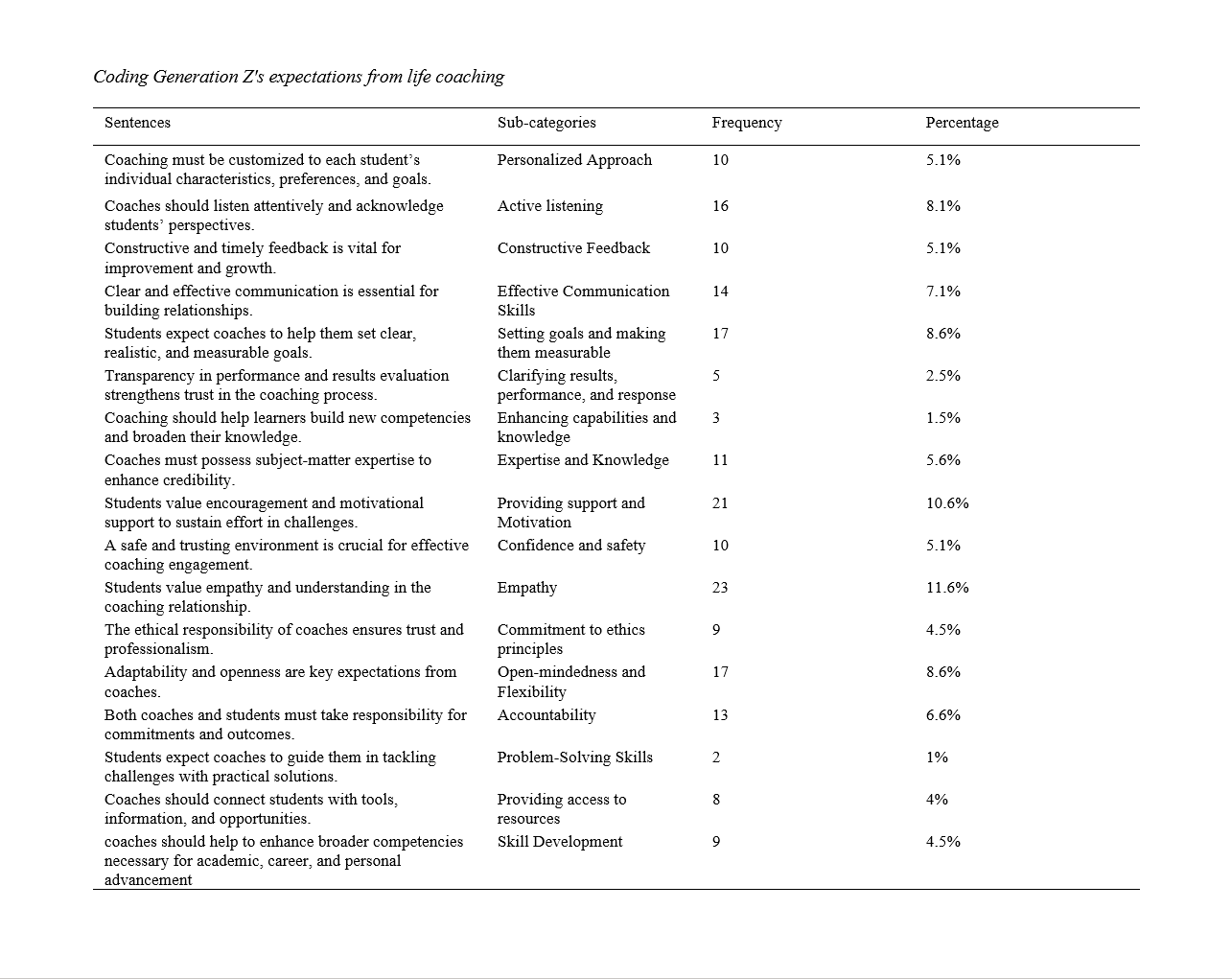
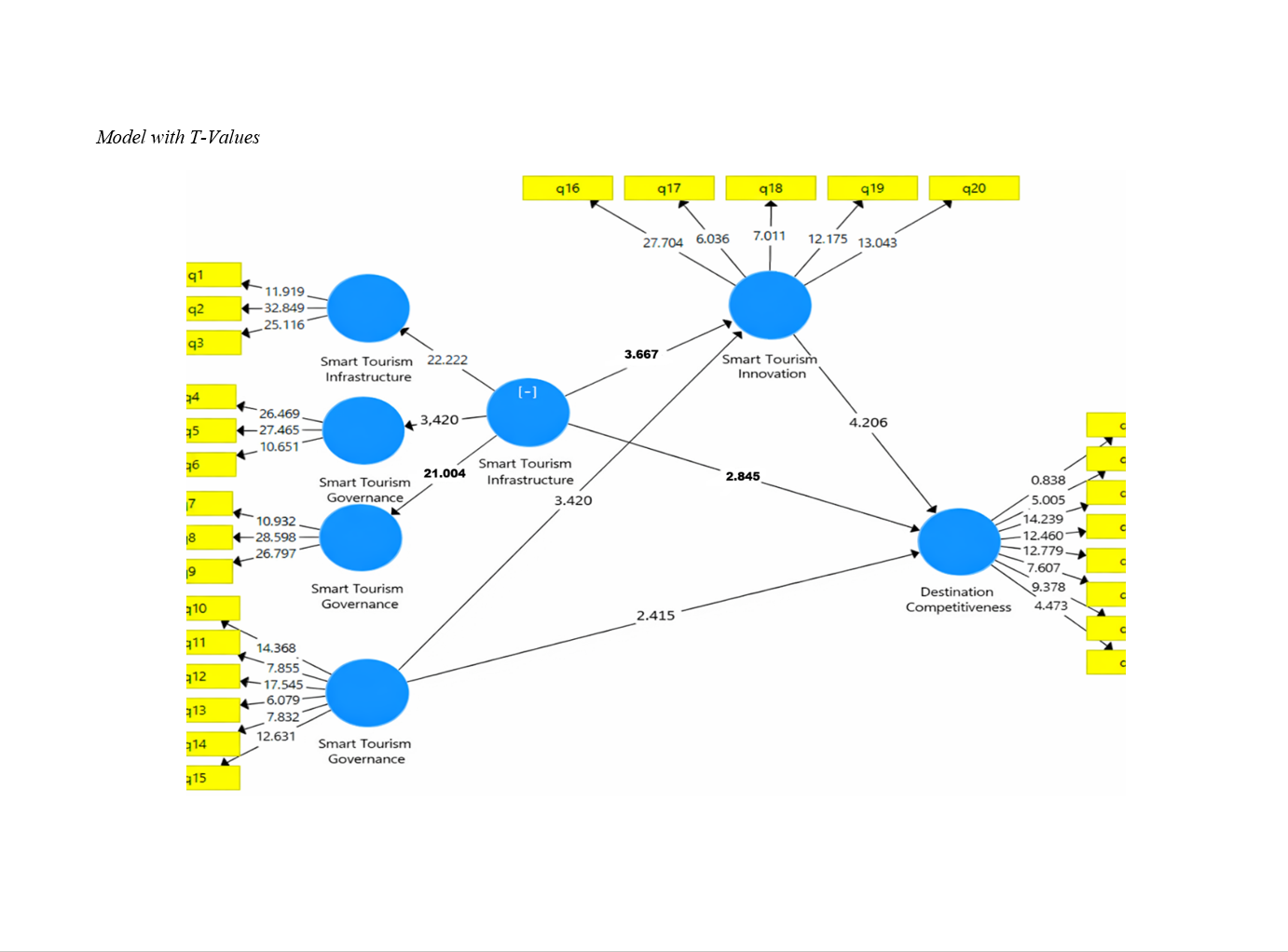
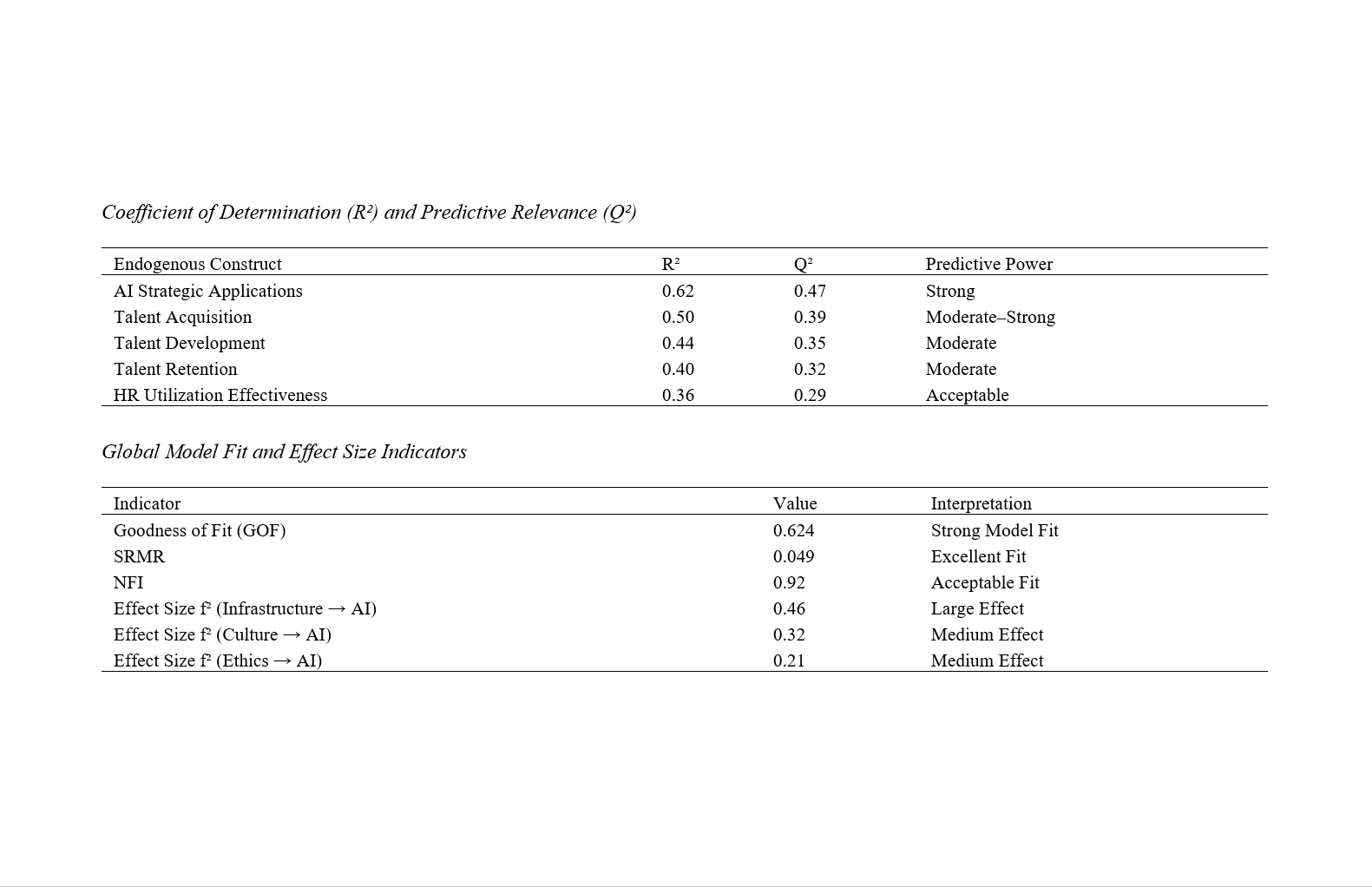
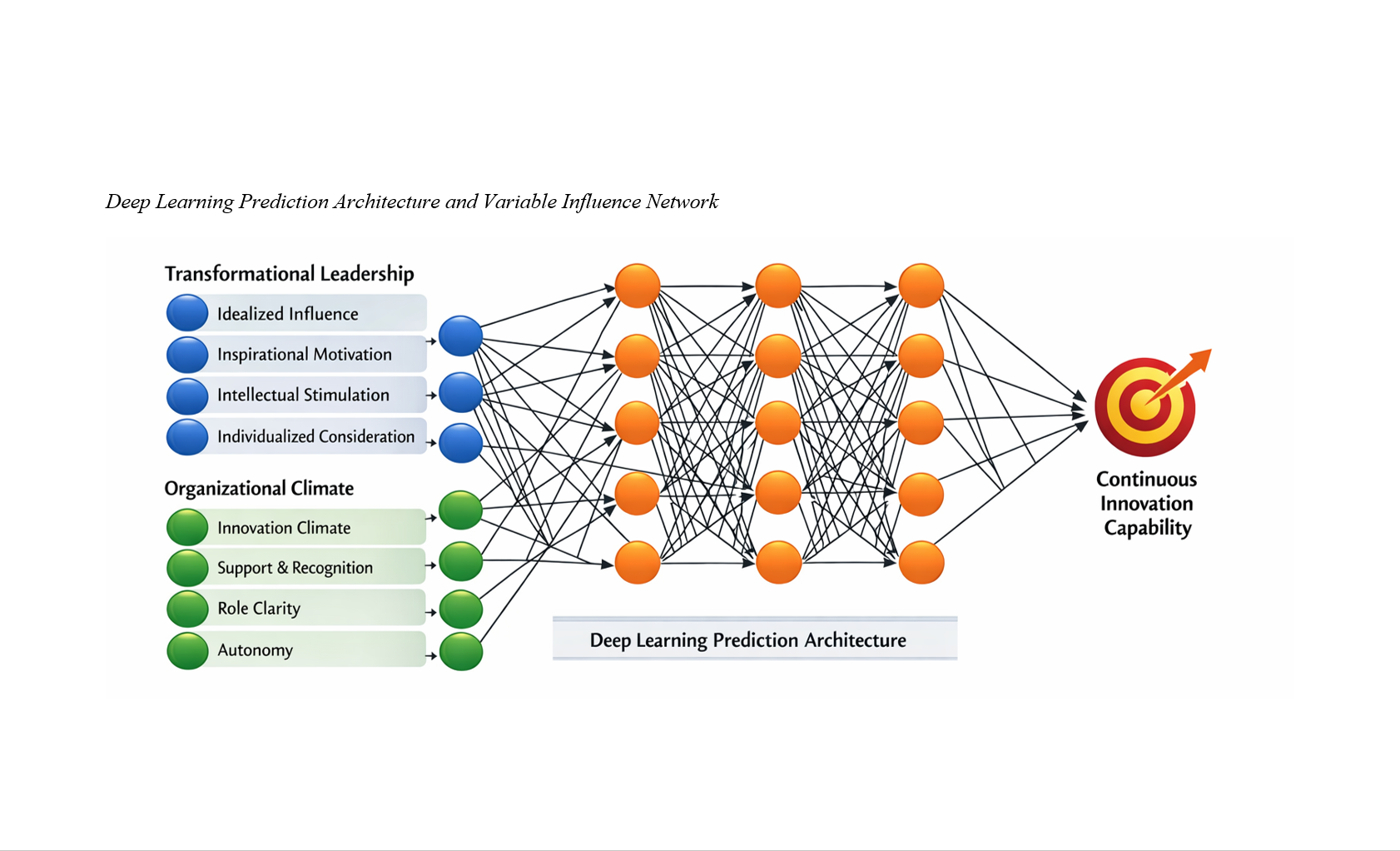
About the Journal
- ISSN: 3041-8992
- Director in Charge: Sepehr Khajeh Naeini
- Editor-in-chief: Dr. Yus Nugraha
- Owner: KMAN Research Institute
- Publisher: KMAN Publication Inc. (KMANPUB)
- Email: ijimob@kmanpub.com / journalimobs@gmail.com
- Open Access: YES
International Journal of Innovation Management and Organizational Behavior (IJIMOB) is a scientific open access peer-reviewed journal. The primary purpose of the International Journal of Innovation Management and Organizational Behavior (IJIMOB) is to publish scholarly research articles in the fields of Management and Organizational Behavior. As an official journal of the KMANPUB, the IJIMOB is recognized as an instrument for projecting and supporting the goals and objectives of this organization, which include scholarly research and the free exchange of ideas. IJIMOB appreciates original articles, review articles, short-papers, and conceptual papers research on all aspects of Innovation Management and Organizational Behavior.
About the Publisher
Publisher: KMAN Publication Inc.
Publisher Office: Unit 5‑10825 Yonge St, Richmond Hill, Ontario, Canada, L4C 3E3
https://journals.kmanpub.com
Email: kmanpu@kmanpub.com
Telegram: +1 (647) 656‑4401 | WhatsApp: +1 (437) 429‑3507
Germany Office: Dratelnstrasse, Wohnung A60, 21119 Hamburg, Germany (+4915207720487)
Current Issue