Evaluation of the Judicial Human Resources Productivity Model Using Structural Equations
Keywords:
Human Resources Productivity, Judges, Judiciary, Human Resource ManagementAbstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to evaluate the judicial human resources productivity model using structural equations.
Methodology: This study utilized a quantitative-survey method with an applied objective. The statistical population included judges from across the country, with a sample size of 88 individuals selected randomly. The research instrument was a researcher-made questionnaire based on qualitative findings and literature. The instrument's validity was established through face validity, and its reliability was confirmed with a Cronbach's alpha of 0.90. Data analysis was performed using structural equation modeling (confirmatory factor analysis) with the Smart-PLSv3 software.
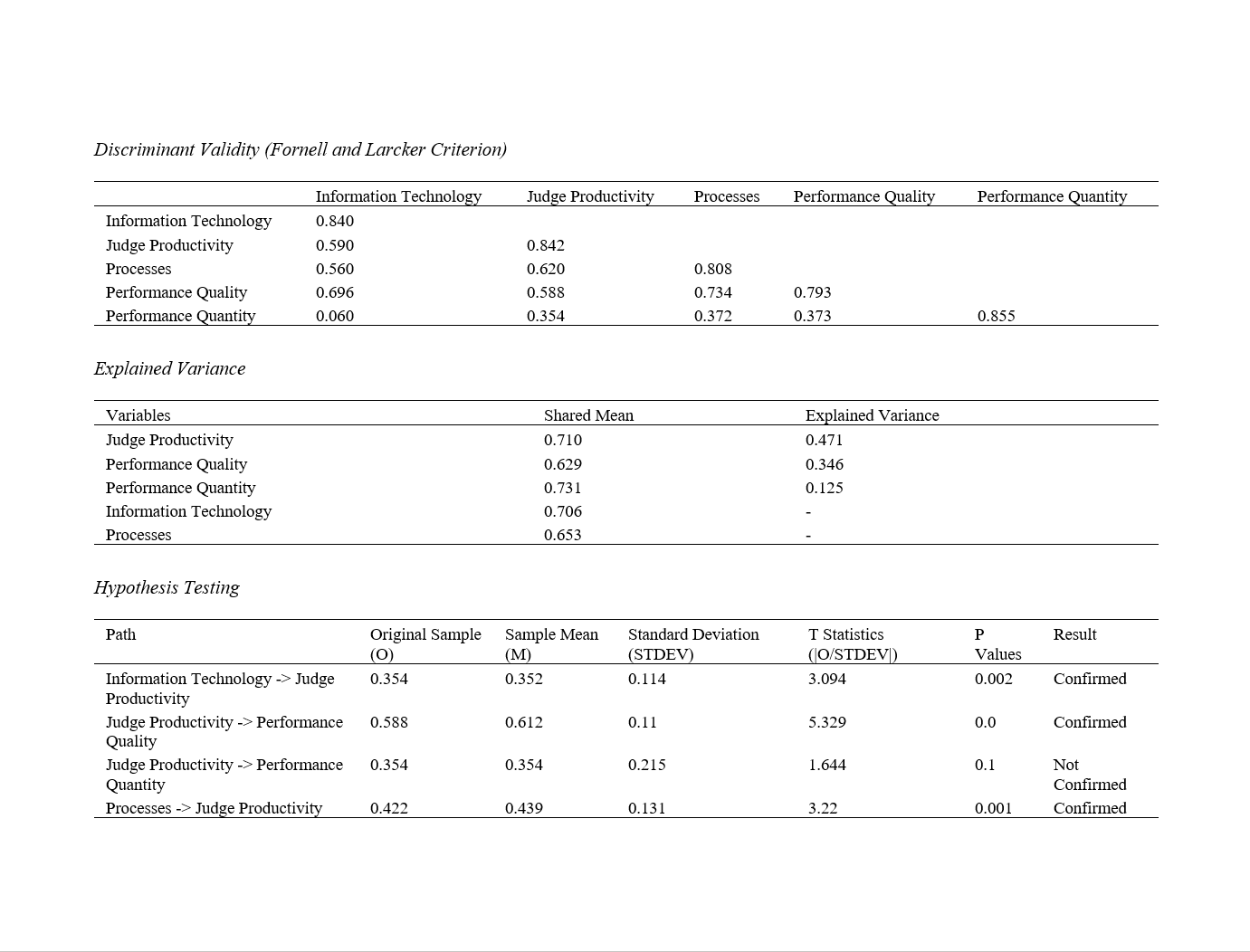
Findings: The results indicated that organizational processes, with a coefficient of 0.422, had the greatest impact on judges' productivity, followed by information technology, with a coefficient of 0.354. Additionally, performance quality (0.588) had a significantly greater impact on judges' productivity compared to performance quantity (0.354), approximately 1.7 times more. It was determined that the factor loading of performance quality was approximately 2.8 times greater than that of performance quantity. Furthermore, the results showed that the explained variance of the productivity variable as the dependent (mediating) variable of this study was 47%. This means that the independent variables of the study collectively explained 47% of the changes in the judges' productivity variable.
Conclusion: It can be concluded that to enhance the productivity of the country's judges, it is essential to focus on the highly impactful variables of organizational processes and information technology, as this can improve the quality of judges' services.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Ali Mohamamd Hosseini, Rashid Zolfaghari Zaferani, Seyed Mahmoud Hashemi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















