Providing an Analytical Model of the Relationship Between Advertising Content Risks and Behavioral Intention in Social Networks
Keywords:
Advertising, Social Networks, Advertising RisksAbstract
Objective: The objective of this study is to examine how various risks affect consumers' reactions and purchase intentions in social media advertising.
Methodology: The research employed a mixed-method approach. Initially, Interpretive Structural Modeling (ISM) was used to identify relationships between risks, followed by Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) using SMART PLS to test these relationships quantitatively. Data were collected through a cross-sectional survey of social media users, and the relationships between identified risks were analyzed.
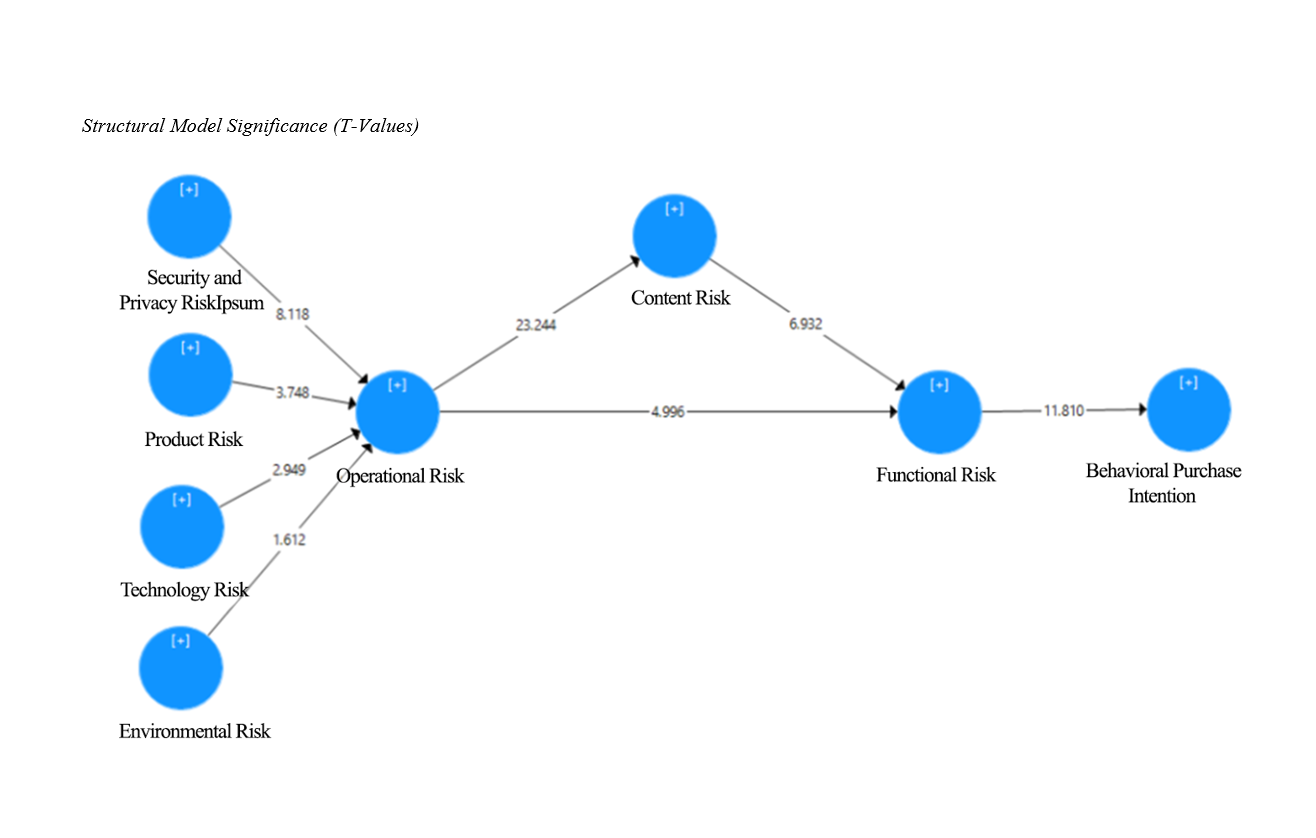
Findings: The results show that "environmental risk," "technology risk," "product risk," and "security and privacy risk" influence "operational risk." Moreover, operational risk positively affects "content risk," which in turn influences "functional risk." "Functional risk" negatively impacts consumers' behavioral intentions to purchase, while content risk undermines the credibility of ads, diminishing their perceived functionality and value. Findings support the theoretical literature on risks in online advertising and consumer behavior.
Conclusion: The study concludes that managing advertising risks, particularly content, functional, and operational risks, is crucial for enhancing consumer trust and purchase intentions. Marketers should focus on transparent ad content, secure payment systems, and addressing product information risks to mitigate the impact of these risks. Future research should explore additional variables, such as trust and commitment, to provide a more comprehensive understanding of risk perceptions in social media advertising.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















