Identifying the Components of Job Leaving Intention Among Faculty Members of Azad Universities in Fars Province
Keywords:
Job Turnover Intention, Faculty Members, Azad Universities, Fars ProvinceAbstract
Objective: In the contemporary era, having a capable workforce is considered a competitive advantage for universities, and the job turnover intention among faculty members is one of the fundamental challenges for universities. Accordingly, this study aimed to examine the job leaving intention among faculty members of Azad Universities in Fars Province.
Methodology: This research was an exploratory sequential mixed-methods study of the instrument development type. In the qualitative section, using purposive sampling and the theoretical saturation technique, 16 experts were selected for the study on job turnover intention among faculty members of Azad Universities in Fars Province. Initially, the main influencing indicators were extracted from the theoretical foundations and validated by experts using the fuzzy Delphi methodology. Since consensus among experts is the decision criterion in the Delphi method, the questionnaire was distributed and collected over three stages to achieve overall expert consensus on the classification. Then, using the matrix questionnaire and interpretive structural modeling technique distributed among specialists, the leveling of these factors was carried out.
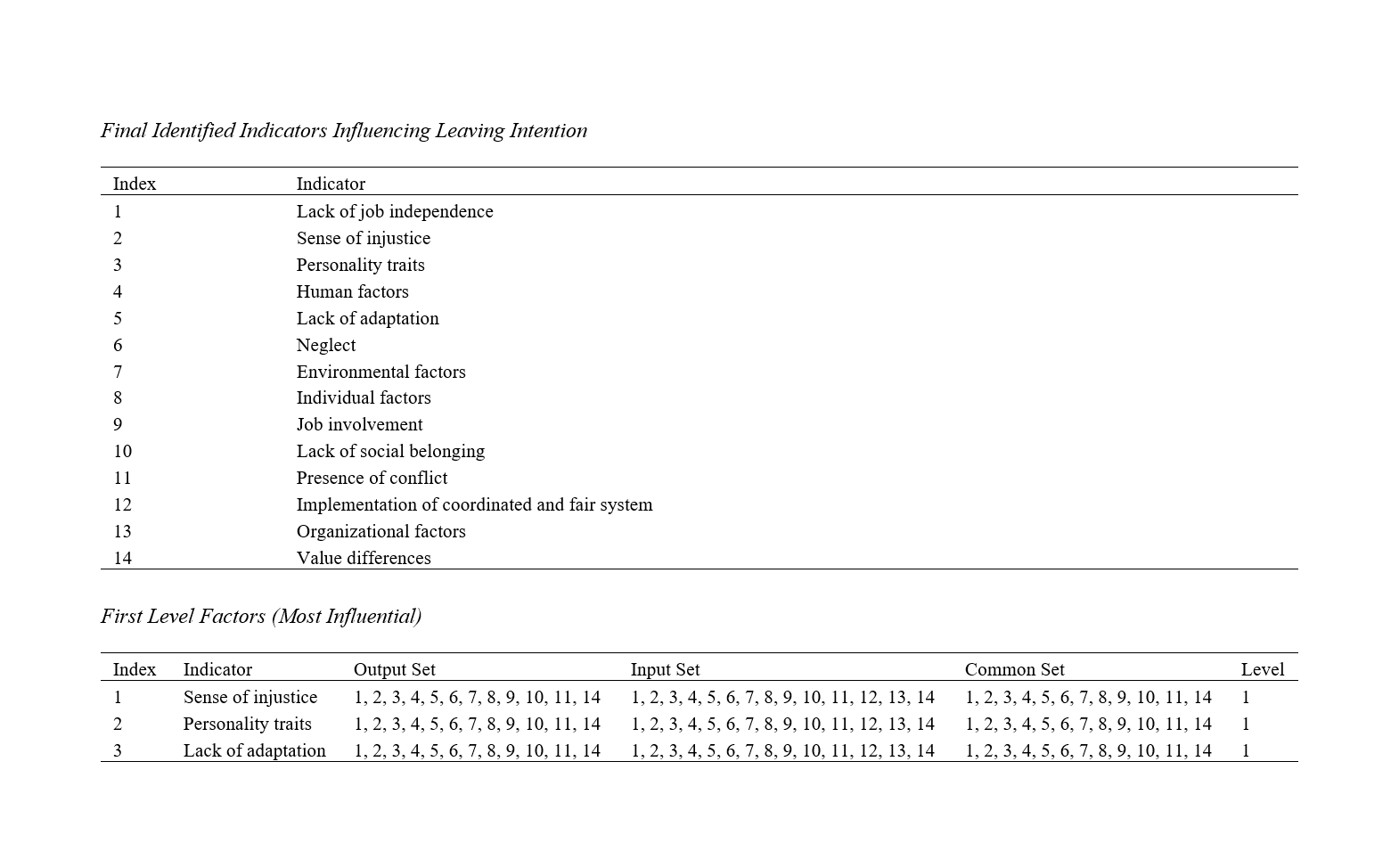
Findings: According to the obtained results, it is shown that ten factors pertain to the first level: a sense of injustice, personality traits, lack of adaptability, neglect, environmental factors, individual factors, job involvement, lack of social belonging, presence of conflict, and value differences. Additionally, two factors belong to the second level: organizational factors and human factors. The only factor related to the third level is the lack of employee work independence. The factor of non-implementation of a coordinated and fair system remains in the model and pertains to the fourth level of the model.
Conclusion: It is recommended that attention to key dimensions such as organizational empathy, participative management, understanding employees in the workplace, attention to their individual issues and problems, addressing their demands, understanding discriminations, striving to reduce them, and focusing on positive psychology can contribute to organizational growth and excellence. This can lead to reducing or eliminating the adverse effects of job turnover intention, such as increasing intra-organizational conflicts, tensions, lack of organizational participation, secrecy, job abandonment, and damage to organizational performance.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Mohammad Rahsar (Author); Alireza Ghasemizad (Corresponding Author); Pari Mashayekh, Amin Bagheri Karachi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















