Machine Learning Identification of Innovation Bottlenecks: A Behavioral Analytics Approach Using Gradient Boosting Models
Keywords:
Innovation bottlenecks, behavioral analytics, organizational behavior, leadership, psychological safety, innovation managementAbstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to develop and validate a machine learning–based behavioral analytics framework for identifying organizational innovation bottlenecks through the interaction of leadership, psychological, and behavioral factors.
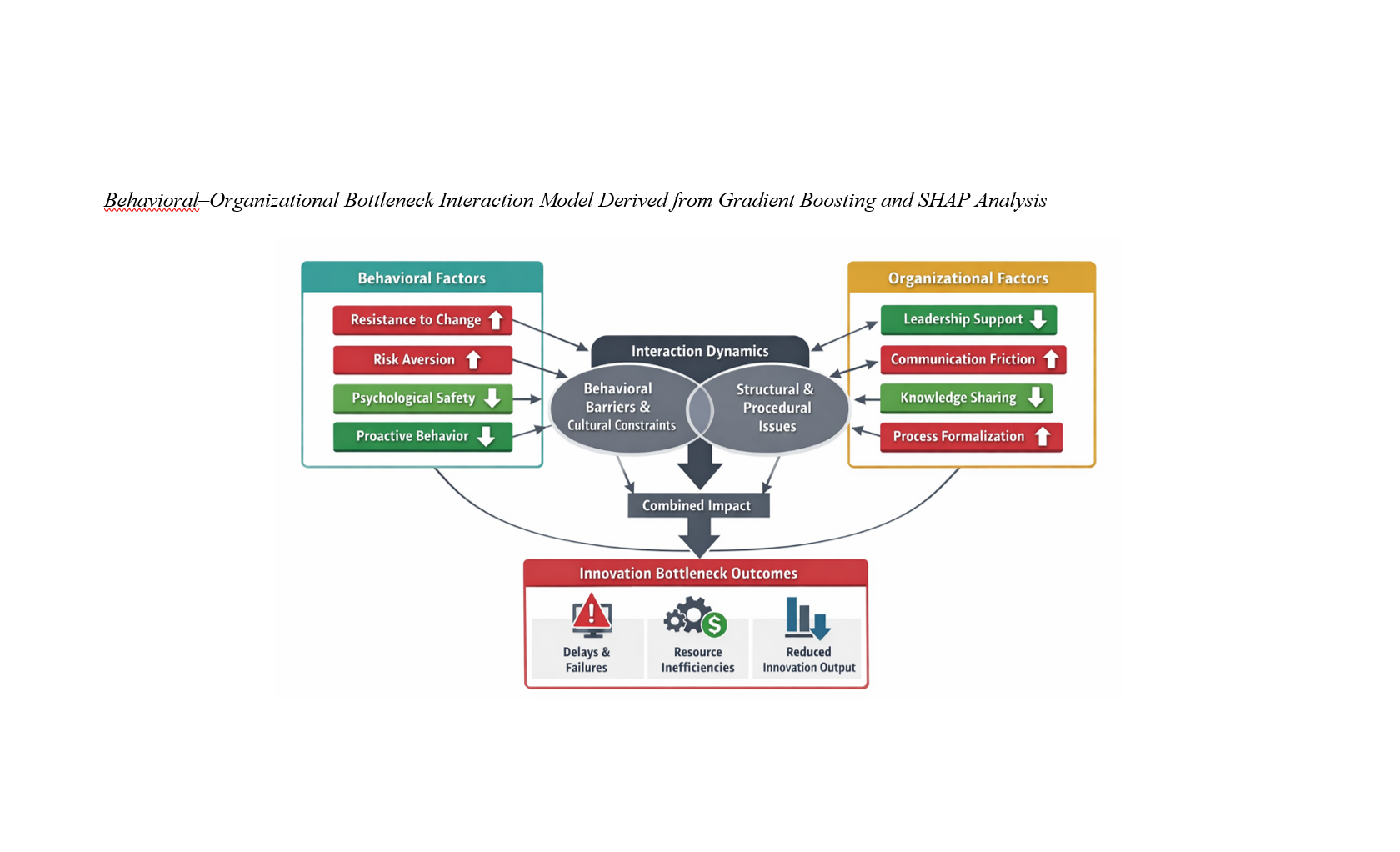
Methods and Materials: This study employed a cross-sectional explanatory design involving 547 employees and middle-level managers from diverse organizations in Georgia. Data were collected using validated behavioral, psychological, and organizational measures capturing resistance to change, psychological safety, leadership support, communication friction, knowledge sharing, learning orientation, and innovation outcomes. Organizational performance indicators were integrated with survey data to enhance behavioral signal extraction. Gradient boosting algorithms (XGBoost, LightGBM, CatBoost) and an optimized ensemble model were implemented using five-fold cross-validation and Bayesian hyperparameter tuning. Feature engineering and explainable artificial intelligence techniques (SHAP values) were applied to uncover the relative importance and interaction effects of predictors.
Findings: The ensemble model demonstrated strong predictive performance (R² = 0.846, RMSE = 0.387), explaining nearly 85% of the variance in innovation bottleneck intensity. Resistance to change was the strongest positive predictor, while leadership support for innovation, psychological safety, knowledge sharing quality, and proactive behavior significantly reduced bottleneck severity. Communication friction and excessive process formalization amplified innovation constraints. Behavioral segmentation revealed four distinct innovation profiles, with “Resistant Traditionalists” exhibiting the highest bottleneck levels and “Adaptive Innovators” the lowest.
Conclusion: The findings confirm that innovation bottlenecks are systemic behavioral–organizational phenomena emerging from complex non-linear interactions among leadership dynamics, employee psychology, communication structures, and organizational culture.
Downloads
References
Acar, O. A., Tunçdoğan, A., Knippenberg, D. v., & Lakhani, K. R. (2023). Collective Creativity and Innovation: An Interdisciplinary Review, Integration, and Research Agenda. Journal of Management, 50(6), 2119-2151. https://doi.org/10.1177/01492063231212416
Ahmad, T., Hamid, A. R., Abbas, A., Anwar, A., Ekowati, D., Fenitra, R. M., & Suhariadi, F. (2023). Empowering Leadership: Role of organizational Culture Of self-Esteem and Emotional Intelligence on Creativity. The Journal of Management Development, 42(3), 201-214. https://doi.org/10.1108/jmd-10-2021-0288
Alshahrani, M. A., Yaqub, M. Z., Ali, M., Hakimi, I. E., & Salam, M. A. (2025). Could Entrepreneurial Leadership Promote Employees’ IWB? The Roles of Intrinsic Motivation, Creative Self-Efficacy and Firms’ Innovation Climate. International Journal of Innovation Science. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijis-08-2024-0211
Bamel, N., Kumar, S., Bamel, U., Lim, W. M., & Sureka, R. (2022). The State of the Art of Innovation Management: Insights From a Retrospective Review of the European Journal of Innovation Management. European Journal of Innovation Management, 27(3), 825-850. https://doi.org/10.1108/ejim-07-2022-0361
Barkova, K. (2025). Evaluating the Effectiveness of Team Building in Leadership and Human Resource Development. Actual Problems of Innovative Economy, 2025(3), 36-39. https://doi.org/10.36887/2524-0455-2025-3-7
Du, S., & Wang, J. (2022). The Employee Relationship Analysis on Innovation Behavior of New Ventures Under the Organizational Psychology and Culture. Frontiers in psychology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.804316
Fauzi, M. A. (2022). A Review of Knowledge Hiding in Team: Evaluation of Critical Research Streams. Team Performance Management, 28(5/6), 281-305. https://doi.org/10.1108/tpm-01-2022-0009
Huang, Z., Sindakis, S., Aggarwal, S., & Thomas, L. (2022). The Role of Leadership in Collective Creativity and Innovation: Examining Academic Research and Development Environments. Frontiers in psychology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1060412
Javed, A., Khoso, R. A., & Nadeem, A. (2025). Servant Leadership and Its Role in Promoting Organizational Citizenship Behaviour, Employee Wellbeing, and Workplace Trust in Service-Oriented Industries. Ijss, 4(3), 249-261. https://doi.org/10.63544/ijss.v4i3.163
Najafi, Z., Hoseini, A. S. S., Imanipour, M., & Mosadeghrad, A. M. (2022). Factors Affecting Nurses' Retention in Iranian Hospitals. Journal of nursing management, 30(3), 785-794. https://doi.org/10.1111/jonm.13568
Naseem, W., & Khan, A. B. (2024). Evaluating the Impact of Behavioral Stress on Employee Productivity and Innovation in the Higher Education Sector of Pakistan. Bbe, 13(3), 219-229. https://doi.org/10.61506/01.00477
Shahid, M., Chaudhry, S. A., Bilal, M., Amber, H., Aslam, S., Malik, S., & Shahzad, K. (2022). The Link Between Team Identification, Entrepreneurial Orientation, and Innovative Work Behavior and Its Dimensions in the Context of Pakistan. Sage Open, 12(1). https://doi.org/10.1177/21582440221079893
Song, W., Ma, Y., Fan, X., Jin, X., & Peng, X. (2024). Servant Leadership, Workplace Well‐being and Employee Creativity: The Roles of Psychological Availability and Experienced Creative Time Pressure. Creativity and Innovation Management, 33(3), 399-413. https://doi.org/10.1111/caim.12595
Supriyanto, A. S., Ekowati, V. M., Rokhman, W., Ahamed, F., Munir, M., & Miranti, T. (2023). Empowerment Leadership as a Predictor of the Organizational Innovation in Higher Education. International Journal of Professional Business Review, 8(2), e01538. https://doi.org/10.26668/businessreview/2023.v8i2.1538
Takeed, Z., Ali, M. D., Shah, S. I., Muhammad, A., & Qiu, S. (2025). The Effect of Entrepreneurial Leadership on Innovative Work Behavior: The Mediating Roles of Creative Self-Efficacy and Organizational Learning. Journal of Entrepreneurship in Emerging Economies, 17(5), 1288-1310. https://doi.org/10.1108/jeee-08-2024-0326
Udin, U. (2025). Paradoxical Leadership: A Bibliometric Analysis and Research Agenda. Discover Sustainability, 6(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43621-025-01490-5
V, D. K. (2025). Managerial Influence on Employee Psychological Safety in High-Performance Teams. Lex Localis - Journal of Local Self-Government, 23(S6), 5413-5425. https://doi.org/10.52152/hqt0pq76
Verma, S., & Singh, V. (2022). Impact of Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Job Characteristics and Perceived Substitution Crisis on Innovative Work Behavior of Employees From High-Tech Firms. Computers in human Behavior, 131, 107215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2022.107215
Waheed, K. Z., & Khan, M. I. (2025). Fostering Innovative Work Behavior in New Product Development Projects: A Theoretical Review. Pakistan Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, 13(2), 479-495. https://doi.org/10.52131/pjhss.2025.v13i2.2884
Wang, X., & Lin, L. (2025). The Innovation Paradox in Human-Ai Symbiosis: Ambidextrous Effects of AI Technology Adoption on Innovative Behavior. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/frai.2025.1635246
Ye, J., & Liu, G. (2022). Analysis on the Development of Automation and Intelligence in China’s Manufacturing Industry—Taking R &Amp; D Collaboration Among Automobile Enterprises. Mobile Information Systems, 2022, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/6811605