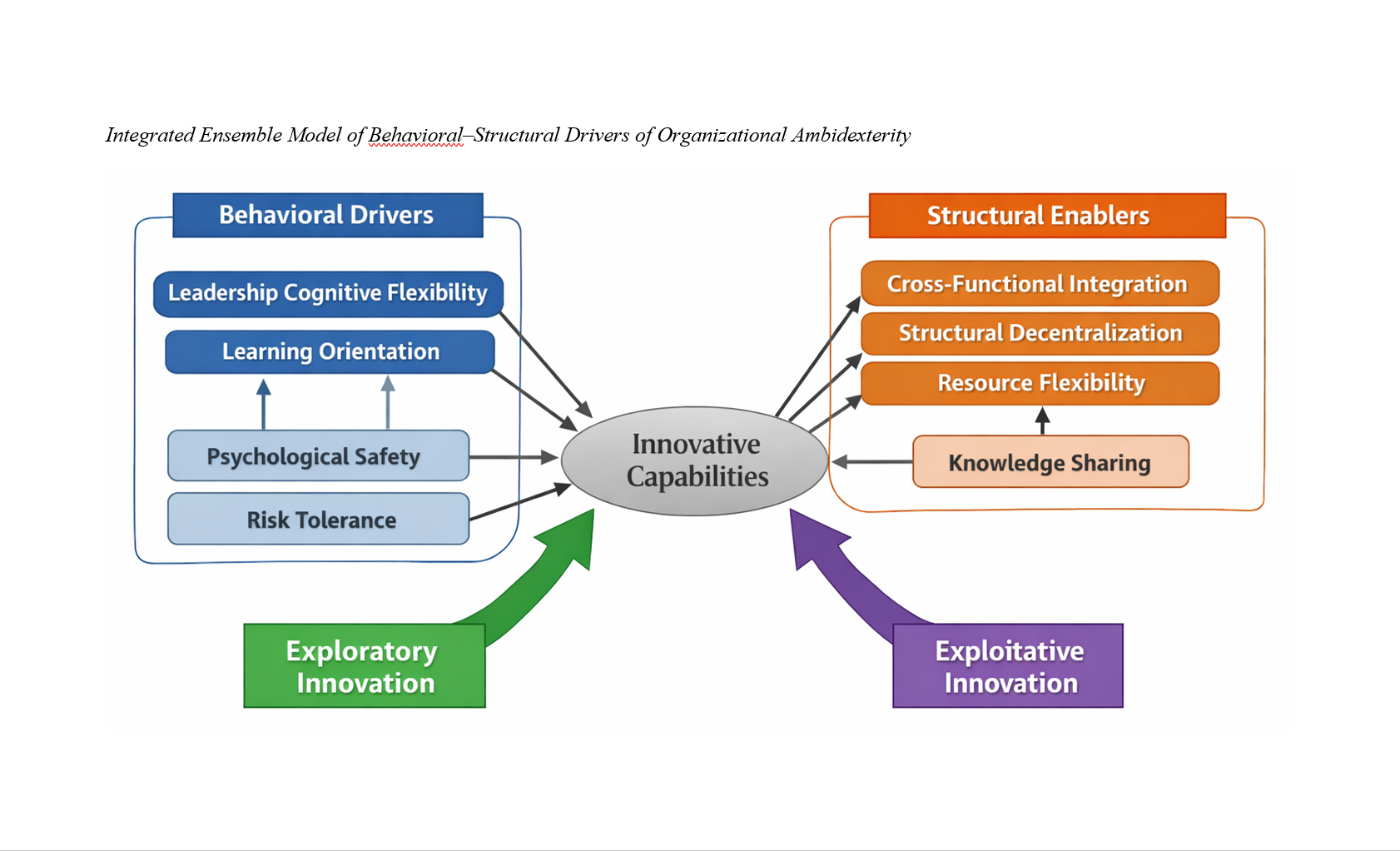
Modeling Organizational Ambidexterity through Ensemble Learning: Behavioral and Structural Predictors of Exploratory and Exploitative Innovation
Keywords:
organizational ambidexterity, ensemble learning, exploratory innovation, exploitative innovation, behavioral predictors, structural enablers, machine learning, innovation managementAbstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to model organizational ambidexterity by applying ensemble machine learning techniques to identify the behavioral and structural predictors of exploratory and exploitative innovation.
Methods and Materials: This explanatory study employed a cross-sectional design involving 487 middle- and senior-level managers from medium and large organizations across major industries in Chile. Data were collected using validated instruments measuring leadership cognitive flexibility, learning orientation, psychological safety, risk tolerance, cross-functional integration, decentralization, resource flexibility, knowledge-sharing systems, and dual innovation outcomes. The analytical framework integrated traditional statistical validation with an ensemble learning architecture composed of Random Forest, Gradient Boosting, XGBoost, and Support Vector Regression models. Model training applied stratified sampling, five-fold cross-validation, and hyperparameter optimization, while performance was evaluated using R², RMSE, MAE, and explained variance. Explainable AI techniques based on SHAP were employed to interpret nonlinear relationships and predictor contributions.
Findings: The ensemble model demonstrated superior predictive performance for both exploratory innovation (R² = 0.81, RMSE = 0.25) and exploitative innovation (R² = 0.84, RMSE = 0.22), significantly outperforming individual machine learning algorithms. Leadership cognitive flexibility and learning orientation emerged as the strongest predictors of exploratory innovation, whereas cross-functional integration and structural decentralization exerted the greatest influence on exploitative innovation. Psychological safety, risk tolerance, knowledge sharing, and resource flexibility contributed significantly to both innovation dimensions, with SHAP analysis revealing asymmetric and nonlinear interaction effects across predictors.
Conclusion: The results confirm that organizational ambidexterity is a systemic, nonlinear phenomenon driven by the dynamic interaction of behavioral and structural factors and that ensemble learning provides a powerful methodological approach for modeling this complexity, offering both theoretical advancement and practical guidance for innovation management.
Downloads
References
Abdulzahra, Q. F. (2024). Ambidextrous Leadership and Its Impact on Organizational Ambidexterity: Exploratory Study in General Company for Ports of Iraq. Muthanna Journal of Administrative and Economics Sciences, 14(1), 103-117. https://doi.org/10.52113/6/2024-14-1/103-117
Alshiha, A. A., Alkhozaim, S. M., Alnasser, E. M., Khairy, H. A., & Al‐Romeedy, B. S. (2024). Psychological Empowerment and Employee Resilience in Travel Agencies and Hotels. Tourism Review, 80(7), 1394-1412. https://doi.org/10.1108/tr-03-2024-0208
Cahilo, S. D., Limos-Galay, J. A., & Tampol, R. A. (2023). Antecedents of Motivation, Job Satisfaction and Organizational Citizenship Behavior of Contract of Service Employees in SAMARICA: A Basis for Human Resource Intervention. International Journal of Research Studies in Management, 11(1). https://doi.org/10.5861/ijrsm.2023.1004
Chen, C., & Zhang, D. (2022). How Innovation Types Affect Users' Continuous Knowledge Sharing Intention: A self-Determination Perspective. Aslib Journal of Information Management, 75(2), 297-317. https://doi.org/10.1108/ajim-12-2021-0386
Faraon, M., Rönkkö, K., Milrad, M., & Tsui, E. (2025). International Perspectives on Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education: An Explorative Study of Students’ Intention to Use ChatGPT Across the Nordic Countries and the USA. Education and Information Technologies, 30(13), 17835-17880. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-025-13492-x
Hill, J., Kim, M., Oja, B. D., Kim, H. S., & Lee, H. W. (2023). Innovation Is the Key: Identifying Factors to Increase Career Satisfaction and Psychological Well-Being in Millennial and Generation Z Sport Employees. Sport Business and Management an International Journal, 14(3), 360-379. https://doi.org/10.1108/sbm-05-2023-0064
Iman, N. (2025). Balancing Order and Entropy: The Role of Innovation and Organizational Disorder in Performance Across Startups and Banking. International Journal of Innovation Science. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijis-03-2025-0142
Li, K., Wijaya, T. T., Chen, X., & Harahap, M. S. (2024). Exploring the Factors Affecting Elementary Mathematics Teachers’ Innovative Behavior: An Integration of Social Cognitive Theory. Scientific reports, 14(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-52604-4
Lin, C. Y. C., Hu, S., & Chiu, C. K. (2025). Achieving Job Performance Through Agility and Innovativeness by Strategizing Learning Ambidexterity. Journal of managerial psychology, 40(7), 999-1015. https://doi.org/10.1108/jmp-12-2023-0752
Maluche, R. B. P., & Orozco, L. A. (2023). Organizational Innovation and Business Model Innovation: Bridges From a Systematic Literature Review. International Journal of Innovation Science, 16(3), 596-613. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijis-08-2022-0143
Mehralian, G., Akhavan, P., Jansen, J. J., & Pak, J. (2025). Improvising for Learning: How and When Firm‐Level HRM Systems Drive Team Exploratory and Exploitative Learning. Human Resource Management. https://doi.org/10.1002/hrm.70026
Peyravi, B., & Jakubavičius, A. (2022). Drivers in the Eco-Innovation Road to the Circular Economy: Organiational Capabilities and Exploitative Strategies. Sustainability, 14(17), 10748. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710748
SİYahtaŞ, A., & Çakır, V. O. (2025). The Relationship Between Leisure Satisfaction and Individual Innovativeness Behavior: A Study of Young Individuals. Asr Chiang Mai University Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities, 12(2). https://doi.org/10.12982/cmujasr.2025.014
Sofwan, M., Habibi, A., Attar, R. W., Alqahtani, T. M., Alahmari, S. A., & Alhazmi, A. H. (2024). Factors Affecting Teachers’ Behavior of Innovative Teaching With Technology: Structural Equation Modelling. Sustainability, 16(19), 8496. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16198496
Taleb, M. A., Tantawi, P., Ragheb, M., & Amara, D. F. (2025). Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises’ Resilience to Socioeconomic Challenges in Emerging Economies: The Impact of Entrepreneurial Orientation on Organisational Ambidexterity. Socioeconomic Challenges, 9(2), 156-179. https://doi.org/10.61093/sec.9(2).156-179.2025
Tho, N. D., Trang, N. T. M., & Thu, N. N. (2025). Ambidextrous Leadership and Innovation Ambidexterity in a Business Function: The Role of Managers’ Psychological Capital and Proactive Personality. Journal of Knowledge Management, 29(5), 1446-1464. https://doi.org/10.1108/jkm-09-2024-1109
Wahid, M., & Ayub, N. (2024). Predictive Role of Psychological Capital and Perceived Organizational Support on Innovative Work Behavior Among Higher Education Teachers of Pakistan. Tuning Journal for Higher Education, 11(2), 191-219. https://doi.org/10.18543/tjhe.2715
Xie, J. (2025). Social Psychological Drivers of Environmental Behavior: Impact on Operational Efficiency of an Electric Power Supply Company in Hebei. Environment and Social Psychology, 10(8). https://doi.org/10.59429/esp.v10i8.3955
Xu, Y., & Phanniphong, K. (2025). The Impact of Organizational Commitment on Innovative Work Behavior in TCM Universities: A Social-Psychological Driving Mechanism Perspective. Environment and Social Psychology, 10(7). https://doi.org/10.59429/esp.v10i7.3882
Ye, B., Li, M., Ni, J., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Please Do Not Respond Asap: Impact of Workplace Telepressure on Employees’ Innovative Behavior in the Digital Era. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-6983834/v1
Zhang, J., Long, J., & Alexandra Martina Eugenie von, S. (2021). How Does Digital Transformation Improve Organizational Resilience?—Findings From PLS-SEM and fsQCA. Sustainability, 13(20), 11487. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132011487