Effectiveness of Lifestyle Modification Training on Psychological Symptoms and Self-Care in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
Objective: Diabetes is a disease that endangers the health of many individuals in society. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of lifestyle modification training on psychological symptoms and self-care in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods and Materials: The study employed a pre-test post-test design with experimental and control groups. The research population consisted of all patients with type 2 diabetes from the Diabetes Association and hospitals in Gilangharb province, in 2020. A total of 45 individuals (divided into a lifestyle modification intervention group and a control group) were selected using a convenience sampling method. Data were collected using the SCL-90-R and the Toobert and Glasgow Self-Care Questionnaires. Data were analyzed using multivariate and univariate analysis of covariance tests, as well as the LSD post hoc test, utilizing the SPSS software.
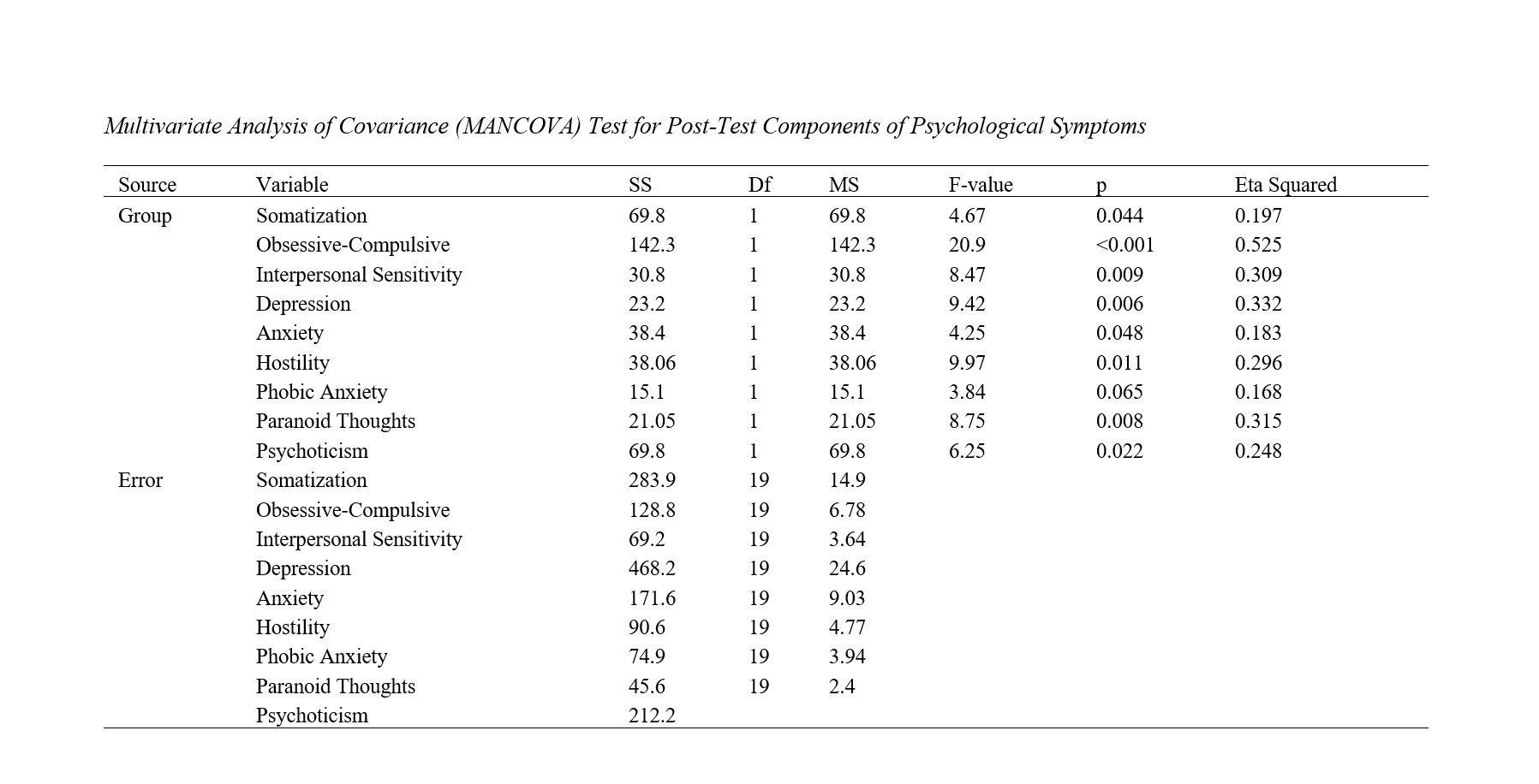
Findings: The results of the multivariate analysis of covariance indicated that after controlling for pre-test effects, F was significant at the 0.05 level for "psychological symptoms" components. In other words, there were significant differences in the post-test scores of these variables between the "experimental group" and the "control group". The results also showed differences between the two intervention groups and the control group in the self-care variable. Furthermore, the lifestyle modification training intervention was effective in components of psychological symptoms, including somatization, obsessive-compulsive, anxiety, aggression, phobia, paranoid ideation, and psychoticism dimensions.
Conclusion: It can be concluded that lifestyle modification training was effective in improving psychological symptoms and self-care in patients with type 2 diabetes, and this psychological approach can be used to improve the condition of patients with type 2 diabetes.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








