Designing a Skill-Based Education Model in Schools Based on the Real Needs of Society Using Grounded Theory
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to design an appropriate model in the field of skill-based education based on the real needs of society using grounded theory.
Methods and Materials: The method of this research is grounded theory with a qualitative approach. Data were analyzed using MaxQDA software. The sampling method was purposive, reaching saturation after conducting 10 interviews with professors and experts in the fields of educational management and skill-based education.
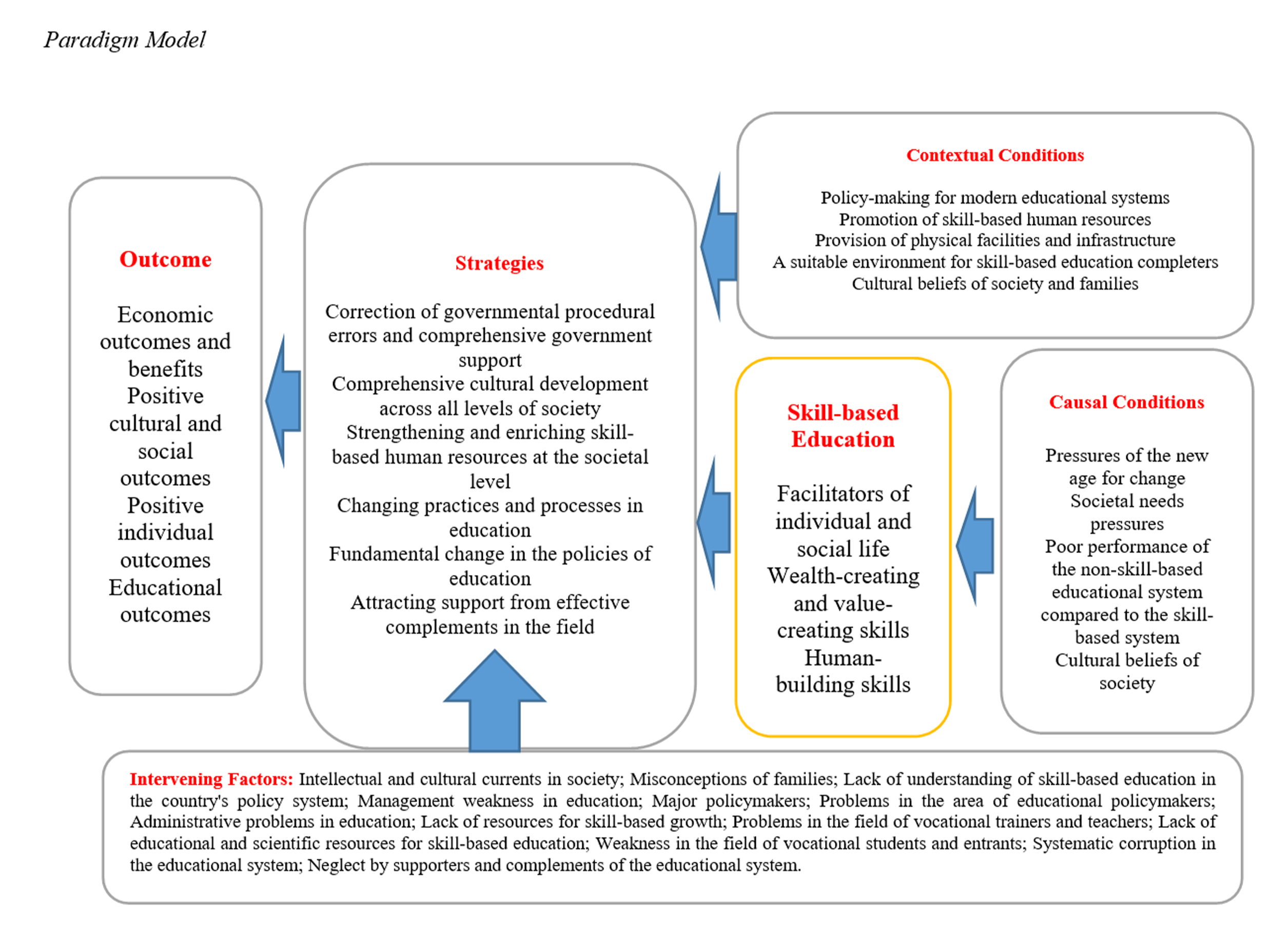
Findings: The research results showed that the central phenomenon of skill-based education consists of three components: facilitating personal and social life; value-creating and wealth-generating skills; and human-developing skills. The causal conditions of the research that lead to the phenomenon of the skill-based education model in schools based on the real needs of society were categorized into four groups: pressures of the new age for change; societal needs pressure; poor performance of the non-skill-based educational system compared to the skill-based system; and cultural beliefs of society. Contextual conditions consisted of five main components: policy-making for modern educational systems; enhancing skill-based human resources; providing physical facilities and infrastructure; suitable environment for skill-based education completers; and cultural beliefs of society and families.
Conclusion: Appropriate strategies for achieving skill-based education based on the real needs of society were categorized into six groups: correcting government's wrong processes and comprehensive government support; comprehensive culture-building at all levels of society; strengthening and enriching skill-based human resources at the societal level; changing procedures and processes in education; fundamental change in educational policies; and attracting support from effective supplements in the area. The outcomes of implementing these strategies were categorized into four components: economic outcomes and benefits; positive social and cultural outcomes; positive personal outcomes; and educational outcomes.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Atefeh Khosravirad (Author); Ahmad Akbari (Corresponding Author); Mohammad Karimi , Moslem Cherabin (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








