Investigating the Effectiveness of Motivational Interviewing on Social Anxiety and Academic Procrastination among Students
Abstract
Objective: The student period is an exciting and challenging time for students. During this period, due to facing more stress-inducing factors and the necessity for appropriate adaptation, all students must have greater mental health and self-reliance to achieve greater success in their studies and, ultimately, in their profession. This research aims to investigate the impact of motivational interviewing on social anxiety and academic procrastination among students of the Islamic Azad University, Saravan branch.
Methods and Materials: The research method is descriptive-analytical. The statistical population includes all students of the Islamic Azad University, Saravan branch. Forty individuals suffering from social anxiety and academic procrastination were selected via convenience sampling method and introduced as the statistical sample, randomly divided into two groups (each group containing 20 participants) for motivational interviewing and control. The experimental group received concepts and strategies of motivational interviewing by Rollnick and Miller (2002) in eight 70-minute sessions. Solomon and Rothblum's (1984) Academic Procrastination Questionnaire and Connor's (2000) Social Anxiety Questionnaire were used to collect data. Covariance analysis with pre-test statistical control was used to examine the hypotheses of this research.
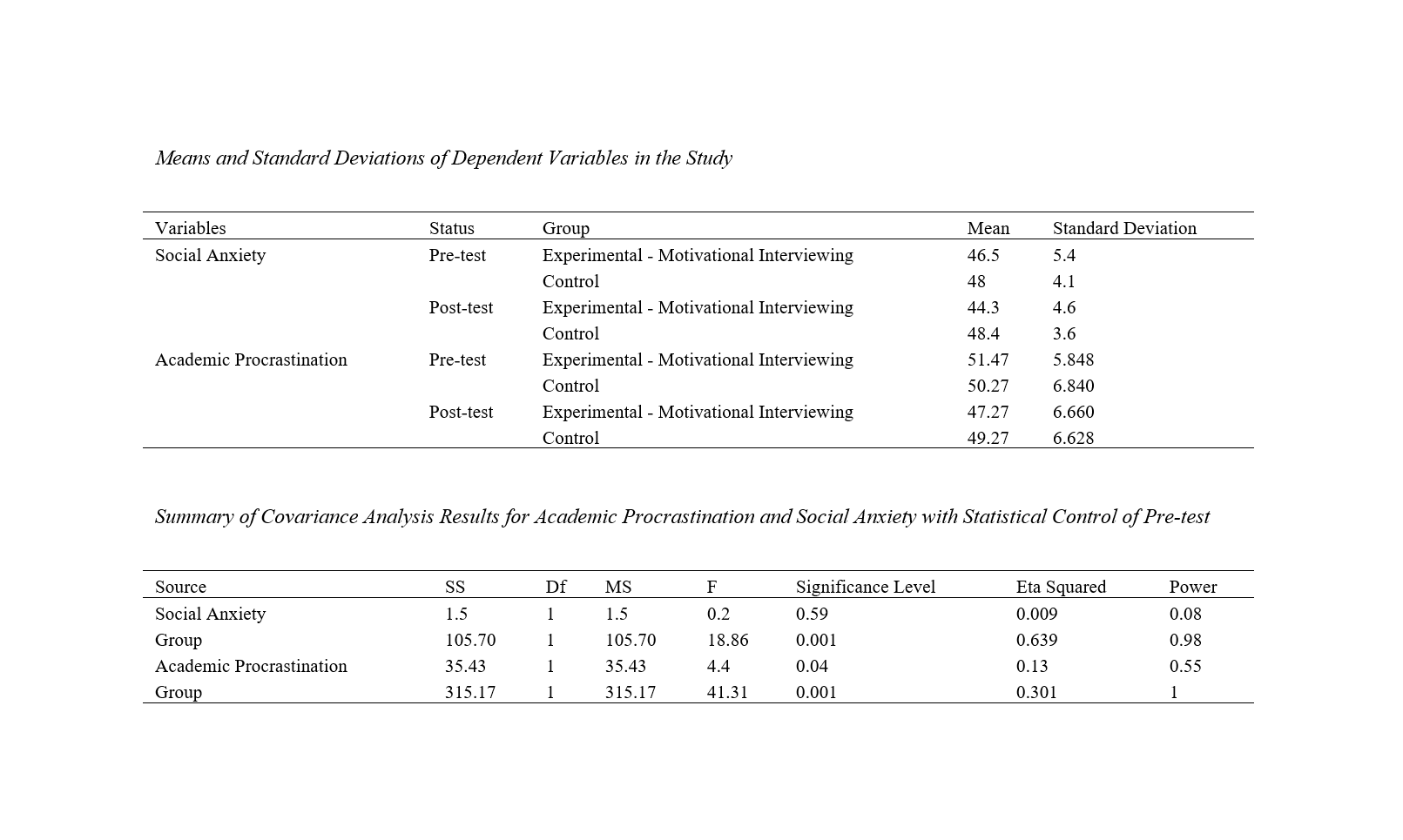
Findings: Based on the results, motivational interviewing explains 63.9% of the variance in post-test scores in the academic procrastination variable and 30.1% of the variance in post-test scores in the social anxiety variable.
Conclusion: Therefore, it can be concluded that motivational interviewing was effective on social anxiety and academic procrastination among students.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Abdolhamid Parsafar (Author); Ali Asghar Asgharnejad Farid (Corresponding Author); Fariborz Dortaj , Mehdi Zare Bahramabadi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








