Academic Performance Model Based on Academic Emotions and Academic Motivation with the Mediation of Emotional Intelligence in First Grade Secondary School Students in Tabriz City
Keywords:
Academic Performance, Academic Emotions, Academic Motivation, Emotional Intelligence, StudentsAbstract
Objective: One of the important groups in every country is students who play a significant role in shaping the future and the excellence of nations. Therefore, the purpose of the present study was to develop a model of academic performance based on academic emotions and academic motivation with the mediation of emotional intelligence in first-grade secondary school students in Tabriz city during the academic year 2024-2023.
Methods and Materials: This study is descriptive-correlational in terms of objective and quantitative in terms of approach. Structural equation modeling was used to evaluate the relationships between the current variables and the measured variables in the proposed conceptual model. The population of the present study included all first-grade secondary school students in Tabriz city during the academic year 2024-2023. To select the sample size, initially, 250 students from first-grade secondary school students in Tabriz city were selected using cluster random sampling method based on the Morgan formula, and then they responded to the Fam and Taylor (1990) academic performance progress questionnaire, Pakravan (2005) academic emotions questionnaire, Frederick, Blumenfield, Paris (2004) academic motivation questionnaire, and the adolescent version of Petrides and Furnham's emotional intelligence questionnaire (2006). The data were analyzed using Pearson correlation test and structural equation modeling through SPSS-26 and AMOS version 24 software.
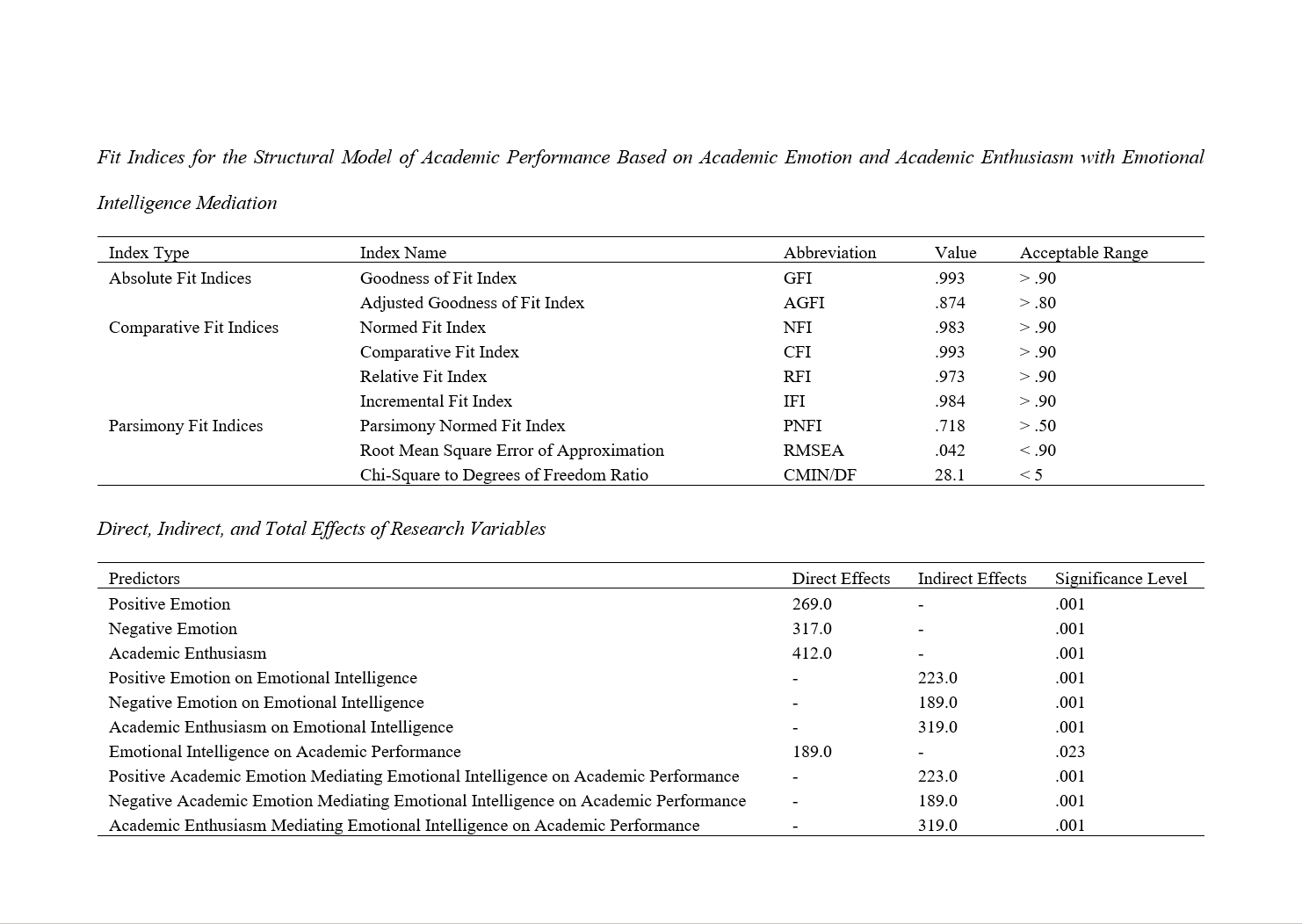
Findings: The results showed a positive indirect effect of academic emotions on academic performance through emotional intelligence (β = 0.223, p < .001). The negative indirect effect of academic emotions on academic performance through emotional intelligence was also significant (β = -0.189, p < .001). The indirect effect of academic motivation on academic performance through emotional intelligence was positive and significant (β = 0.319, p < .001).
Conclusion: Therefore, the results of the present study can be of interest to the education organization, teachers, and students.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Noushin Derakhshan, Roghayeh Poursabri (Author); Nahideh Yousefpour (Corresponding Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








