Examining the Fit of the Psychological Well-being Model of Adolescents Based on Attachment Styles with the Mediation of Emotion Regulation
Keywords:
psychological well-being, attachment styles, emotion regulationAbstract
Objective: Adolescence is a critical period of human development during which adolescents encounter numerous factors. This study aimed to examine the fit of the psychological well-being model of adolescents based on attachment styles, with the mediation of emotion regulation.
Methods and Materials: The research design was applied in nature, using a descriptive-correlational method with a structural modeling approach. The statistical population included all adolescents studying in the second secondary school level in Tehran during the 2020-2021 academic year. The sample consisted of 400 individuals selected from the research population using cluster sampling. The tools used in this study included the Psychological Well-being Questionnaire (Ryff, 1989), the Attachment Questionnaire (Collins & Read, 1990), and the Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Questionnaire (Gratz & Roemer, 2004). For data analysis, SPSS-24 software was used for descriptive statistics, and the AMOS-22 software was used for inferential statistical analyses to test and confirm or reject the hypotheses through structural equation modeling.
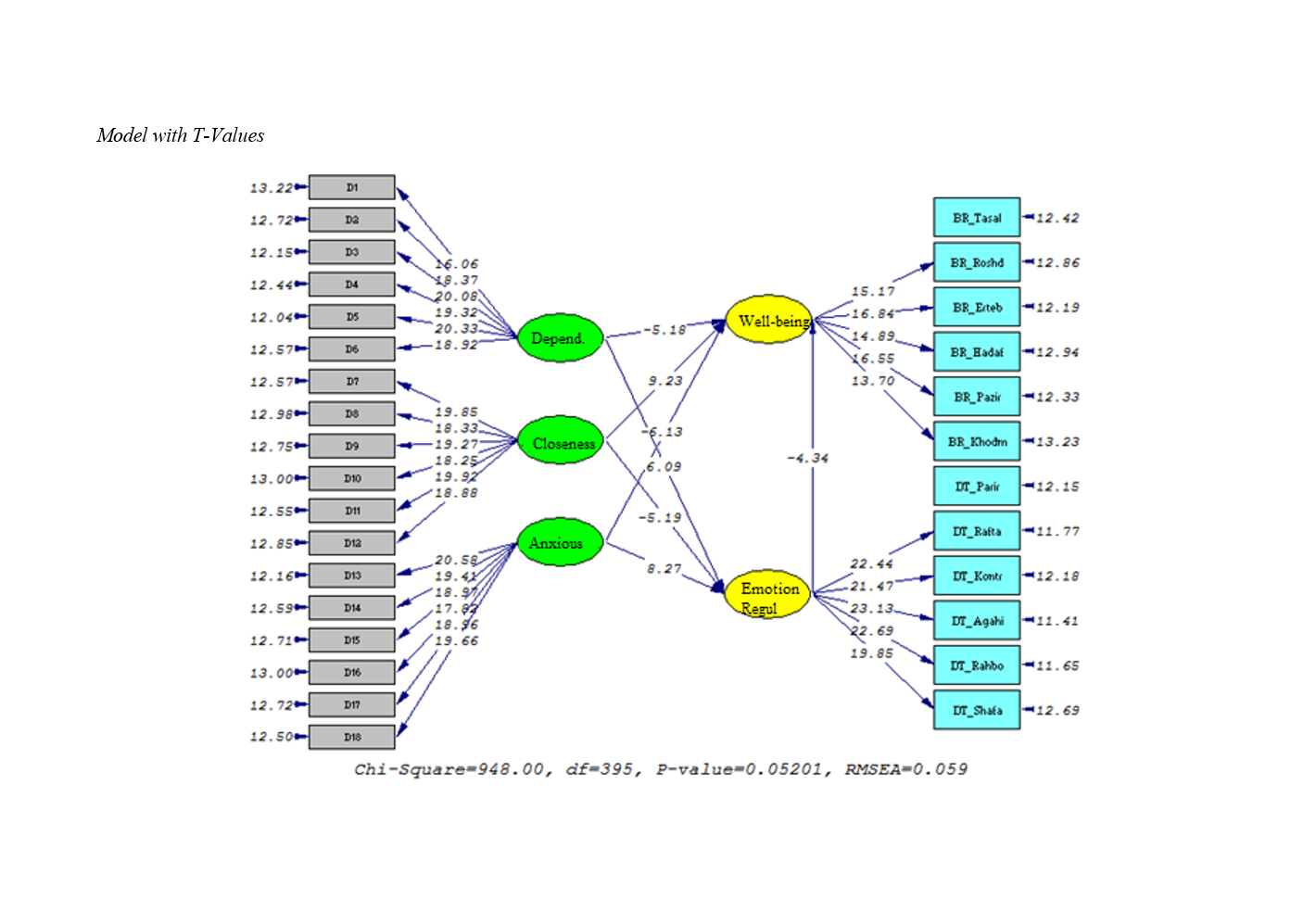
Findings: The findings indicated that, considering the chi-square and RMSEA criteria, the psychological well-being model of adolescents based on attachment styles, with the mediation of emotion regulation, provided a suitable fit to the data.
Conclusion: Emotion regulation mediates between psychological well-being and attachment style, meaning that attachment style can indirectly enhance psychological well-being by reducing emotional dysregulation.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Roja Khanizadeh (Author); Davood Taghvaei (Corresponding Author); Firoozeh Zanganeh Motlagh (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








