Examining the Causal Pattern of Cognitive emotion Regulation and Impulsiveness with the Mediating Role of Executive Functions, Working Memory, and Stress Coping Strategies in Female Students with Conduct Disorder
Keywords:
Cognitive emotion regulation, impulsiveness, executive functions, working memory, stress coping strategiesAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to examine the causal pattern of cognitive emotion regulation and impulsiveness with the mediating role of executive functions, working memory, and stress coping strategies in female students with conduct disorder.
Methods and Materials: This study can be examined from two perspectives: from the perspective of implementation method, it falls under descriptive research of a predictive correlational type, and from the perspective of purpose, it is considered applied research. The statistical population of this study included all first-year high school female students in the city of Kermanshah in the academic year 2022-2023, from which 200 individuals were selected as the sample. A simple random sampling method was used. In the data collection domain, both library and field methods were employed. In the field section, for collecting the necessary research information, the following questionnaires were used: Behavioral Problems of Quay and Peterson (2013), Emotion Regulation of Gross and John (2003), Impulsiveness of Barratt (1995), Behavioral Rating Inventory of Executive Functions of Gioia et al. (2000), Working Memory of Daneman and Carpenter (1980), and Coping Strategies of Moos and Billings (1981). Subsequently, SPSS22 and PLS statistical software were used for data analysis.
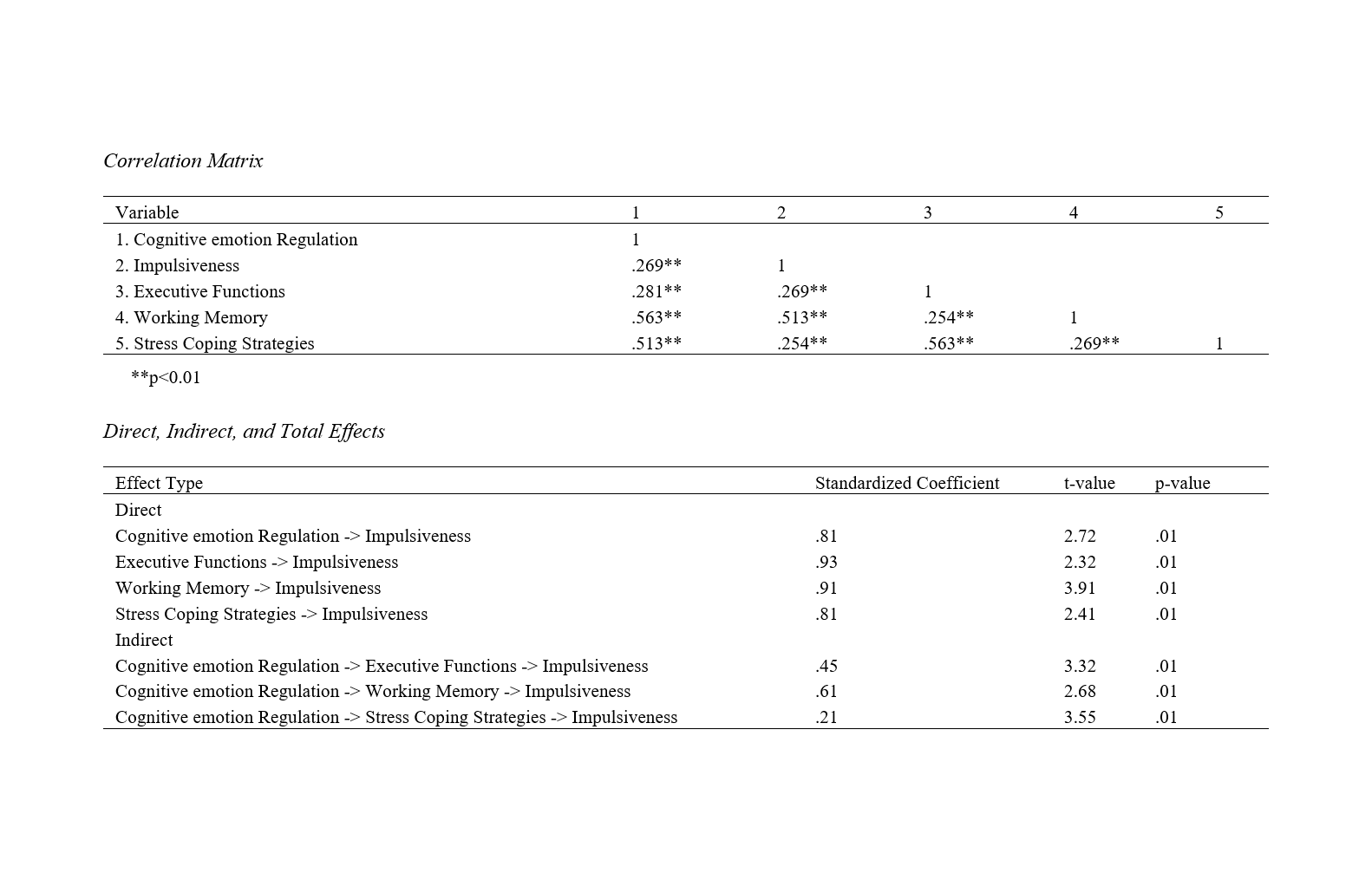
Findings: The study results indicated that cognitive emotion regulation affects the impulsiveness of female students with conduct disorder. Executive function affects the impulsiveness of female students with conduct disorder. Working memory affects the impulsiveness of female students with conduct disorder. Stress coping strategies affect the impulsiveness of female students with conduct disorder.
Conclusion: The results showed that cognitive emotion regulation affects the impulsiveness of female students with conduct disorder with the mediation of executive function. Cognitive emotion regulation affects the impulsiveness of female students with conduct disorder with the mediation of working memory. Additionally, the results indicated that cognitive emotion regulation affects the impulsiveness of with the mediation of stress coping strategies.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








