Effectiveness of Moral Motivation and Reasoning Training on Violent Behaviors of Male Students
Keywords:
Moral reasoning, Moral motivation, ViolenceAbstract
Objective: The emergence of violent and deviant behaviors among students, educators, and officials is a fundamental problem in society. These behaviors, besides causing economic and familial problems, also lead to numerous ethical, social, cultural, and political damages. Therefore, this study aimed to determine the effectiveness of moral motivation and reasoning training on violent behaviors in male middle school students.
Methods and Materials: The research method was quasi-experimental with one experimental group and one control group, including pre-test and post-test assessments. The study population consisted of all middle school students with violent behaviors in Tabriz during the academic year 2020-2021. For selecting the research sample, multi-stage cluster random sampling and screening methods were used. Thirty students who scored above the cut-off point on the Conflict Tactics Scale (CTS, 1972) were selected as the sample of students with violent behaviors and were randomly divided into experimental and control groups. The experimental group received twelve two-hour sessions of moral motivation and reasoning training, while the control group received regular school education. Both groups completed the Conflict Tactics Scale questionnaire as pre-test and post-test. Multivariate covariance analysis was used for data analysis.
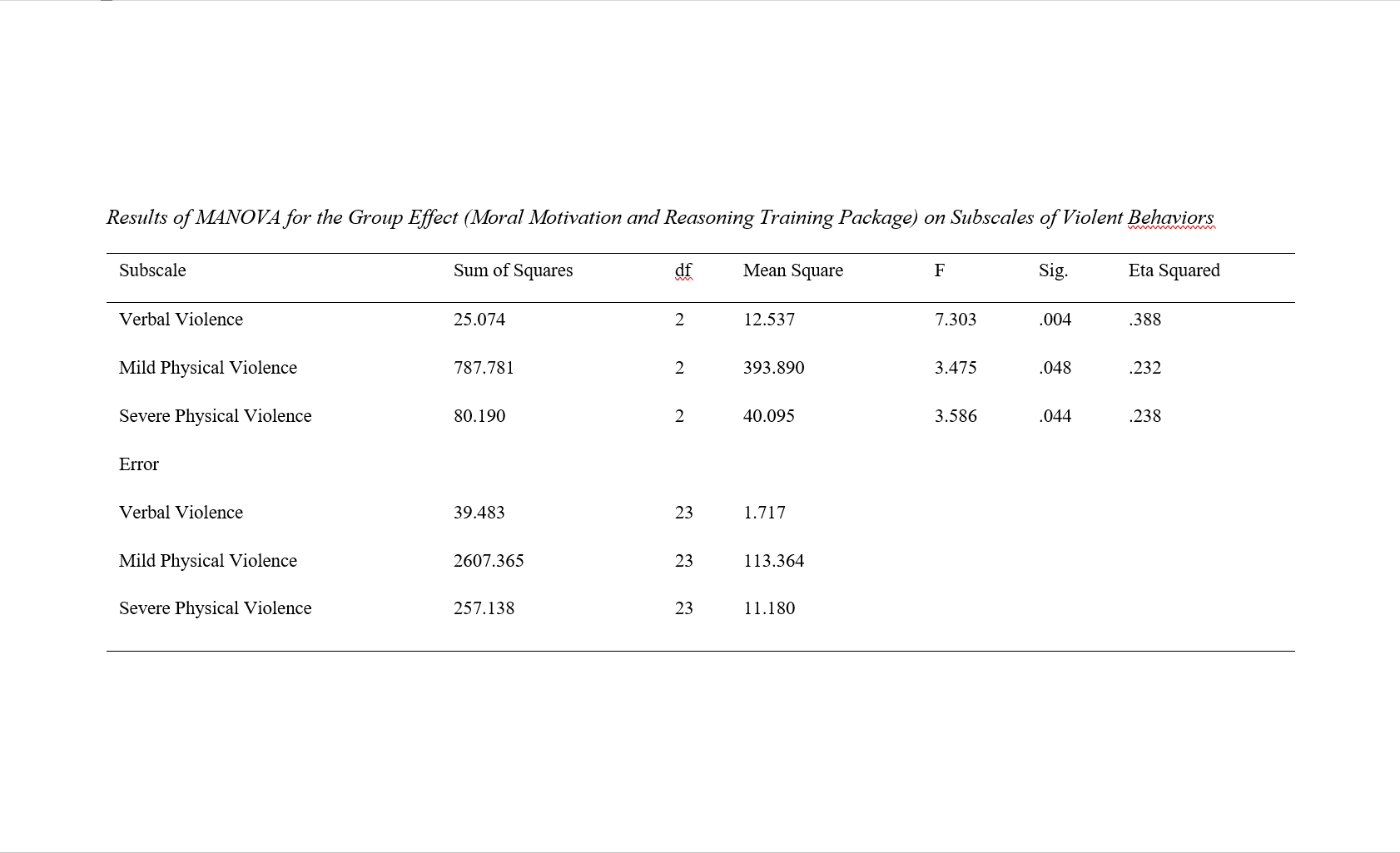
Findings: The results of multivariate covariance analysis showed that the effectiveness of moral motivation and reasoning training was significant for all three subscales, including verbal violence (F=7.30, α=0.004), mild physical violence (F=3.47, α=0.48), and severe physical violence (F=3.58, α=0.04) (α>0.05).
Conclusion: The results of this study indicate that among the subscales of violent behaviors, verbal violence received the most significant impact from the provision of moral motivation and reasoning training.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








