Development of a Structural Model of School Belonging Based on Academic Identity: The Mediating Role of Academic Engagement
Keywords:
School Belonging, Female Students, Academic Engagement, Academic IdentityAbstract
Objective: The sense of school belonging is a type of psychological need that has been confirmed to have positive psychological outcomes and supports the positive functioning of students in learning environments. Therefore, identifying individual and motivational factors that affect this sense is important. This study aimed to develop a structural model of school belonging based on academic identity, with the mediating role of students' academic engagement.
Methods and Materials: This correlational study utilized structural equation modeling. The statistical population included all female high school students in Khorramabad during the 2023-2024 academic year. Among them, 800 students were selected through multistage cluster sampling. They were then evaluated using the School Belonging Questionnaire (Barry et al., 2004), Academic Identity Scales (Vaz & Isakson, 2008), and Academic Engagement Scale (Reeve, 2013). Structural equation modeling was used for data analysis.
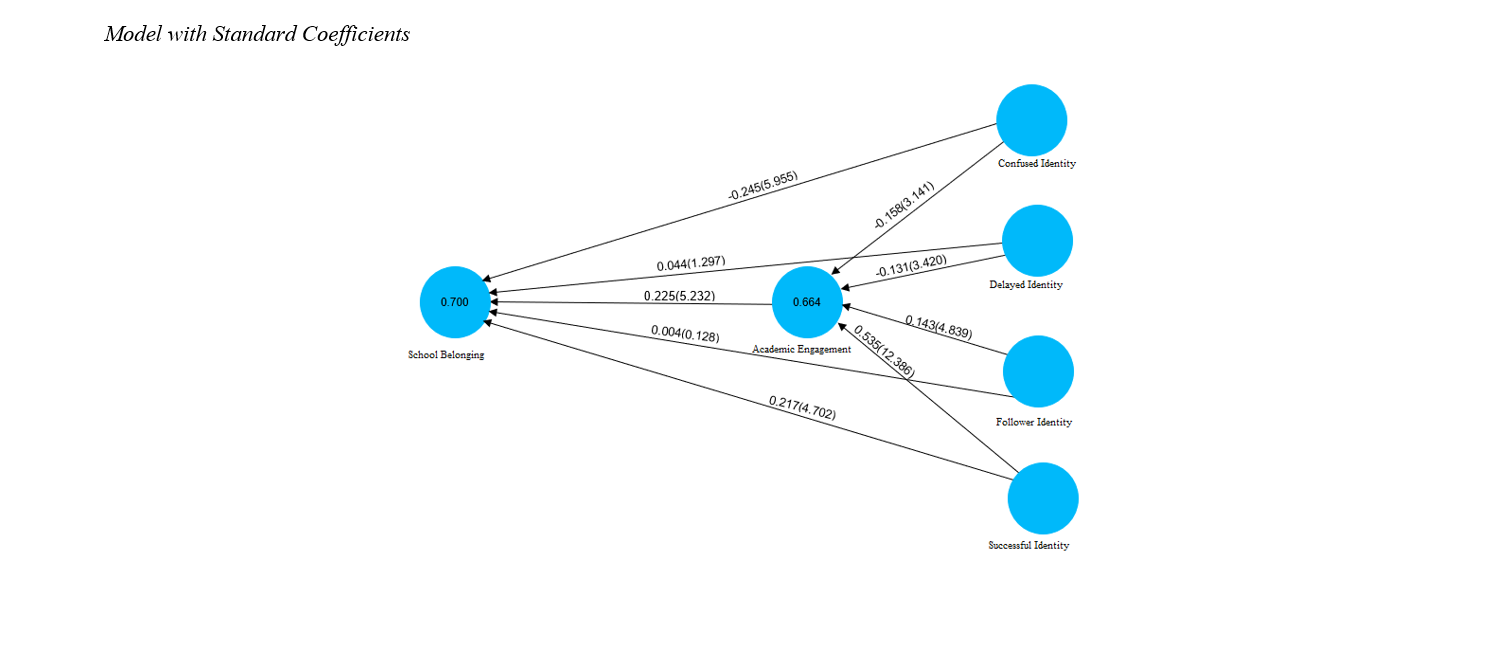
Findings: A positive and direct relationship was found between successful academic identity and academic engagement with school belonging, while a confused academic identity had a direct and negative relationship with school belonging (P<0.001). Successful and follower academic identities had a positive and direct relationship with academic engagement; confused and delayed academic identities had a direct and negative relationship with academic engagement (P<0.001). Academic engagement mediated the relationship between academic identity and school belonging. The overall model fit indices also indicated that the proposed model had a good fit.
Conclusion: Based on the study's findings, it can be concluded that students' academic identity and academic engagement contribute to their sense of school belonging.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Somayeh Ramezanifar (Author); Nasrolah Erfani (Corresponding Author); Rohollah Karimi Khoygani (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




























