Predicting Students' Academic Performance Based on Academic Self-Concept, Academic Resilience, Academic Engagement, Emotional Self-Regulation, and Self-Esteem
Keywords:
academic self-concept, academic resilience, academic engagement, emotional self-regulation, self-esteem, academic performanceAbstract
Objective: The aim of the present study was to predict academic performance based on academic self-concept, academic resilience, academic engagement, emotional self-regulation, and self-esteem among students.
Methods and Materials: The statistical population of this correlational- descriptive study included all students of the Faculty of Educational Sciences and Humanities at the University of Wasit, Iraq, in 2023. From this population, a sample of 306 students (115 female students and 185 male students) was selected using a multi-stage cluster random sampling method. Data were collected through the Academic Performance Questionnaire (Pham & Taylor, 1999), Academic Self-Concept Questionnaire (Chen & Thompson, 2004), Academic Engagement Questionnaire (Reeve & Tseng, 2011), Academic Resilience Questionnaire (Samuels, 2006), Emotional Self-Regulation Questionnaire (Hoffman & Kashdan, 2010), and Self-Esteem Questionnaire (Rosenberg, 1965) and were analyzed using Pearson correlation coefficient and stepwise regression analysis.
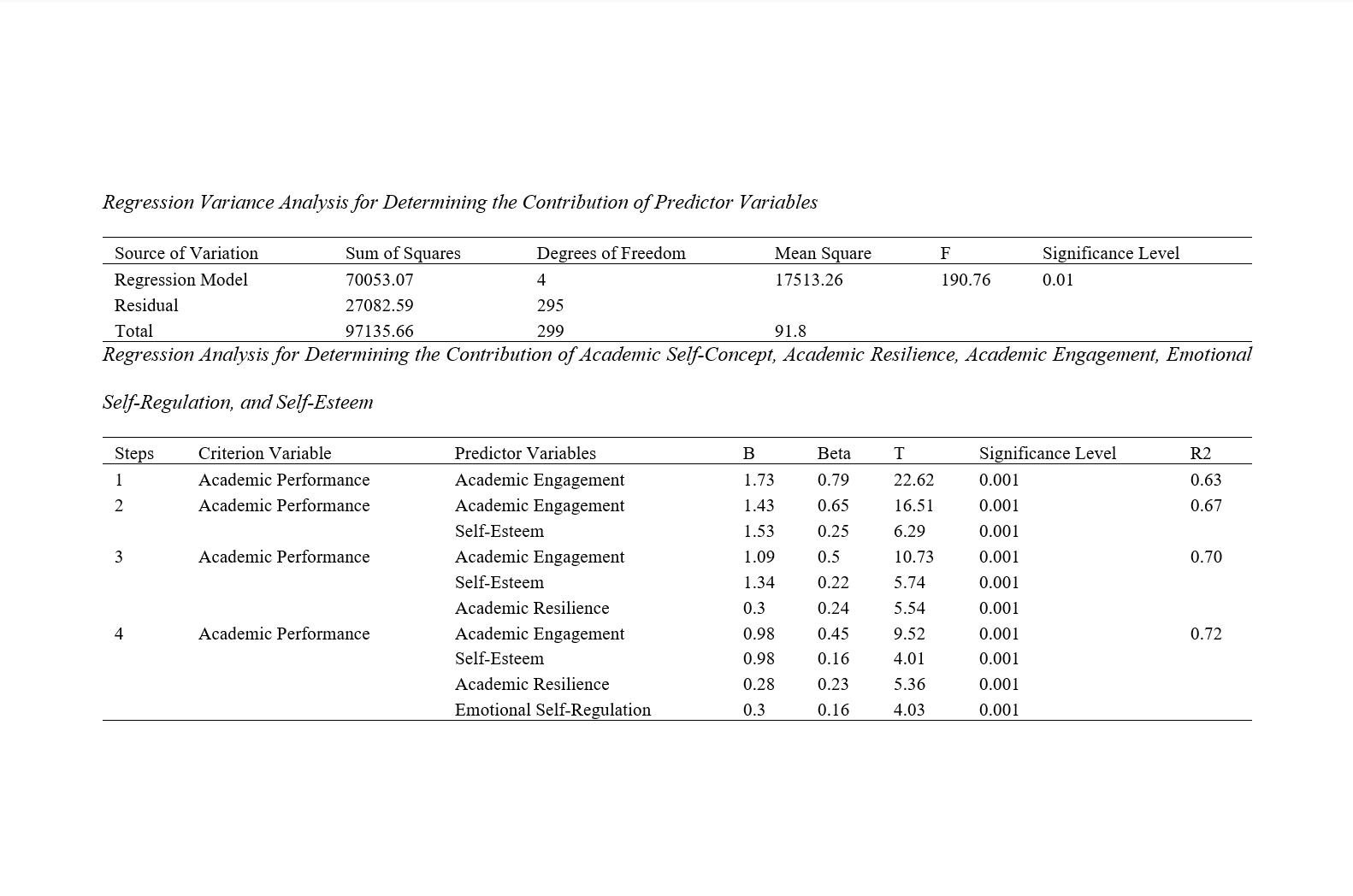
Findings: The findings of the study indicated that there was a significant positive relationship between all research variables and academic performance (P<0.001). Additionally, the results of the stepwise regression analysis showed that in four steps, academic engagement, self-esteem, academic resilience, and emotional self-regulation could collectively predict 72% of the variance in academic performance, with academic engagement having the highest predictive power at 63%.
Conclusion: Based on the findings of this study, it is suggested that the policymakers of higher education at the University of Wasit prioritize the enhancement of academic engagement and the strengthening of personality and psychological variables such as self-esteem and self-regulation, as well as contextual factors such as academic self-concept and academic resilience, to empower students and advance educational goals and academic success.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Haidar Dawood Salman (Author); Ali Mahdad (Corresponding Author); Rasheed Nassir Khalifa Al-Hashmy, Gholamreza Manshaee (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








