The Effectiveness of Mindfulness Training on Social Media Addiction and Academic Procrastination in Students
Keywords:
Mindfulness, Social Media, Academic Procrastination, Internet AddictionAbstract
Objective: Social media addiction and academic procrastination are common and prevalent problems among students, leading to numerous negative consequences. The aim of this study was to determine the effectiveness of mindfulness training on social media addiction and academic procrastination in students.
Methods and Materials: The research method was quasi-experimental with a pre-test, post-test, and control group design. From the student population of the Faculty of Psychology at Tehran University of Medical Sciences, 35 individuals were selected using convenience sampling and randomly assigned to experimental and control groups. Research tools included the Social Media Addiction Questionnaire (Ahmadi et al., 2016) and the Academic Procrastination Questionnaire (Solomon & Rothblum, 1984). The experimental group underwent mindfulness training intervention for 10 sessions of 90 minutes each. At the end, a post-test was administered to both groups, and the data were analyzed using covariance analysis.
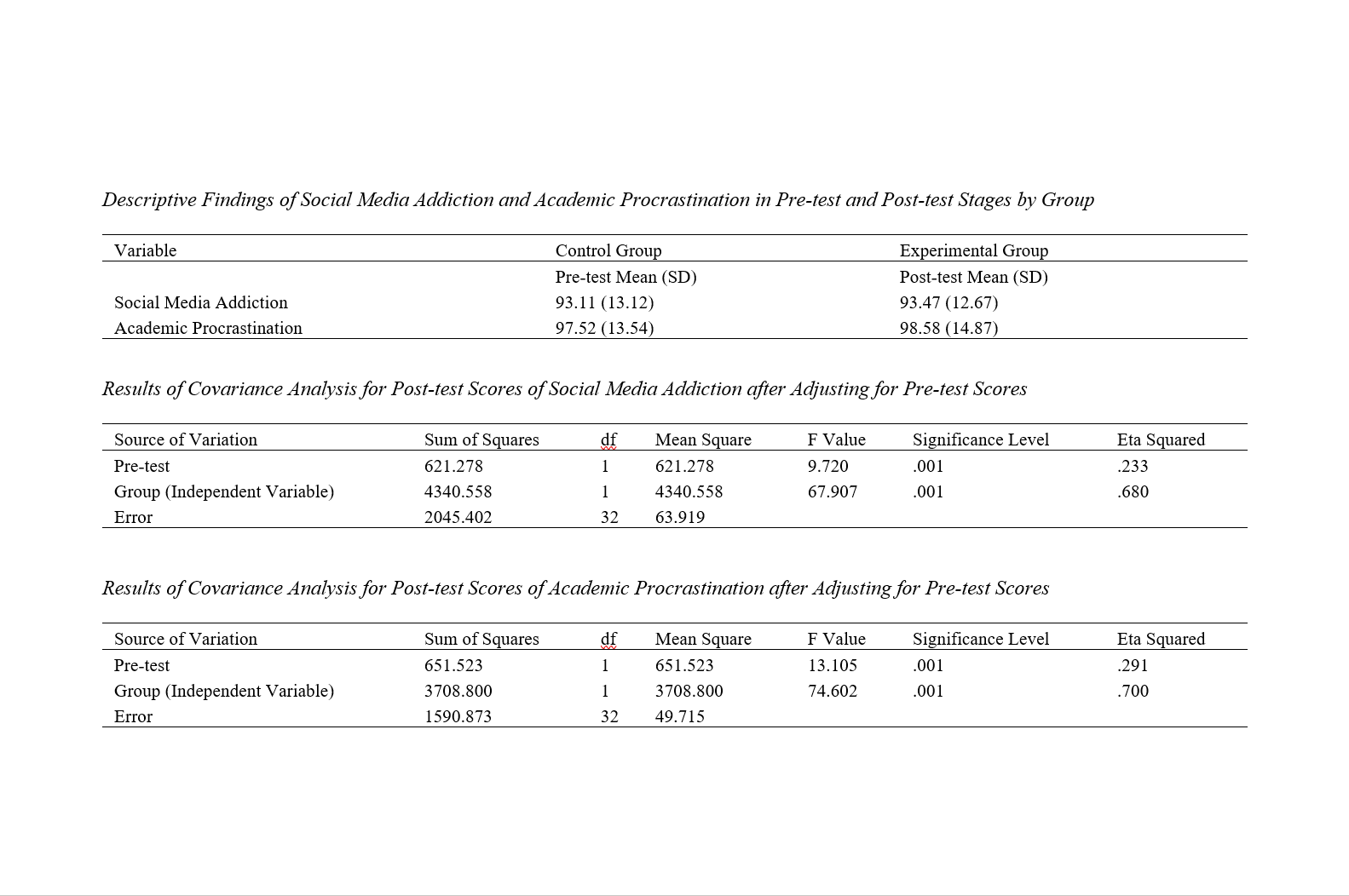
Findings: The results of the covariance analysis showed that mindfulness training had an effect on social media addiction (F = 21.456) and academic procrastination (F = 17.878) in students (p ≤ 0.001).
Conclusion: Based on the research findings, it is suggested that psychological interventions such as mindfulness be used to reduce social media usage and academic procrastination in students.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Maryam Zare, Raheleh Zamani Mazdeh (Author); Mehdi Badali (Corresponding Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








