Comparison of the Effectiveness of Cognitive Hypnotherapy and Successful Intelligence Training on the Mental Toughness of Twelfth-Grade Male Students in District 4 of Tehran
Keywords:
Cognitive Hypnotherapy, Successful Intelligence Training, Psychological ResilienceAbstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to compare the effectiveness of cognitive hypnotherapy and successful intelligence training on enhancing mental toughness among twelfth-grade male students in District 4 of Tehran.
Methods and Materials: The research utilized a quasi-experimental design with pre-test, post-test, and follow-up stages. The participants were 45 twelfth-grade male students selected through convenience sampling, divided into two experimental groups (15 students each) and one control group (15 students). Data were collected using the Clough Mental Toughness Questionnaire (2002), the Cognitive Hypnotherapy Intervention protocol (Alaeddin, 2011), and the Successful Intelligence Training protocol (Shoushtari et al., 2016). Data analysis was conducted using ANCOVA to assess the impact of the interventions.
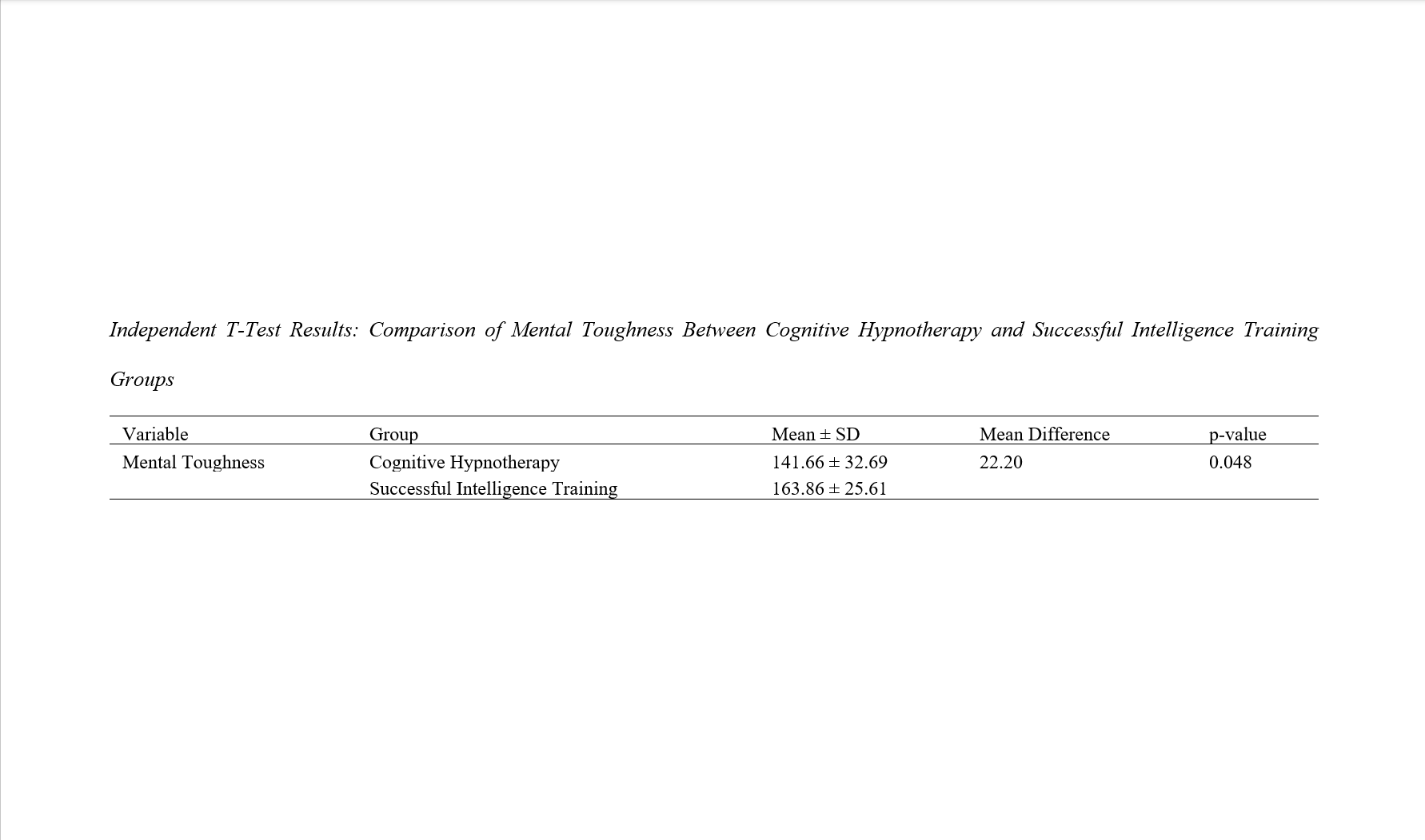
Findings: The results showed that both cognitive hypnotherapy and successful intelligence training significantly improved mental toughness compared to the control group. Moreover, the successful intelligence training group demonstrated higher mean resilience scores than the cognitive hypnotherapy group, and this difference was statistically significant (p < 0.05). The findings support the effectiveness of both interventions in enhancing students' mental toughness.
Conclusion: Cognitive hypnotherapy and successful intelligence training are both effective interventions for improving mental toughness among high school students. However, successful intelligence training appears to have a stronger impact on resilience outcomes. These interventions can be valuable tools for educators and mental health professionals in supporting students' emotional and cognitive development.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 MohammadHassan Khaleghinejad , Pantea Jahangir, Farideh Dokaneifard (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








