Effectiveness of CBT on Self-Harming Thoughts, Impulsivity, and Suppressed Anger in Adolescents with Depression Syndrome
Keywords:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, adolescents, self-harming thoughts, impulsivity, suppressed anger, randomized controlled trial, emotional regulationAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) in reducing self-harming thoughts, impulsivity, and suppressed anger in adolescents.
Methods and Materials: A randomized controlled trial was conducted with 30 adolescents (15 in the CBT group and 15 in the control group). The participants were assessed at three stages: pre-test, post-test, and follow-up, using validated self-report measures to evaluate self-harming thoughts, impulsivity, and suppressed anger. The CBT intervention consisted of 12 weekly sessions, focusing on cognitive restructuring, emotion regulation, and behavioral skills. Data were analyzed using repeated measures ANOVA and Bonferroni post-hoc tests to assess within-group and between-group differences over time.
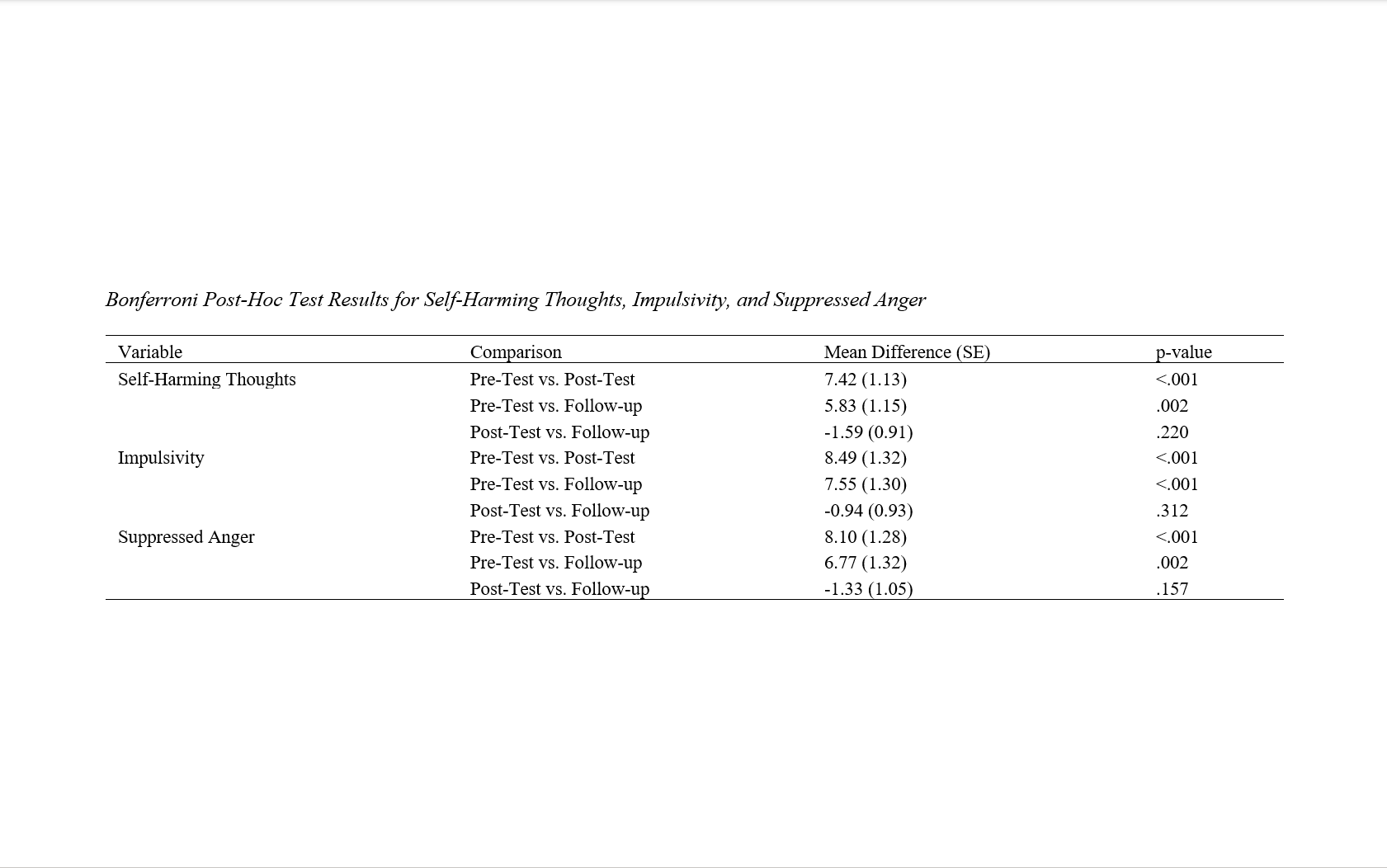
Findings: The results revealed significant reductions in self-harming thoughts, impulsivity, and suppressed anger for the CBT group compared to the control group across all three stages. Specifically, the CBT group showed greater improvement at the post-test and follow-up compared to the control group, with significant between-group differences in all three variables. The effect size for the self-harming thoughts (η² = 0.25), impulsivity (η² = 0.32), and suppressed anger (η² = 0.28) indicated moderate to large effects. The findings suggest that CBT is highly effective in addressing emotional dysregulation and impulsive behaviors in adolescents.
Conclusion: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy significantly reduced self-harming thoughts, impulsivity, and suppressed anger in adolescents, indicating its potential as an effective intervention for emotional and behavioral issues in this population. Further research is needed to examine long-term effects and the role of individual differences in treatment outcomes.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Fatemeh Forghani Elahabadi (Corresponding Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.

























