Predicting Academic Burnout Based on School Belongingness, Parenting Styles, and Academic Resilience
Keywords:
School belongingness, academic resilience, parenting styles, academic burnoutAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to predict academic burnout based on school belongingness, parenting styles, and academic resilience.
Methods and Materials: The current research is applied in nature, with a descriptive and correlational design. The statistical population included female high school students in the second cycle of secondary education in District 19 of Tehran, who were enrolled during the second semester of the 2023–2024 academic year. Using convenience sampling and based on the Krejcie and Morgan table, a sample of 400 female high school students was selected. Participants completed the Maslach Burnout Inventory, Barry’s (2004) School Belongingness Questionnaire, Baumrind’s (1973) Parenting Styles Questionnaire, and Samuels’ (2004) Academic Resilience Scale. Data were analyzed using Pearson correlation, univariate regression, and multivariate regression methods through SPSS version 22.
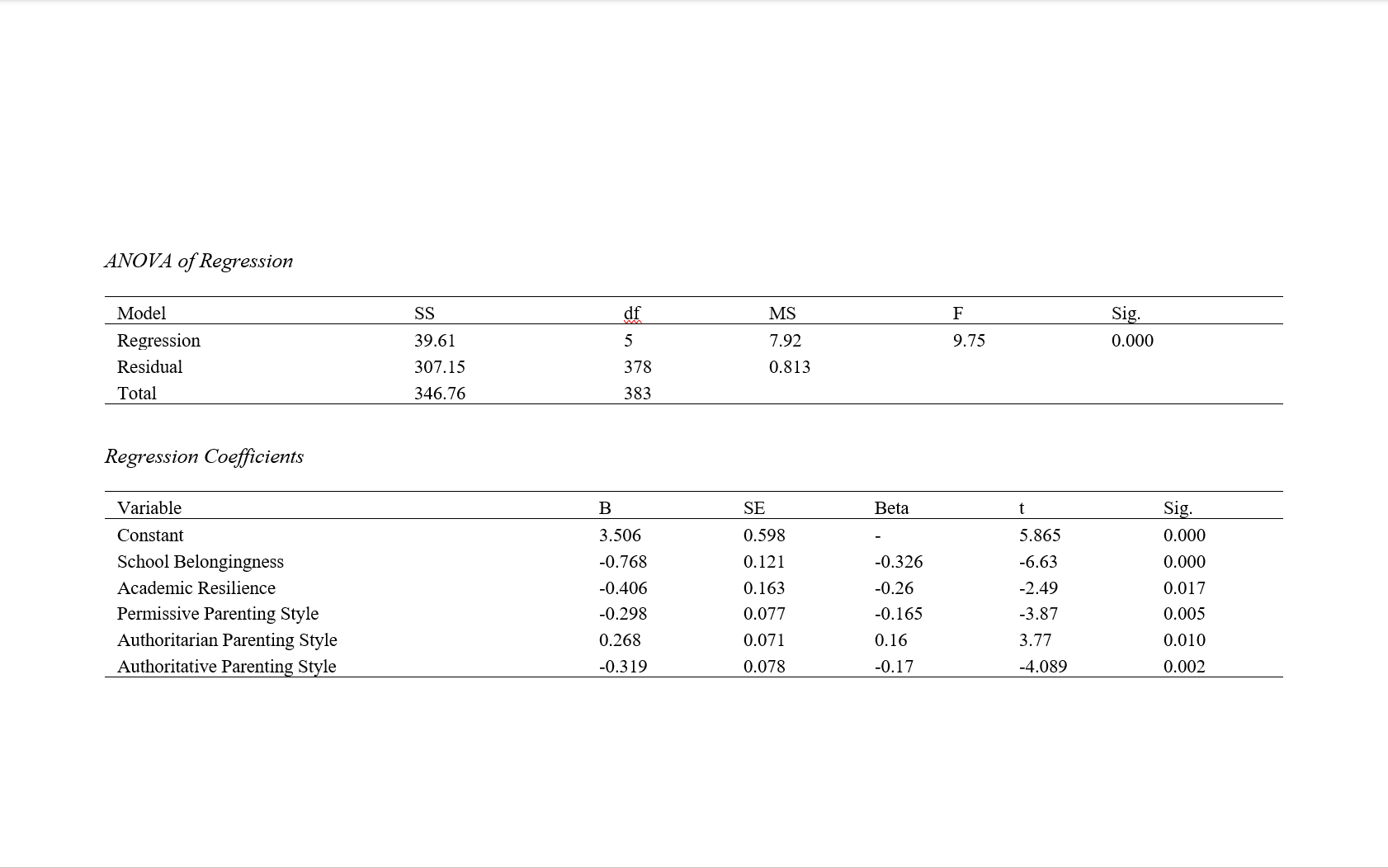
Findings: Regression analysis revealed that the correlation coefficient (R) was 0.638, indicating a strong relationship between academic burnout and the independent variables of school belongingness, parenting style, and academic resilience. The coefficient of determination (R²) was 0.407, suggesting that approximately 40.7% of the variance in the dependent variable (academic burnout) could be explained by the independent variables of school belongingness, parenting style, and academic resilience, which is statistically significant (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: It can be concluded that enhancing school belongingness, adopting effective parenting styles, and fostering resilience can play a preventive role in reducing academic burnout among students.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Sara Bazaz Abkenar (Author); Ali Farhadian (Corresponding Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








