The Effect of Traditional and Game-Based Teaching Models on Learning Volleyball Skills in Adolescent Boys
Keywords:
Traditional teaching, game-based teaching, volleyball skills, adolescentsAbstract
Objective: This study aims to compare the effects of traditional and game-based teaching models on the acquisition of volleyball skills in adolescent boys.
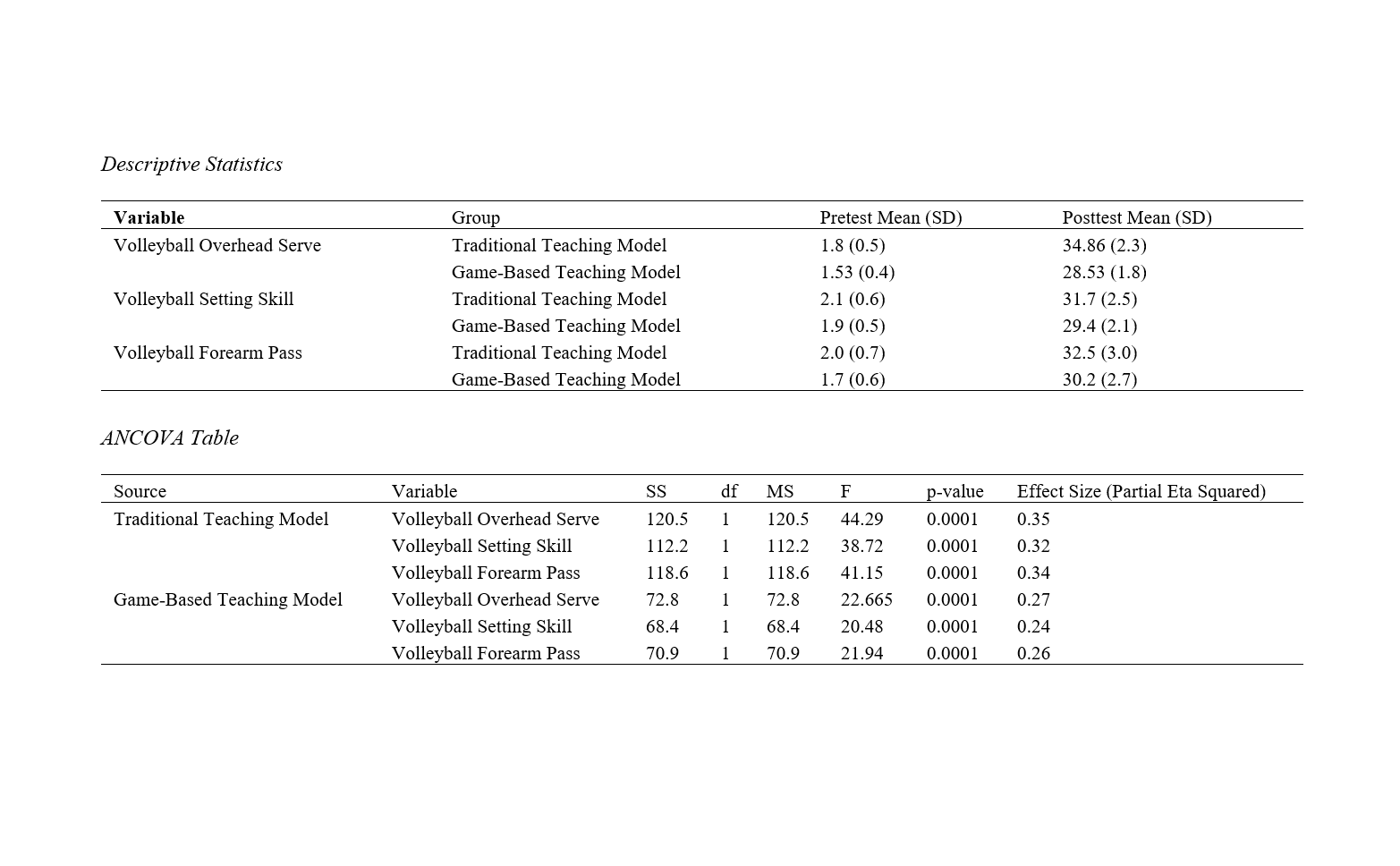
Methods and Materials: This quasi-experimental study employed a pretest-posttest design with two experimental groups: the traditional teaching model and the game-based teaching model. A total of 40 male students aged 10–13 years, with no prior volleyball experience, were randomly assigned to either the traditional group (n = 20) or the game-based group (n = 20). Participants underwent an 8-week training program (2 sessions per week). Volleyball skills were measured using standardized tests for overhead serve, forearm pass, and setting skills. Descriptive statistics were calculated, and ANCOVA was used to analyze the differences between groups while controlling for baseline scores.
Findings: Both teaching models significantly improved volleyball skills across all variables (p < .05). The traditional teaching model showed slightly higher posttest scores for technical skills, with moderate effect sizes (partial eta squared = 0.32–0.35). The game-based teaching model demonstrated significant improvements as well, particularly in fostering applied and situational learning, with effect sizes ranging from 0.24 to 0.27.
Conclusion: While both methods are effective in improving volleyball skills, the traditional teaching model excels in enhancing technical precision, whereas the game-based teaching model better supports decision-making, teamwork, and applied skill development. Combining these approaches is recommended to optimize skill acquisition and overall performance in volleyball training for adolescents.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Elnaz Ebrahimi Khayat, Maedeh Ahmadpoor , Sasan Bahremand (Author); Meysam Rezaee (Corresponding Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








