Key Factors Contributing to Emotional Suppression in Male Adolescents
Keywords:
emotional suppression, male adolescents, qualitative research, Pakistan, gender norms, emotional socialization, family dynamicsAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to explore the key sociocultural, familial, emotional, and intrapersonal factors contributing to emotional suppression in male adolescents in Pakistan.
Methods and Materials: Using a qualitative research design, data were collected through semi-structured interviews with 24 male adolescents aged 14 to 18 years from urban and semi-urban areas of Pakistan. Participants were selected through purposive sampling, and data collection continued until theoretical saturation was reached. The interviews, lasting 45 to 60 minutes, focused on adolescents’ experiences and beliefs related to emotional expression and suppression. All interviews were transcribed verbatim and analyzed using thematic analysis, supported by NVivo software to identify and organize recurring themes and subthemes.
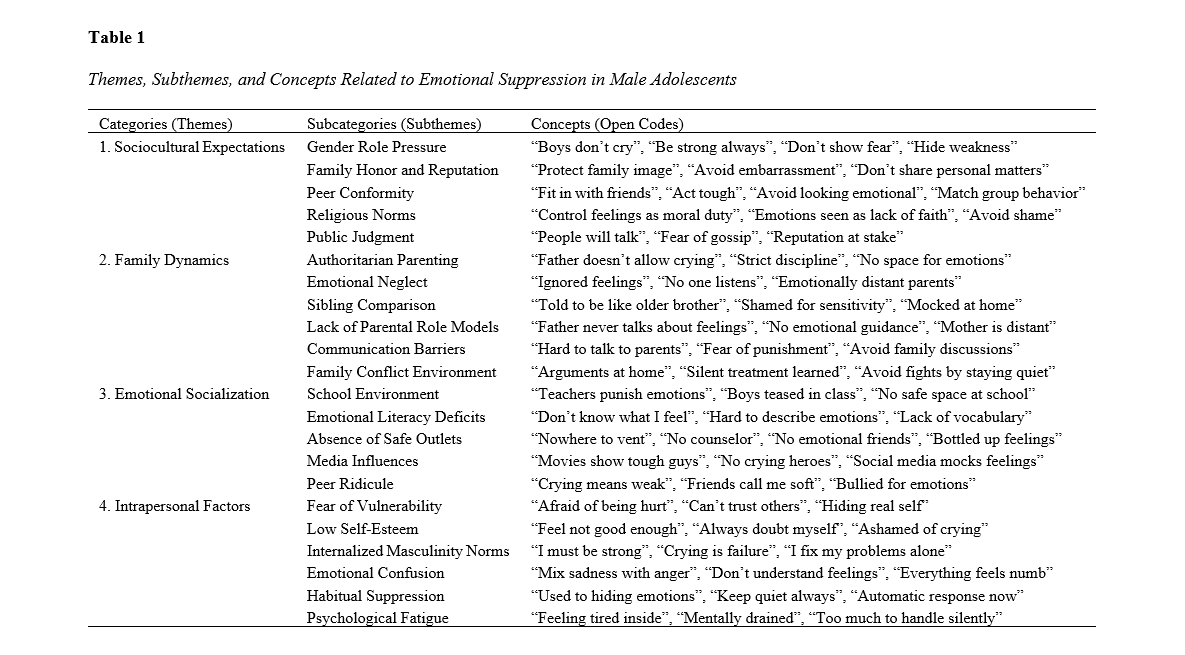
Findings: Analysis revealed four main themes: sociocultural expectations, family dynamics, emotional socialization, and intrapersonal factors. Subthemes included gender role pressure, family honor, authoritarian parenting, emotional neglect, school environment, media influence, fear of vulnerability, and habitual suppression. Adolescents consistently reported suppressing emotions due to cultural expectations of masculinity, fear of peer ridicule, lack of parental emotional support, and internalized beliefs about strength and emotional control. Many participants described emotional suppression as both a learned behavior and a protective mechanism, often resulting in emotional fatigue and confusion.
Conclusion: Emotional suppression in male adolescents is a multifaceted phenomenon rooted in cultural, familial, and psychological contexts. The findings highlight the need for culturally sensitive emotional education, supportive family environments, and school-based interventions that challenge harmful gender norms and promote emotional expression and well-being in adolescent boys.
Downloads
References
Allen, K. B., Tan, P. Z., & Prinz, R. J. (2022). Introduction to the Special Issue: Interplay of Family Factors and Cognitive-Affective Processes in Youth. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 25(1), 1-4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-022-00394-4
Breaux, R., Eadeh, H. M., Swanson, C. S., & McQuade, J. D. (2021). Adolescent Emotionality and Emotion Regulation in the Context of Parent Emotion Socialization Among Adolescents With Neurodevelopmental Disorders: A Call to Action With Pilot Data. Research on Child and Adolescent Psychopathology, 50(1), 77-88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-021-00833-w
Cameron, D., Millings, A., Fernando, S., Collins, E. C., Moore, R. K., Sharkey, A., Evers, V., & Prescott, T. J. (2018). The Effects of Robot Facial Emotional Expressions and Gender on Child–robot Interaction in a Field Study. Connection Science, 30(4), 343-361. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540091.2018.1454889
Clifford, M. E., Nguyen, A. J., & Bradshaw, C. P. (2020). Emotion Processing Associated With Aggression in Early Adolescents: A Focus on Affective Theory of Mind. Aggressive Behavior, 47(2), 173-182. https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.21936
Dillon-Owens, C., Nostrand, D. F., Ojanen, T., Buchholz, C., & Valdes, O. (2022). Early Adolescent Cognitive and Affective Empathy. Social Psychology, 53(5), 292-302. https://doi.org/10.1027/1864-9335/a000499
Eranda, K. (2024). A Hegemonic Study on Youth Problems Appeared in Modern Sinhala Poetry (From the 1970s to Present). Vidyodaya Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, 09(02), 179-195. https://doi.org/10.31357/fhss/vjhss.v09i02.12
Grigoryeva, M. V. (2020). Affective Factors in the Manifestation of Discriminatory Attitudes of the Personality in Behavior. Общество Социология Психология Педагогика(11). https://doi.org/10.24158/spp.2020.11.9
Guo, J., Mrug, S., & Knight, D. C. (2017). Emotion Socialization as a Predictor of Physiological and Psychological Responses to Stress. Physiology & Behavior, 175, 119-129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2017.03.046
Hu, Y., Dong, S., Guan, F., Chen, O., Chen, J., & Xu, S. (2021). Emotion Understanding Correlates With Parental Emotional Expressivity in Chinese Youths With Hearing Loss and Typical Hearing. Frontiers in psychology, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.662356
Jun, S.-K., & Jung, I.-S. (2022). Exploration of the Differences in Positive-Negative Psychological Factors Influencing the Life Satisfaction and Depression of College Students by Gender and Family Economic Level. International Journal of Advanced and Applied Sciences, 9(4), 88-96. https://doi.org/10.21833/ijaas.2022.04.011
Karłyk-Ćwik, A. (2021). Humor and Expression of Anger in Socially Maladapted Youth. Social Education Research, 67-79. https://doi.org/10.37256/ser.3120221191
Kwon, Y. S., & Byun, S. H. (2023). The Mediating Effect of Interpersonal Problems in the Ambivalent Relationship Between Attachment and Emotional Expression in Maladaptive Multicultural Adolescents. Korean Correction Counseling Psychological Association, 8(2), 79-99. https://doi.org/10.33614/kccpa.2023.8.2.79
Litchke, L. G., Liu, T., & Castro, S. (2018). Effects of Multimodal Mandala Yoga on Social and Emotional Skills for Youth With Autism Spectrum Disorder. International Journal of Yoga, 11(1), 59-65. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijoy.ijoy_80_16
Lozada, F. T. (2024). The Role of Afrocultural Ethos in African American Youth's Emotion Skill Development. Child Development Perspectives, 18(3), 107-114. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdep.12509
Lu, S., Huang, C. C., Cheung, S., Ríos, J. A., & Chen, Y. (2020). Mindfulness and Social‐emotional Skills in Latino Pre‐adolescents in the U.S.: The Mediating Role of Executive Function. Health & Social Care in the Community, 29(4), 1010-1018. https://doi.org/10.1111/hsc.13135
Malti, T. (2020). Children and Violence: Nurturing Social‐Emotional Development to Promote Mental Health. Social policy report, 33(2), 1-27. https://doi.org/10.1002/sop2.8
Morningstar, M., Dirks, M. A., Rappaport, B. I., Pine, D. S., & Nelson, E. E. (2017). Associations Between Anxious and Depressive Symptoms and the Recognition of Vocal Socioemotional Expressions in Youth. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 48(3), 491-500. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374416.2017.1350963
Neag, A., & Supa, M. (2020). Emotional Practices of Unaccompanied Refugee Youth on Social Media. International Journal of Cultural Studies, 23(5), 766-786. https://doi.org/10.1177/1367877920929710
Nyquist, A. C., & Luebbe, A. M. (2021). Parents’ Beliefs, Depressive Symptoms, and Emotion Regulation Uniquely Relate to Parental Responses to Adolescent Positive Affect. Family Process, 61(1), 407-421. https://doi.org/10.1111/famp.12657
Pizarro‐Campagna, E., Terrett, G., Jovev, M., Rendell, P. G., Henry, J. D., & Chanen, A. M. (2023). Cognitive Reappraisal Impairs Negative Affect Regulation in the Context of Social Rejection for Youth With Early-Stage Borderline Personality Disorder. Journal of personality disorders, 37(2), 156-176. https://doi.org/10.1521/pedi.2023.37.2.156
Rabinowitz, J. A., Osigwe, I., Byrne, A., Drabick, D. A. G., & Reynolds, M. (2017). Father- And Youth-Reported Family Affective Expression Differentially Predicts Youth Internalizing and Externalizing Symptoms. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 47(sup1), S264-S277. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374416.2017.1280801
Racz, J. I., Mathieu, S., McKenzie, M. L., & Farrell, L. J. (2022). Paediatric Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder and Comorbid Body Dysmorphic Disorder: Clinical Expression and Treatment Response. Child Psychiatry & Human Development, 54(4), 1005-1014. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-022-01314-x
Rajni, M., & Singh, S. P. (2016). A Review of Emotional Intelligence on Self Esteem: It’s Impact on Adolescents Stage. International Journal of Indian Psychology, 3(3). https://doi.org/10.25215/0303.081
Villafania, R. J. B. (2023). Turning Challenges Into Opportunities: Mental Health and Coping Styles Among Filipino Youth During Pandemic Towards Program and Policy Development Framework. Arts & Humanities Open Access Journal, 5(1), 23-31. https://doi.org/10.15406/ahoaj.2023.05.00183
Wang, Y., Wang, J., Liu, J., Zang, F., & Zhu, T. (2019). Identifying Linguistic Differences Between Empty‐nest and Non‐empty‐nest Youth on Weibo. Human Behavior and Emerging Technologies, 1(3), 190-199. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbe2.161
Zaff, J. F., Aasland, K., McDermott, E. R., Carvalho, A. B., Joseph, P. L., & Jones, E. P. (2016). Exploring Positive Youth Development Among Young People Who Leave School Without Graduating High School: A Focus on Social and Emotional Competencies. Qualitative Psychology, 3(1), 26-45. https://doi.org/10.1037/qup0000044
Zaini, M. K. N., Hussin, N., Ibrahim, Z., Bakar, A. A., Hashim, H., & Shahibi, M. S. (2023). A Conceptual Framework on Emotional Maturity Towards Social Media Usage Among Youth in Malaysia. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 13(5). https://doi.org/10.6007/ijarbss/v13-i5/16644
Zampella, C., Bennetto, L., & Herrington, J. D. (2020). Computer Vision Analysis of Reduced Interpersonal Affect Coordination in Youth With Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism Research, 13(12), 2133-2142. https://doi.org/10.1002/aur.2334
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








