The Effect of Parental Monitoring and Moral Identity on Youth Delinquency
Keywords:
Youth delinquency, parental monitoring, moral identity, adolescent behavior, BangladeshAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to examine the effect of parental monitoring and moral identity on youth delinquency among adolescents in Bangladesh.
Methods and Materials: A correlational descriptive design was employed using a sample of 403 adolescents aged 14 to 18 years, selected through stratified random sampling based on the Morgan and Krejcie table. Participants were recruited from secondary schools across urban and semi-urban areas in Bangladesh. Data were collected using three standard self-report instruments: the Self-Reported Delinquency Scale (SRDS) by Elliott et al. (1985), the Parental Monitoring Scale by Stattin and Kerr (2000), and the Moral Identity Questionnaire by Aquino and Reed (2002). All instruments demonstrated acceptable validity and reliability in prior research. Data analysis was conducted using SPSS version 27, involving descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation to assess bivariate relationships, and linear regression to evaluate the combined predictive value of parental monitoring and moral identity on youth delinquency.
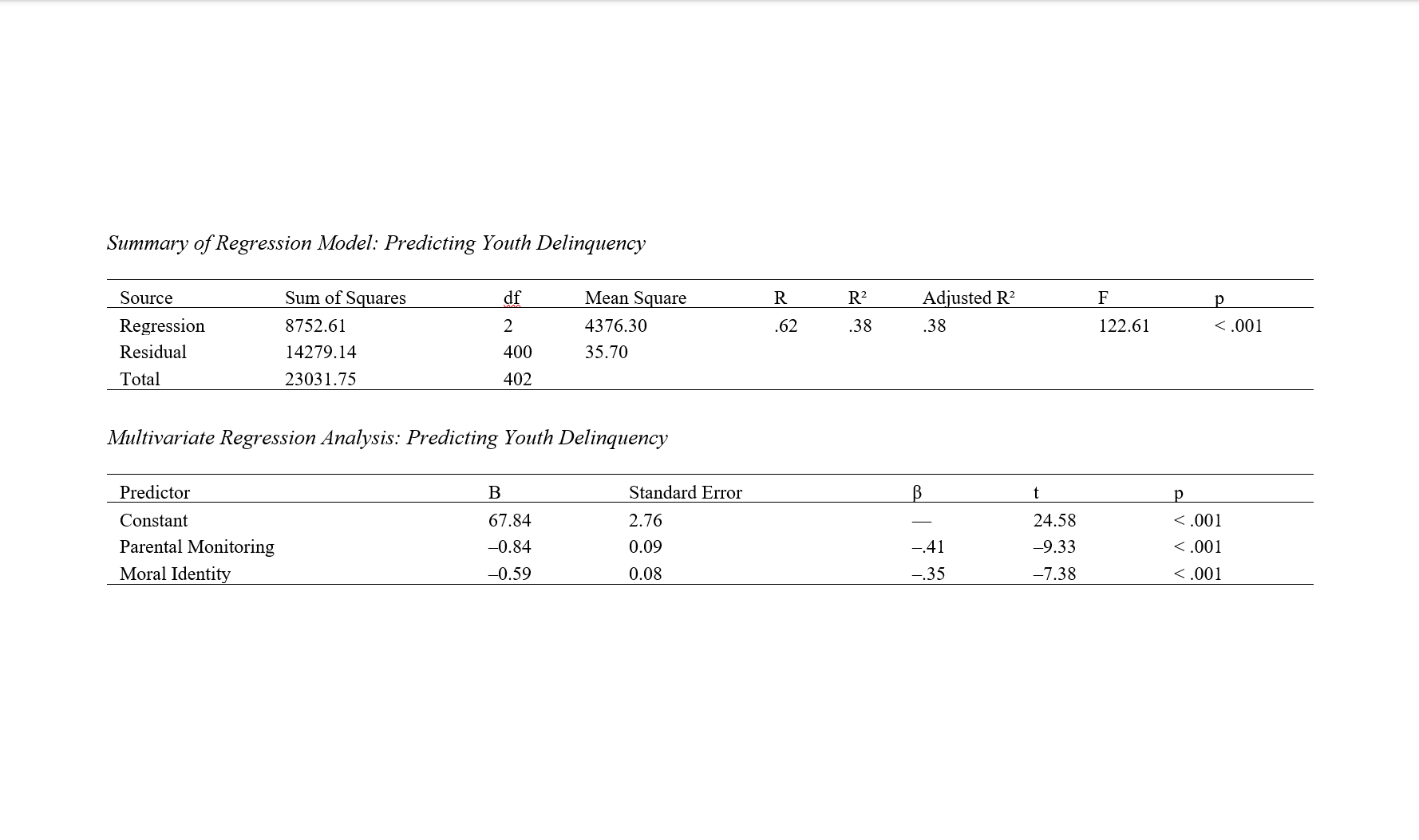
Findings: The results revealed significant negative correlations between youth delinquency and both parental monitoring (r = –.52, p < .001) and moral identity (r = –.47, p < .001). Linear regression analysis indicated that parental monitoring and moral identity together significantly predicted youth delinquency (R² = .38, F(2, 400) = 122.61, p < .001). Parental monitoring (β = –.41, p < .001) emerged as a slightly stronger predictor than moral identity (β = –.35, p < .001), suggesting that both external supervision and internal value systems independently contribute to the reduction of delinquent behavior.
Conclusion: The findings highlight the critical role of both parental monitoring and moral identity in deterring youth delinquency. Intervention programs targeting adolescent behavior should integrate family-based strategies that promote effective monitoring and support the development of moral identity to enhance protective factors against deviance.
Downloads
References
Ahmad, N. L., & Amidi, A. (2019). Parental Behaviors as a Risk Factor Associated With Delinquency Among High School Students. International Journal of Academic Research in Progressive Education and Development, 8(4). https://doi.org/10.6007/ijarped/v8-i4/6906
Azimi, K., Shahni Yeilagh, M., & Khoshnamvand, M. (2023). Designing and testing a causal model of the relationship between moral identity and bullying with the mediation of moral disengagement among Iranian adolescents. Journal of Social Psychology Research, 13(52), 13-30. https://www.socialpsychology.ir/article_194355.html
Aziz, S., Ajib, M., Razak, A., Nen, S., Manap, J., Hoesni, S. M., & Nasir, M. K. M. (2023). Impact of Parental Monitoring and Communication Factors on Deviant Behavior Among Teenagers in Malaysia. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 58(6). https://doi.org/10.35741/issn.0258-2724.58.6.26
Cicerali, L. K., & Cicerali, E. E. (2017). Parental Influences on Youth Delinquency. Journal of Criminal Psychology, 8(2), 138-149. https://doi.org/10.1108/jcp-03-2017-0018
Dittus, P., Li, J., Verlenden, J. V., Wilkins, N., Carman-McClanahan, M., Cavalier, Y., Mercado, M. C., Welder, L. E., Roehler, D. R., & Ethier, K. A. (2023). Parental Monitoring and Risk Behaviors and Experiences Among High School Students — Youth Risk Behavior Survey, United States, 2021. MMWR supplements, 72(1), 37-44. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.su7201a5
Folorunsho, S., Ajayi, V., & Abdulrazaq, O. (2024). Juvenile Delinquency as a Contemporary Issue in Nigeria: Unraveling the Impact of Parenting Styles and Family Structures. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202401.1659.v1
Freemon, K., Herrera, V. M., Cheon, H., & Katz, C. M. (2022). Family Structure and Delinquency in the English-Speaking Caribbean: The Moderating Role of Parental Attachment, Supervision, and Commitment to Negative Peers. Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice, 21(2), 149-171. https://doi.org/10.1177/15412040221132192
Gearhart, M. C. (2019). Parent and Child Perceptions of Collective Efficacy as Predictors of Delinquency. The British Journal of Social Work, 50(1), 25-41. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjsw/bcz146
Haruyama, D., Prince, M. A., Swaim, R. C., & Chavez, E. L. (2023). The Relationship Between Depressed Affect, Parental Monitoring, and Sex on Cannabis Use Among American Indian Youth. American Journal on Addictions. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajad.13416
Huffman, L. G., Oshri, A., & Caughy, M. O. (2020a). An Autonomic Nervous System Context of Harsh Parenting and Youth Aggression Versus Delinquency. Biological Psychology, 156, 107966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2020.107966
Huffman, L. G., Oshri, A., & Caughy, M. O. (2020b). An Autonomic Nervous System Context of Harsh Parenting and Youth Aggression Versus Delinquency (Accepted for Publication in Biological Psychology). https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/pxh5c
Jeon, H. S., & Chun, J. (2017). The Influence of Stress on Juvenile Delinquency: Focusing on the Buffering Effects of Protective Factors Among Korean Adolescents. Social Work in Public Health, 32(4), 223-237. https://doi.org/10.1080/19371918.2016.1274704
Ji, M. (2023). The Ways Psychological Trauma Affect Juvenile Delinquency. 2022 3rd International Conference on Big Data Economy and Information Management (BDEIM 2022),
Kim, Y. S., & Lo, C. C. (2016). Short- And Mid-Term Effects of Violent Victimization on Delinquency. Journal of interpersonal violence, 31(16), 2643-2665. https://doi.org/10.1177/0886260515580368
Lassi, N. (2023). Evidence for the Influence of Confucian Filial Piety on Deviancy Among Young People. Journal of Social Science, 4(4), 896-905. https://doi.org/10.46799/jss.v4i4.196
Lee, B., & Cochran, J. (2023). The Influence of Perceived Parenting Styles on Korean Children's Delinquent Behaviors When Accounting for Gender Differences. Juvenile and Family Court Journal, 74(4), 53-66. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfcj.12250
Lee, S.-H. (2023). Analyzing Delinquent Peer Factors in Cyber Violence Among Out-of-School Youth. Korean Association of Public Safety and Criminal Justice, 32(2), 195-220. https://doi.org/10.21181/kjpc.2023.32.2.195
Lei, M. K., & Beach, S. R. H. (2020). Can We Uncouple Neighborhood Disadvantage and Delinquent Behaviors? An Experimental Test of Family Resilience Guided by the Social Disorganization Theory of Delinquent Behaviors. Family Process, 59(4), 1801-1817. https://doi.org/10.1111/famp.12527
Mambende, B., Nyandoro, T., Maunganidze, L., & Sawuti, A. (2016). ‘‘Factors Influencing Youth Juvenile Delinquency at Blue Hills Children’s Prison Rehabilitation Centre in Gweru, Zimbabwe: An Explorative Study’’. International Journal of Humanities Social Sciences and Education, 3(4). https://doi.org/10.20431/2349-0381.0304004
Mowen, T. J., & Schroeder, R. D. (2015). Maternal Parenting Style and Delinquency by Race and the Moderating Effect of Structural Disadvantage. Youth & Society, 50(2), 139-159. https://doi.org/10.1177/0044118x15598028
NeMoyer, A., Wang, Y., Álvarez, K., Canino, G., Duarte, C. S., Bird, H., & Alegrı́a, M. (2020). Parental Incarceration During Childhood and Later Delinquent Outcomes Among Puerto Rican Adolescents and Young Adults in Two Contexts. Law and Human Behavior, 44(2), 143-156. https://doi.org/10.1037/lhb0000354
Oh, J. K., Lee, T. W., Zhang, J., & Lee, M. W. (2024). The Impact of Negative Parenting Attitudes on Adolescents’ Cyber Delinquency: The Dual Mediating Effects of Grit and Aggression. Korean Association for Learner-Centered Curriculum and Instruction, 24(21), 577-593. https://doi.org/10.22251/jlcci.2024.24.21.577
Ray, J. V., Frick, P. J., Thornton, L. C., Myers, T. D. W., Steinberg, L., & Cauffman, E. (2017). Callous–unemotional Traits Predict Self-Reported Offending in Adolescent Boys: The Mediating Role of Delinquent Peers and the Moderating Role of Parenting Practices. Developmental Psychology, 53(2), 319-328. https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0000210
Reynolds, A. D., & Crea, T. M. (2015). Peer Influence Processes for Youth Delinquency and Depression. Journal of adolescence, 43(1), 83-95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2015.05.013
Robinson, B., Winiarski, D. A., Brennan, P. A., Foster, S. L., Cunningham, P. B., & Whitmore, E. (2015). Social Context, Parental Monitoring, and Multisystemic Therapy Outcomes. Psychotherapy, 52(1), 103-110. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0037948
Sabatine, E., Lippold, M. A., & Kainz, K. (2017). The Unique and Interactive Effects of Parent and School Bonds on Adolescent Delinquency. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 53, 54-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appdev.2017.09.005
Shadjoo, R., Ghanbaripanah, A., Dortaj, F., & Ghasemi, M. (2022). Structural model of self-defeating behaviors based on the basic psychological needs, moral identity and emotional self-awareness of young girls. Journal of Applied Family Therapy, 3(3), 263-279. https://doi.org/10.22034/aftj.2022.332110.1429
Tapia, M., Alarid, L. F., & Clare, C. (2018). Parenting Styles and Juvenile Delinquency: Exploring Gendered Relationships. Juvenile and Family Court Journal, 69(2), 21-36. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfcj.12110
Walters, G. D. (2021). Parents and Best Friends Perceived Reaction to Participant Deviance and Self-Reported Delinquency: Moderation by Sex and Mediation by Youth Attitude Toward Deviance in Mid- To Late Adolescence. Criminal Justice Review, 47(3), 302-317. https://doi.org/10.1177/07340168211015728
Yun, H. (2023). Discrete-Time Survival Analysis of the Determinants of Onset of Multicultural Adolescents’ Status Delinquency. Korean Association for Learner-Centered Curriculum and Instruction, 23(14), 617-627. https://doi.org/10.22251/jlcci.2023.23.14.617
Zakaria, E., Kamarudin, N. N., Mohamad, Z. S., Suzuki, M., Rathakrishnan, B., Singh, S. S. B., Rahman, Z. A., Sabramani, V., Shaari, A. H., & Kamaluddin, M. R. (2022). The Role of Family Life and the Influence of Peer Pressure on Delinquency: Qualitative Evidence From Malaysia. International journal of environmental research and public health, 19(13), 7846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19137846
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








