The Impact of a Digital Literacy Intervention on Internet Addiction and Social Skills in Undergraduate Students
Keywords:
Digital Literacy, Internet Addiction, Social Skills, Undergraduate Students, Randomized Controlled TrialAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to examine the effectiveness of a digital literacy intervention on reducing internet addiction and enhancing social skills among undergraduate students.
Methods and Materials: A randomized controlled trial was conducted with 30 undergraduate students from Romania, randomly assigned into intervention (n = 15) and control groups (n = 15). The intervention consisted of ten sessions, each lasting 60–75 minutes, delivered twice weekly over five weeks. The content included digital literacy skills such as self-regulation, critical evaluation of online information, ethical communication, emotional regulation, and face-to-face social interactions. Data were collected at pre-test, post-test, and at a five-month follow-up using the Internet Addiction Test (Young, 1998) and Social Skills Inventory (Riggio, 1986). Statistical analysis involved repeated measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc tests, performed using SPSS version 27.
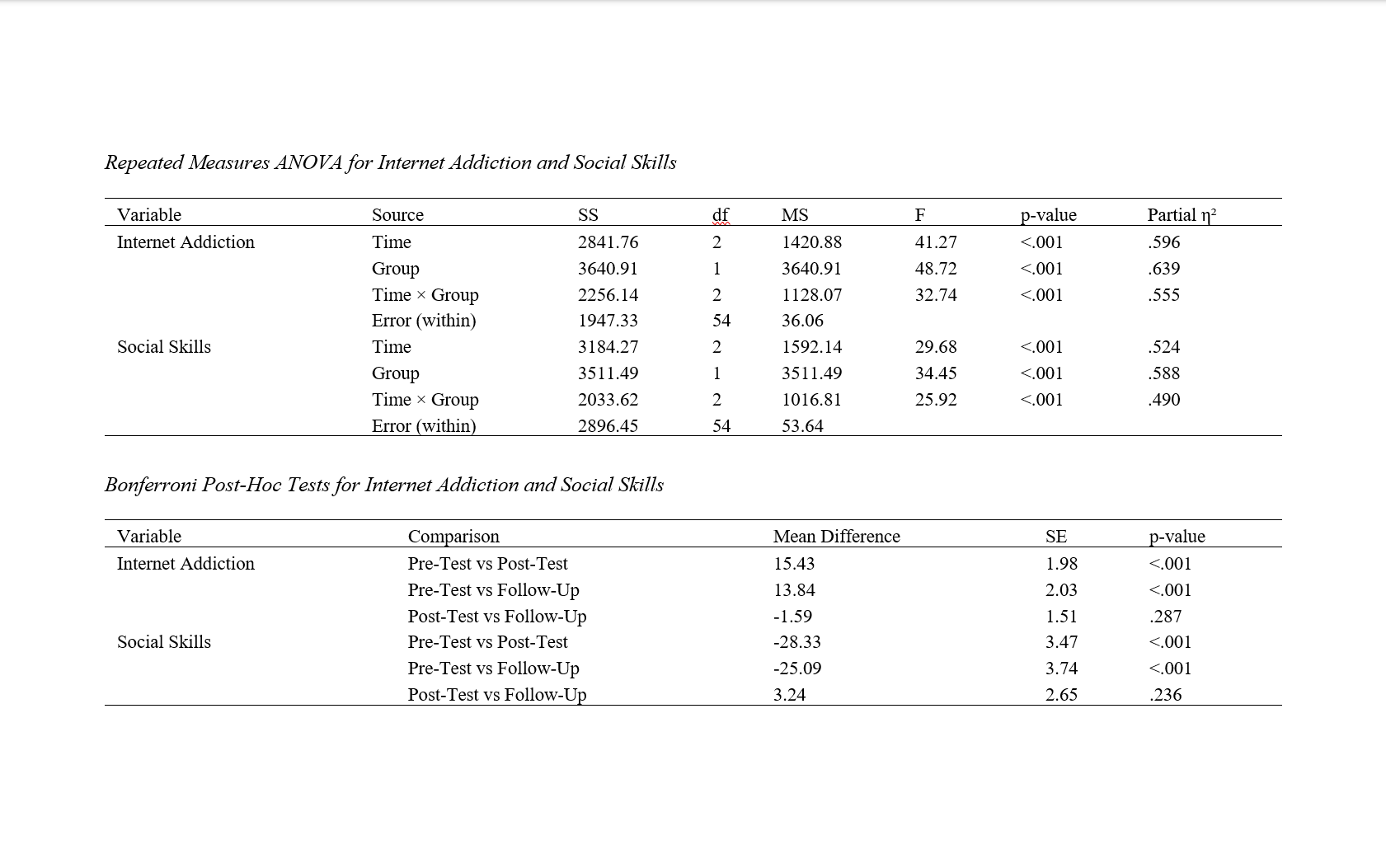
Findings: Results indicated significant improvements in both internet addiction and social skills among the intervention group compared to the control group. For internet addiction, the intervention group’s mean scores significantly decreased from pre-test (M = 71.86, SD = 5.24) to post-test (M = 56.43, SD = 6.15) and remained low at follow-up (M = 58.02, SD = 6.47), while the control group showed negligible changes. Social skills significantly improved from pre-test (M = 251.34, SD = 14.09) to post-test (M = 279.67, SD = 15.02) and remained stable at follow-up (M = 276.43, SD = 15.84) for the intervention group. ANOVA results revealed significant interaction effects of group × time for internet addiction (F(2,54)=32.74, p<.001, η²=.555) and social skills (F(2,54)=25.92, p<.001, η²=.490). Bonferroni post-hoc tests confirmed these significant differences.
Conclusion: The findings are suggesting the intervention value as a preventive and developmental tool in higher education settings.
Downloads
References
Agol, R. B., Osias, N. C., & Comon, J. D. (2024). Use of Digital Technology for Learners’ Cognitive Skills and Academic Performance in Social Studies. European Modern Studies Journal, 8(5), 322-349. https://doi.org/10.59573/emsj.8(5).2024.29
Alomoush, R., & Alkhozahe, H. (2022). The Role of E-Training Programs on Developing the Digital Skills of Social Studies Teachers in the Twenty-First Century as Perceived by School Directors. Dirasat Human and Social Sciences, 49(5), 125-146. https://doi.org/10.35516/hum.v49i5.3459
Aslamiah, S., & Sa’adah, N. (2025). Teknologi Dalam Pembelajaran Ips: Analisis Keterampilan Digital Bagi Calon Guru Madrasah Ibtidaiyah. Fikruna Jurnal Ilmiah Kependidikan Dan Kemasyarakatan, 6(2), 210-226. https://doi.org/10.56489/fik.v6i2.311
Bağatarhan, T. (2023). Digital Game Addiction Tendency and Social Competence in Preschool Children: The Mediating Role of Self-Regulation. İnsan Ve Sosyal Bilimler Dergisi, 6(2), 424-443. https://doi.org/10.53048/johass.1374193
Busnawir, B., Kodirun, K., Sumarna, N., & Alfari, Z. (2023). Analysis of the Effect of Social Skills and Disposition of Digital Literacy on Mathematical Literacy Ability. European Journal of Educational Research, volume-12-2023(volume-12-issue-1-january-2023), 59-69. https://doi.org/10.12973/eu-jer.12.1.59
Cheng, Q., Zhu, Y., Li, L., & Liu, C. (2024). The Impact of Digital Skills on Health: Evidence From the China General Social Survey. Digital Health, 10. https://doi.org/10.1177/20552076241304592
Fazil, N. F. M., Ahmad, N. L., & Yusof, R. (2022). Digital Skills in Igniting Accounting Undergraduates’ Entrepreneurship Intention. Ibej, 15(2), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.37134/ibej.vol15.2.1.2022
Harper, M.-G., Quan‐Haase, A., & Hollingshead, W. (2022). Mobilizing Social Support: New and Transferable Digital Skills in the Era of COVID-19. First Monday. https://doi.org/10.5210/fm.v27i4.12559
Imjai, N., Aujirapongpan, S., Jutidharabongse, J., & Usman, B. (2024). Impacts of Digital Connectivity on Thailand’s Generation Z Undergraduates’ Social Skills and Emotional Intelligence. Contemporary Educational Technology, 16(1), ep487. https://doi.org/10.30935/cedtech/14043
Kocaer, S., & Aydın, M. E. (2023). The Investigation of the Pre-Service Social Studies Teachers Perceptions of Self-Efficacy on the Digital Literacy Skills. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/k8eqs
Li, J., Chen, P., & Man, L. (2025). Understanding the Influence of Social Media on University Students' Communication Skills in Digital Information Environment. Profesional De La Información, 33(6). https://doi.org/10.3145/epi.2024.ene.0603
Lu, J., Tang, X., Jin, X., Luo, X., Fan, T., & Shen, Y. (2025). A network analysis-based study of the correlations between internet addiction, insomnia, physical activity, and suicide ideation in adolescents. Computers in human Behavior, 163, 108483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2024.108483
Lybeck, R., Koiranen, I., & Koivula, A. (2023). From Digital Divide to Digital Capital: The Role of Education and Digital Skills in Social Media Participation. Universal Access in the Information Society, 23(4), 1657-1669. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10209-022-00961-0
McNaughton, S., Rosedale, N., Zhu, T., Teng, L. S., Jesson, R., Oldehaver, J., Hoda, R., & Williamson, R. (2023). A School-Wide Digital Programme Has Context Specific Impacts on Self-Regulation but Not Social Skills. E-Learning and Digital Media, 21(6), 517-534. https://doi.org/10.1177/20427530231156282
Mulyani, L. S., Ardiana, C., & Mulyaningsih, S. (2023). Sosialisasi Literasi Digital Dalam Meningkatkan Keterampilan Penggunaan Media Digital Bagi Siswa SMPN I Limbangan Garut Pada Abad 21 Sesuai Dengan Profil Pelajar Pancasila. Jurnal Pengabdian Literasi Digital Indonesia, 2(2), 135-143. https://doi.org/10.57119/abdimas.v2i2.74
Mustafa, N. (2022). Digital Skills: Social Media. https://doi.org/10.13140/rg.2.2.11027.35368
Nkhi, S. E. (2023). An Investigation Into the Impact of Digital Social Media on the Writing and Speaking Skills of Tertiary Level Students in One Institution in Lesotho. J-Shmic Journal of English for Academic, 10(1), 83-93. https://doi.org/10.25299/jshmic.2023.vol10(1).11784
Pan, T. H., Aung, M. N., Nam, E. W., Koyanagi, Y., Lee, H., Li, L., Kyaw, M. Y., Mulati, N., Moolphate, S., Ka, C. M. H., Dijk, J. v., & Yuasa, M. (2024). Digital Inclusion Among Community Older Adults in the Republic of Korea: Measuring Digital Skills and Health Consequences. European Journal of Investigation in Health Psychology and Education, 14(8), 2314-2336. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe14080154
Qi, J., Li, H., Li, W., Jin, J., & Ye, F. (2024). The Influence of Digital Skills on Farm Households’ Vulnerability to Relative Poverty: Implications for the Sustainability of Farmers’ Livelihoods. Sustainability, 16(19), 8420. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16198420
Ragnedda, M., Ruiu, M. L., & Gómez, D. C. (2024). Examining the Interplay of Sociodemographic and Sociotechnical Factors on Users’ Perceived Digital Skills. Media and Communication, 12. https://doi.org/10.17645/mac.8167
Rahman, M. M., Salamzadeh, A., Dana, L. P., & Braga, V. (2024). Work‐Family Balance, Digital Leadership Skills, and Family Social Support as the Predictors of Subjective Well‐Being of Y‐Generation Managers. Strategic Change. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsc.2628
Şan, İ., Orhan Karsak, H. G., İzci, E., & Öncül, K. (2024). Internet addiction of university students in the Covid-19 process. Heliyon, 10(8), e29135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29135
Sideraki, A., & Drigas, A. (2023). Development of Social Skills for People With ASD Through Intervention With Digital Technologies and Virtual Reality (VR) Tools. Research Society and Development, 12(5), e11512541407. https://doi.org/10.33448/rsd-v12i5.41407
Silva, S., Silva, C., & Oliveira, M. (2025). The Value of Skills for a Sustainable Tourism and Hospitality Industry. Tourism and Hospitality, 6(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/tourhosp6010014
Zervas, I., & Stiakakis, E. (2024). Digital Skills in Vocational Education and Training: Investigating the Impact of Erasmus, Digital Tools, and Educational Platforms. Journal of Infrastructure Policy and Development, 8(8), 8415. https://doi.org/10.24294/jipd.v8i8.8415
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








