The Ecological Model of Prisons in Iran with Emphasis on Prisoners’ Behavioral Reform (Case Study: Tehran Prisons Organization)
Keywords:
Ecological model, national prisons, behavioral reform, Tehran Prisons OrganizationAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to design and analyze a comprehensive ecological model of prisons in Iran with a focus on behavioral reform of inmates, using Tehran Prisons Organization as the case study.
Methods and Materials: This research employed an exploratory mixed-methods design with a qualitative emphasis. The qualitative phase was conducted using a phenomenological approach through in-depth, semi-structured interviews with 16 experts, including senior prison managers and academic faculty with lived experience in the prison system. Data collection continued until theoretical saturation was reached. Thematic analysis was used for qualitative data analysis, based on six systematic stages involving open coding, axial coding, and theme development using ATLAS.ti version 9 software. The conceptual framework was refined based on insights from the interviews, literature review, and expert validation, resulting in a three-level thematic model.
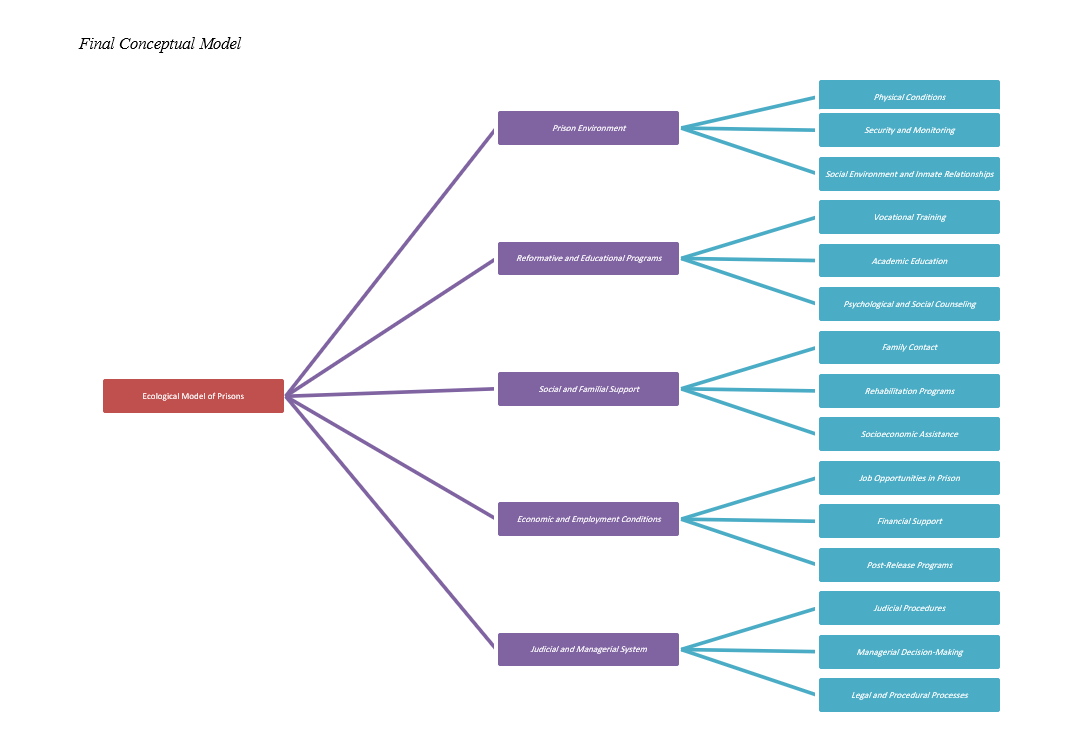
Findings: hematic analysis of expert interviews led to the identification of five overarching dimensions and multiple sub-themes influencing inmate behavior reform: prison environment (including physical conditions, social atmosphere, and security), reformative and educational programs (including vocational and academic training, psychological counseling), social and familial support (including reintegration support and family contact), economic and occupational conditions (including employment opportunities and financial aid), and judicial and managerial systems (including legal procedures and decision-making processes). These themes were integrated into a conceptual ecological model that captures the multi-dimensional and systemic factors contributing to rehabilitation and behavioral transformation in prison settings.
Conclusion: The ecological model developed in this study provides a practical and theoretical foundation for understanding and improving inmate behavior reform through systemic and multidimensional strategies. It emphasizes the need for integrated interventions across environmental, educational, psychological, social, and legal domains to foster sustainable reintegration outcomes.
Downloads
References
Amani, M., & Betyari, T. (2023). The impact of sports on the rehabilitation of prisoners and preventing future criminal behavior: Oral Presentation. International Conference of Sports Science- AESA, 7(1), 33. https://journal.aesasport.com/index.php/AESA-Conf/article/view/422
Aslani, J., Ahmaddost, H., & Bahmani, M. (2016). The effectiveness of positive psychotherapy on depression symptoms and subjective well-being of prisoners. Positive Psychology Research, 1(4), 67-76.
Farsi, B. (2024). The relationship between family functioning and moral intelligence among prisoners. The 14th International Conference on Psychology, Educational Sciences, and Lifestyle,
Fazel, S., Hayes, A. J., Bartellas, K., Clerici, M., & Trestman, R. (2016). Mental health of prisoners: prevalence, adverse outcomes, and interventions. The Lancet Psychiatry, 3(9), 871-881.
Foster, H. (2017). Family complexity and the stress process in prison: How sibling living arrangements of minor children influence maternal role strains. Social Sciences, 6(3), 81.
Gharavi, M. M., Kashani, H., Lotfi, M., Borhani, M., & Akbarzadeh, F. (2015). Comparison of depression, anxiety, general mental health and self-esteem among prisoners in consultancy and ordinary wings. Journal of Fundamentals of Mental Health, 17(1).
Ghazanfari, H., Miri, S., Taebi, M., & Farokhzadian, J. (2023). Psychological wellbeing, family cohesion, and purposeful life in male prisoners: A cross-sectional study [Original Research]. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 13. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1054149
Manesh, S. E., & Malak, S. K. (2025). The Structural Relationships of Emotional Neglect With Risky Behaviors in Prisoners Considering the Mediating Role of Emotion Regulation Strategies. Hn, 3(1), 111-122. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.hn.3.1.12
Meena, B. P. M. (2024). Does Anger Management Among Prisoners Work?-A Review of Recent Meta-Analyses. Qeios. https://doi.org/10.32388/D1SDI8
Moradi, G., Darvishi, S., Asaadi, L., Azimian Zavareh, F., Gouya, M.-M., Tashakorian, M., Alasvand, R., & Mohamadi Bolbanabad, A. (2020). Patterns of drug use and related factors among prisoners in Iran: results from the national survey in 2015. The Journal of Primary Prevention, 41, 29-38.
Pahlewi, R. M. (2024). The Impact of Islamic Counseling on the Mental Health of Prisoners in Yogyakarta Correctional Institution. Journal of Social Sciences and Humanites, 20-28. https://doi.org/10.56943/jssh.v3i3.599
Prakash, O., Sharma, N., Singh, A. R., & Singh Sanger, K. (2015). Effect of incarceration on well-being of prisoners: A study among convicted and under trials. The International Journal of Indian Psychology, 3(1), 155-164.
Robinson, F., & Fernhaber, S. A. (2024). Entrepreneurship after prison: It's complicated. Journal of Business Venturing Insights VL - 21 SP - e00465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbvi.2024.e00465
Shokrzadeh Madieh, J., & Kamkari, K. (2024). Standardization of the third version of the NEO-3 personality questionnaire in the staff of prisons throughout the country. Psychometrics, 49(13), 50-77. https://sanad.iau.ir/fa/Journal/jpsy/Article/1111778
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Pedram Mohammadzadeh (Author); Seyed Ahmad Hosseini gol afshani (Corresponding Author); Seyed Abdullah Sajadi Jagharq, Afsaneh Zamani Moghaddam (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















