Developing a Causal Model of Social Well-Being in HIV Patients Based on Attachment Styles with the Mediating Role of Self-Compassion
Abstract
Objective: This research aimed to develop a causal model of social well-being based on attachment styles with the mediating role of self-compassion in HIV patients.
Methods and Materials: The study employed a cross-sectional, correlational research design. The study population consisted of 400 HIV patients visiting behavioral counseling centers in Alborz province in 2021, selected through convenient and voluntary sampling. Instruments used included the Social Well-Being Scale (Keyes, 1998), Attachment Styles (Hazan & Shaver, 1987), and Self-Compassion (Neff, 2003). Data were analyzed using SPSS-V25 and Smart PLS software, and Structural Equation Modeling was employed to test the research hypotheses.
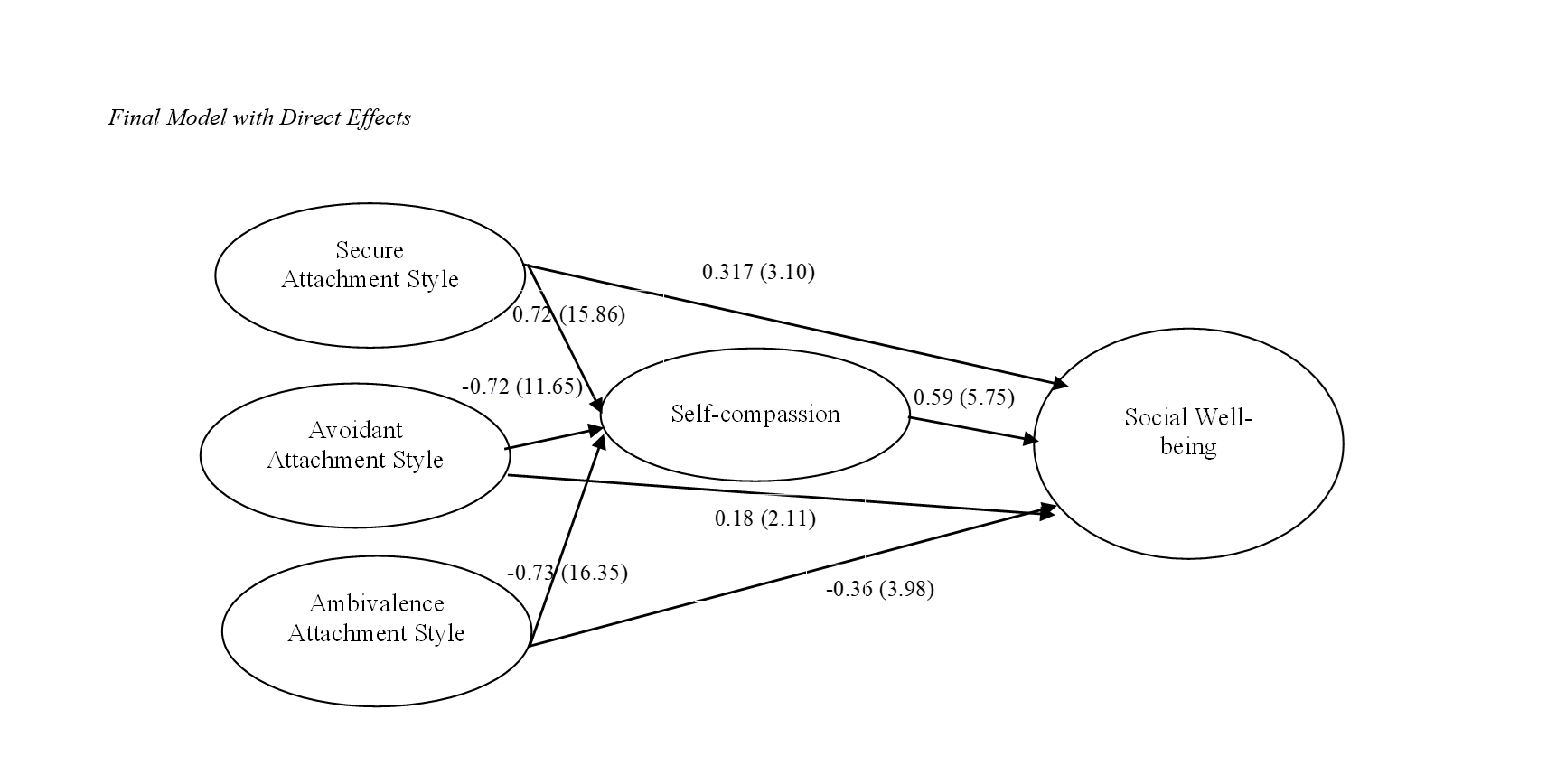
Findings: The findings indicated that the model had an appropriate fit. Results showed that secure attachment style has a direct effect on the social well-being of HIV patients. Avoidant attachment style also directly affects the social well-being of these patients. Ambivalent attachment style directly impacts the social well-being of HIV patients. Secure attachment style, mediated by self-compassion, indirectly affects the social well-being of HIV patients. Similarly, avoidant attachment style, mediated by self-compassion, has an indirect effect on their social well-being. Ambivalent attachment style, through self-compassion, indirectly affects the social well-being of HIV patients.
Conclusion: Thus, attention to these variables aids researchers and therapists in prevention and designing more appropriate treatments.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








