Determining the Effectiveness of Responsibility Training Based on Choice Theory on Students' Academic Motivation and Academic Performance
Keywords:
Responsibility Training, Choice Theory, Academic Motivation, Academic PerformanceAbstract
Objective: The present study aimed to determine the effectiveness of responsibility training based on choice theory on students' academic motivation and academic performance.
Methods and Materials: The research design of the present study was applied in terms of purpose and quasi-experimental in terms of method, with a pre-test-post-test design, including an experimental group and a control group, along with a three-month follow-up phase. The statistical population of the present study included all students referred to counseling centers in a private specialized clinic for child and adolescent counseling and psychotherapy in District 10 of Tehran. Participants were randomly assigned to two groups: experimental (n = 15) and control (n = 15) through convenience sampling. For the experimental group, the responsibility training program based on choice theory was implemented according to the protocol developed by Mirsalar Bakhshi (2019). To collect data, research instruments including Vallerand's Academic Motivation Scale (1998) and students' grade point averages (GPA) were used. Data analysis was conducted in two sections: descriptive (mean and standard deviation) and inferential. In the descriptive section, frequency distribution tables were used, and in the inferential section, data analysis was performed using mixed ANOVA with repeated measures and Bonferroni post hoc test. Data analysis was carried out using a computer and SPSS software version 26.
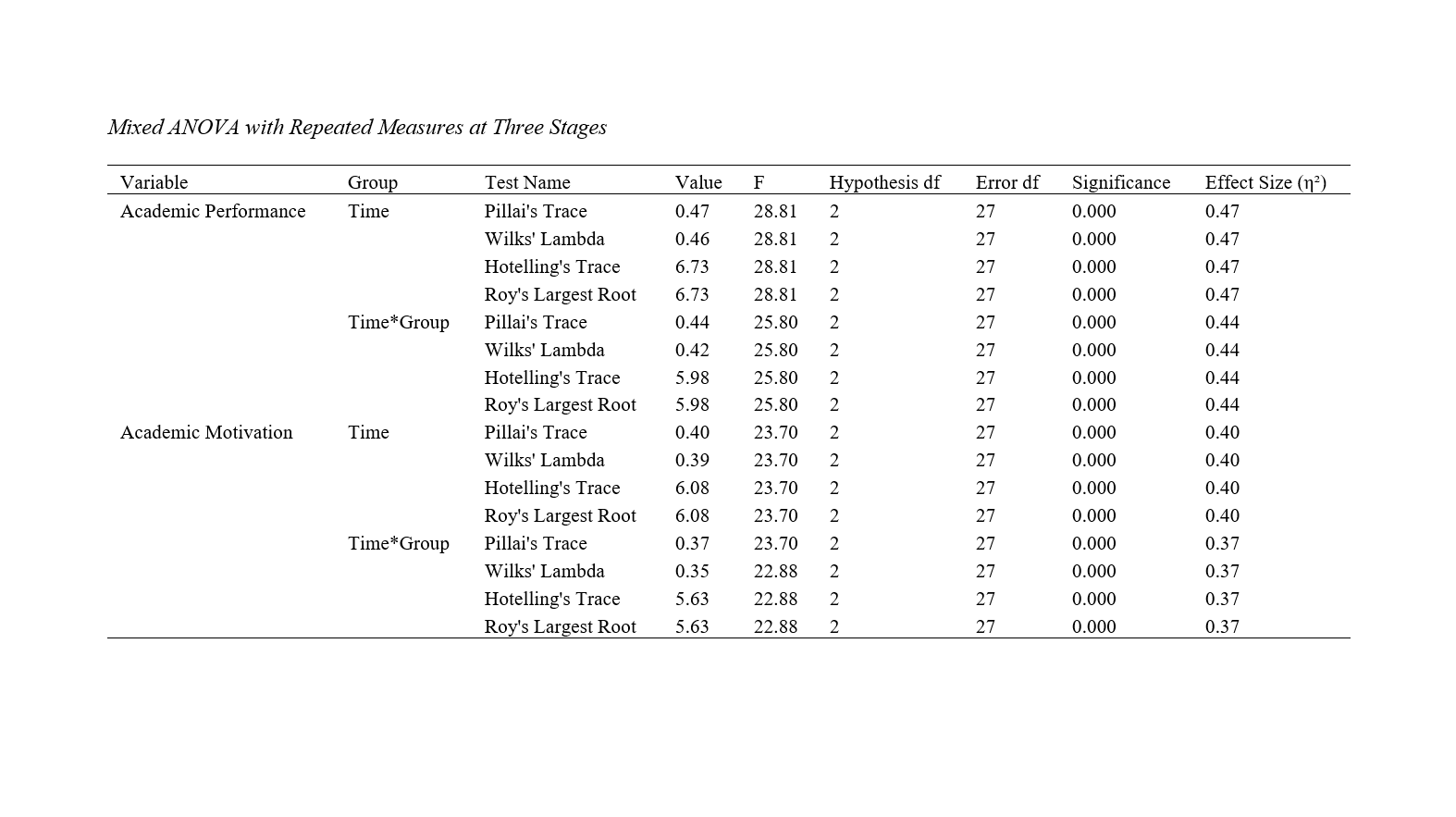
Findings: The findings indicate that the significance level shows that responsibility training based on choice theory had a significant impact on the dependent variables of the study, namely academic performance (F = 25.80, P < 0.01) and academic motivation (F = 23.70, P < 0.01). The changes resulting from this intervention were significant in the three time intervals of pre-test, post-test, and follow-up. The effectiveness of this intervention was also sustained in the follow-up phase according to the Bonferroni post hoc test.
Conclusion: Based on the available findings, it can be concluded that responsibility training based on choice theory can be used to increase academic motivation and improve students' academic performance. Therefore, it is suggested that educational workshops on this method be held for specialists.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Mahsa Seyedghale (Corresponding Author); Maryam Soroushmehr, Zahrasadat Hejazi, Fatemeh Soleimani Dashtaki (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




























