Modeling Substance Use Temptation in Addicts with Relapse History Based on Attention Bias, Emotional Processing Styles, Mediated by Social Support
Keywords:
Social Support, Likelihood of Substance Use, Addiction Relapse, Cognitive Emotion Regulation, Temptation, Attention Bias, DependencyAbstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to present a model of temptation and likelihood of substance use in dependent individuals with a history of relapse based on attention bias and emotional processing styles, with the mediating role of social support.
Methods and Materials: The research method was descriptive and correlational. The statistical population included addicted individuals referred to addiction treatment centers (residential camps) in the city of Rasht. A simple random sampling method was used, and based on the Morgan table, 201 individuals were selected. Data were collected using the following standardized questionnaires: Post-Addiction Temptation to Use Substance Questionnaire, Shostrom Attention Bias Questionnaire (translated by Rezvani), Baker's Emotional Processing Styles Questionnaire, and Wax's Social Support Questionnaire. For statistical data analysis, structural equation modeling and LISREL software were used.
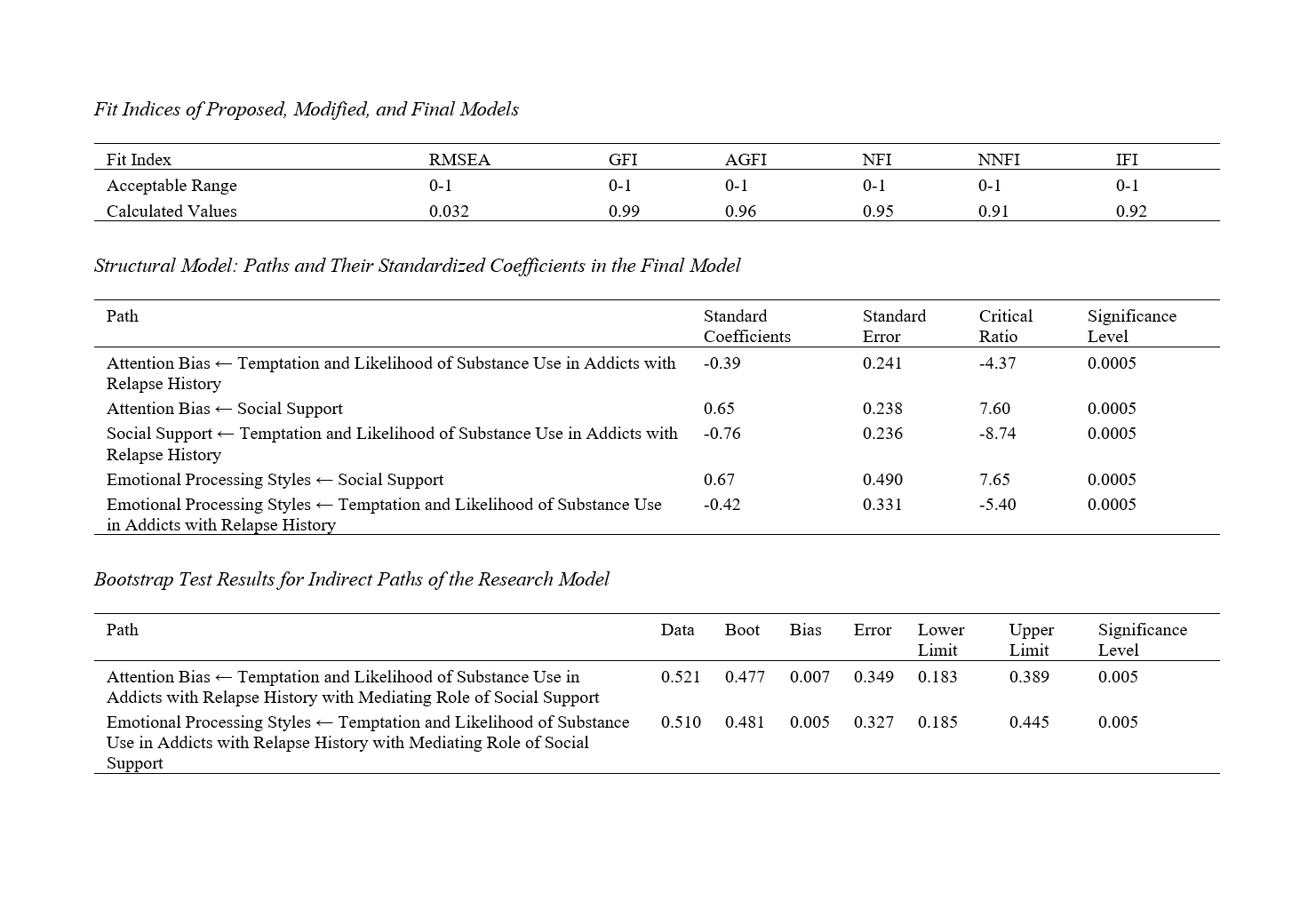
Findings: The results indicated that all the paths in the overall sample were statistically significant. In the final research model, the relationship between variables of temptation and likelihood of substance use in dependent individuals with a history of relapse, based on attention bias and emotional processing styles, with the mediating role of social support, was significant. The highest coefficient (-0.76) was related to the path of social support, while the weakest coefficient (-0.39) was related to the path of attention bias. Therefore, all direct paths were significant (p < 0.50). In the proposed research model, there were two indirect or mediating paths, and to determine the significance of mediating relationships and the indirect effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable through the mediator, the bootstrap method was used (p < 0.01).
Conclusion: It can be concluded that the model has good fitness. Based on the standard coefficients, the direct and indirect paths of the proposed model were significant.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








