Examining the Effectiveness of Cognitive Learning in Enhancing Intrinsic Motivation for Learning Mathematics in Adolescents
Keywords:
Cognitive assessment, Brain-based learning, Students, Learning motivation, MathematicsAbstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to assess the effectiveness of brain-based learning methods in enhancing seventh-grade students' intrinsic motivation and performance in mathematics.
Methods and Materials: An applied, intervention-based study design was employed with 39 seventh-grade male students from a public middle school in Tehran during the 2023-2024 academic year. The study used simple random sampling and included three phases: baseline, intervention, and post-intervention. Quantitative data were collected using the Mathematics Motivation Scale (MMS), while qualitative data were gathered through field notes. The intervention phase incorporated brain-based learning activities such as visual storytelling, role-playing, kinesthetic learning, brainstorming, critical thinking, and creative thinking exercises. Data analysis involved one-way repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) and thematic analysis using SPSS and NVivo software.
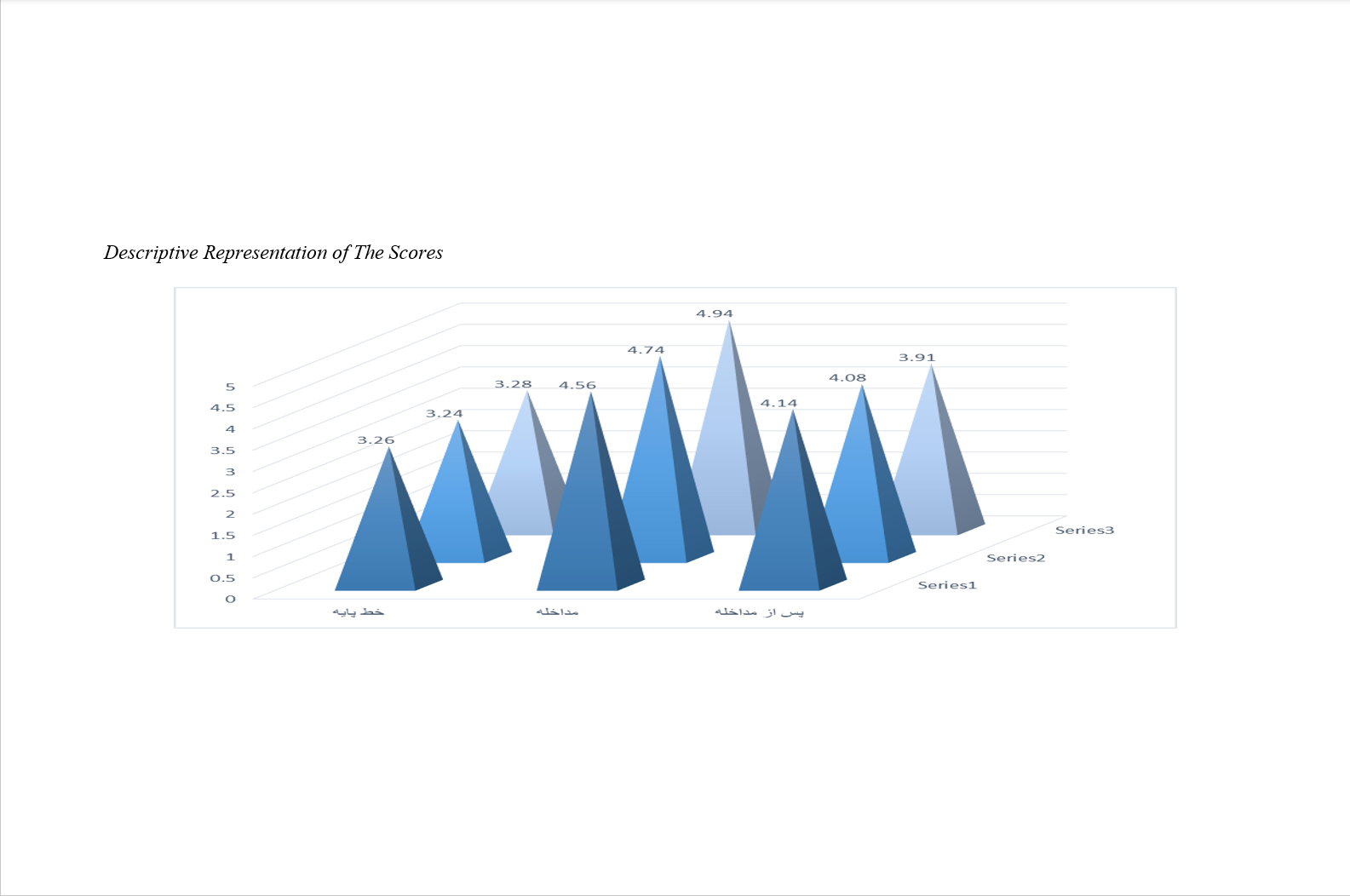
Findings: The results indicated that the students' average scores for intrinsic motivation and performance in mathematics were significantly higher during the intervention phase compared to the baseline phase. Although scores decreased in the post-intervention phase, they remained higher than the baseline scores. The ANOVA results, adjusted using the Huynh-Feldt correction, showed a significant effect of brain-based learning activities on intrinsic motivation (F(2.95) = 111, p < 0.01, ηp2 = 0.75). Qualitative analysis supported these findings, highlighting increased student engagement and participation during the intervention phase.
Conclusion: Brain-based learning activities significantly enhance students' intrinsic motivation and performance in mathematics. The study underscores the importance of incorporating such strategies into regular teaching practices to sustain high levels of student motivation and achievement.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Atefe Sohrabi Omabad (Author); Mahnaz Askarian (Corresponding Author); Beheshte Niusha (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






















